Stay in the know on all smart updates of your favorite topics.
Exploring Smart Parking Solutions in Amsterdam: The Role of Mobypark in Shaping Urban Efficiency

The quest for parking in Amsterdam presents a unique set of challenges, including narrow lanes, constant vehicular flow, and strict parking policies. This iconic city, celebrated for its canal system, historical buildings, and cultural vibrancy, also faces the modern urban dilemma of parking scarcity. Amidst these challenges, Amsterdam's approach to parking, characterized by a zonal system with variable rates, mirrors its commitment to promoting sustainable urban mobility. Within the bustling heart of the city, parking fees can soar to €7.50 per hour, a pricing strategy designed to incentivize public transport and biking, cherished and eco-friendly travel methods among the locals.
Amsterdam's dynamic parking strategy also paves the way for innovative solutions like Mobypark, a platform revolutionizing parking by facilitating the rental of private parking spots. This initiative not only offers a cost-effective alternative to the traditional parking hunt but also optimizes the use of existing spaces, aligning with the city's sustainability goals.
For those seeking affordability without sacrificing convenience, Amsterdam's Park and Ride (P+R) facilities serve as a beacon. Strategically located at the city's periphery, these parking havens offer reduced rates, encouraging drivers to park their vehicles and hop on public transport to reach the city's core. This system significantly mitigates urban congestion and lowers parking costs for both tourists and daily commuters.
The allure of P+R locations is undeniable, especially when juxtaposed with the exorbitant costs of street parking. To access P+R discounts, users must integrate their parking with public transportation, highlighting the city's efforts to weave sustainability into the fabric of urban travel. Mobypark's P+R options stand out for their simplicity and affordability, offering seamless access to the city center without the usual prerequisites. Examples include:
Amsterdam's strategy to curtail on-street parking availability is a deliberate move towards fostering a more sustainable, pleasant cityscape. By endorsing alternatives like public transport, cycling, and Mobypark's innovative parking solutions, Amsterdam is making strides in reducing traffic jams, cutting down on pollution, and improving urban life quality. These initiatives are testament to Amsterdam's dedication to a sustainable future, highlighting Mobypark's pivotal role in transforming the city into a smarter, more navigable urban space.
Find a link to Mobypark here: Amsterdam parking
Open evenementen voor het testen van innovatie [Innovation wanted!]

Evenementen in de stad willen we verder verduurzamen en toegankelijker maken. Vaak vinden evenementen plaats op centrale plekken waar mensen bij elkaar komen en waar veel afval, drinkwater en consumptievoorzieningen zijn. Dit zijn goede plekken om nieuwe innovaties te testen en verder te ontwikkelen. Tot 29 februari kunnen ondernemers zich inschrijven om hun innovatie te testen via het In Residence programma Open Evenementen.
In Residence programma
Innovatieve ondernemers kunnen zich inschrijven voor het In Residence programma van het stedelijk innovatieteam, waarin open evenementen in Amsterdam worden ingezet voor het testen van innovaties. Het doel van dit programma is om kennis te ontwikkelen voor zowel het verduurzamen van evenementen, als voor het vinden van praktische oplossingen voor een toekomstbestendige stad.
Geselecteerde ondernemers krijgen daarbij professionele begeleiding bij het verder ontwikkelen van hun innovatie en de mogelijkheid samen te werken met ambtenaren en evenementenorganisatoren. Voor het testen van hun innovatie krijgen ondernemers een budget tot €15.000,- toegewezen. Het programma duurt 6 maanden, van mei tot en met oktober 2024. Op 26 april worden de 8 ondernemers bekend gemaakt die dit jaar aan het programma mee zullen doen.
Het In Residence programma Open Evenementen vindt plaats in aanloop naar het jubileumjaar 2025 – het jaar van Amsterdam 750 en SAIL – dat groots gevierd zal worden in de hele stad. Innovaties die de komende tijd op evenementen worden getest en door ontwikkeld kunnen mogelijk een rol hebben tijdens de grootschalige evenementen die dat jaar plaatsvinden.
Evenementen als proeftuin
Meerdere grote evenementen nemen deel aan het programma. De organisaties van onder andere Pride en de Marathon bieden geselecteerde ondernemers mogelijkheden om innovaties op thema’s als duurzaamheid, circulair, mobiliteit, inclusie en toegankelijkheid te testen tijdens deze evenementen. Kansrijke innovaties krijgen hierdoor de mogelijkheid om door te ontwikkelen en een positieve bijdrage te leveren aan de opgaven van de stad.
Innovatieve ondernemers kunnen innovaties opgeven binnen de volgende thema's:
- Voedsel
- Circulaire materialen
- Circulaire verpakkingen
- Mobiliteit
- Inclusiviteit en toegankelijkheid
- Extreem weer
- Digitale veiligheid
Er is ook een wildcard voor een kansrijke innovatie die buiten deze categorieën valt.
De Inschrijving verloopt via: https://innovatiepartners.nl/project/open-evenementen-2024/ en sluit op 29 februari.
Meer informatie over hoe wij samenwerken met ondernemers vind je op:www.innovatiepartners.nl. Op 6 en 8 februari vinden er twee informatiewebinars plaats waarin meer verteld zal worden over het In Residence programma en de selectieprocedure. Ook is er dan ruimte om vragen te stellen.
The Netherlands: country of cars and cows

Last months, 25 facets of the quality of streets, neighbourhoods and cities have been discussed on this spot. But what are the next steps? How urgent is improvement of the quality of the living environment actually?
I fear that the quality of the living environment has been going in the wrong direction for at least half a century and in two respects:
Country of cars
Firstly, the car came to play an increasingly dominant role during that period. Step by step, choices have been made that make traveling by car easier and this has had far-reaching consequences for nature, air quality, climate and environmental planning. Our living environment is designed based on the use of the car instead of what is ecologically possible and desirable for our health. At the same time, public transport is rarely a good alternative, in terms of travel time, costs and punctuality.
Country of cows
A second structural damage to the quality of the living environment comes from the agro-industry. About one half of the surface of our country is intended for cows. These cows make an important contribution to greenhouse gas emissions that further destroy the remaining nature. But this form of land use also leads to inefficient food production, which also results in health problems.
In the next months I will explore two themes: 'Are 'self-driving' cars advantageous ' and the 'The merits of the 15-minute city'. These themes are case studies regarding the quality of the living environment and in both cases mobility and nature play an important role.
After the publication of these two miniseries with zeven posts each, the frequency of my posts on this site will decrease, although I will continue to draw attention on the fundamental choices we have to make regarding environmental issues.
Meanwhile, I started a new blog 'Expeditie Muziek' (in Dutch). I have always neglected my love for music and I am making up for it now. I think readers who love music will enjoy my posts in which pieces of text alternate with YouTube videos as much as I enjoy writing them.
Curious? Visit the link below
22. Nature, never far away

This is the 22st episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Its topic is the way how the quality of the living environment benefits from reducing the contrast between urban and rural areas.
Photos from space show a sharp contrast between city and countryside. Urban areas are predominantly gray; rural areas turn green, yellow, and brown, but sharp contrasts are also visible within cities between densely built-up neighborhoods and parks. Even between neighborhoods there are sometimes sharp transitions.
The division between city and country
Large and medium-sized cities on the one hand and rural areas on the other are worlds apart in many respects and local government in municipalities would like to keep it that way. For a balanced development of urban and rural areas, it is much better if mutual cohesion is emphasized, that their development takes place from a single spatial vision and (administrative) organization and that there are smooth transitions between both. The biggest mistake one can made is regarding the contrast between city and country as a contradiction between city and nature. Where large-scale agriculture predominates in the rural area, the remaining nature has a hard time. Where nature-inclusive construction takes place in cities, biodiversity is visibly increasing.
The idea that urban and rural areas should interpenetrate each other is not new. At the time, in Amsterdam it was decided to retain several wedges and to build garden villages. Some of the images in the above collage show such smooth transitions between urban and rural areas: Eko Park, Sweden (top right), Abuja, Nigeria (bottom left), and Xion'an, China (bottom center). The latter two are designs by SOM, an international urban design agency that focuses on biophilic designs.
Pulling nature into the city
Marian Stuiver is program leader Green Cities of Wageningen Environmental Research at WUR. In her just-released book The Symbiotic City, she describes the need to re-embed cities in soil, water and living organisms. An interesting example is a design by two of her students, Piels and Çiftçi, for the urban expansion of Lelystad. The surrounding nature continues into the built-up area: soil and existing waterways are leading; buildings have been adapted accordingly. Passages for animals run between and under the houses (see photo collage, top left). Others speak of rewilding. In this context, there is no objection to a small part of the countryside being given a residential destination. Nature benefits!
Restoration of the rural area
The threat to nature does not come from urban expansion in the first place, but mainly from the expansion of the agricultural area. Don't just think immediately of the clearing of tropical rain woods to produce palm oil. About half of the Dutch land area is intended for cows. Usually, most of them are stabled and the land is mainly used to produce animal feed.
The development of large-scale industrialized agriculture has led to the disappearance of most small landscape features, one of the causes of declining biodiversity. Part of the Climate Agreement on 28 June 2019 was the intention to draw up the Aanvalsplan landschapselementen . Many over-fertilized meadows and fields that are intended to produce animal feed in the Netherlands were once valuable nature reserves. Today they value from a biodiversity point of view is restricted and they are a source of greenhouse gases. Nature restoration is therefore not primarily focusses at increasing the wooded area. Most of the land can continue to be used for agricultural and livestock farming, provided that it is operated in a nature-inclusive manner. The number of farmers will then increase rather than decrease.
Pulling the city into nature
There are no objections against densification of the city as long this respects the green area within the city. So-called vertical forests by no means make up for the loss of greenery. Moreover, space is needed for urban agriculture and horticulture (photo collage, top center), offices, crafts, and clean industry as part of the pursuit of complete districts. Nature in the Netherlands benefits if one to two percent of the land that is currently used to produce animal feed is used for housing, embedded in a green-blue infrastructure. Some expansion and densification also apply to villages, which as a result are once again developing support for the facilities, they saw disappearing in recent decades.
Finally, I mentioned earlier that nature is more than water, soils, plants, and trees. Biophilic architects also draw nature into the built environment by incorporating analogies with natural forms into the design and using natural processes for cooling and healthy air. The 'Zandkasteel' in Amsterdam is still an iconic example (photo collage, bottom right).
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
17. A sociable inclusive neighborhood

This is the 17th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. This post is about the contributions of sociability and inclusivity to the quality of the living environment.
Almost everyone who is going to move looks forward with some trepidation to who the neighbors will be. This post is about similarities and differences between residents as the basis for a sociable end inclusive neighborhood.
"Our kind of people"
The question 'what do you hope your neighbors are' is often answered spontaneously with 'our kind of people'. There is a practical side to this: a family with children hopes for a family with playmates of about the same age. But also, that the neighbors are not too noisy, that they are in for a pleasant contact or for making practical arrangements, bearing in mind the principle 'a good neighbor is better than a distant friend'. A person with poor understanding often interprets 'our kind of people' as people with the same income, religion, ethnic or cultural background. That doesn't have to be the case. On the other hand, nothing is wrong if people with similar identities seeking each other's proximity on a small scale.
All kinds of people
A certain homogeneity among the immediate neighbours, say those in the same building block, can go hand in hand with a greater variety at the neighbourhood level in terms of lifestyle, ethnic or cultural background, age, and capacity. This variety is a prerequisite for the growth of inclusiveness. Not everyone will interact with everyone, but diversity in ideas, interests and capacities can come in handy when organizing joint activities at neighborhood and district level.
Variation in living and living arrangements
The presence of a variety in lifestyles and living arrangements can be inspiring. For example, cohousing projects sometimes have facilities such as a fitness center or a restaurant that are accessible to other residents in the neighbourhood. The same applies to a cohabitation project for the elderly. But it is also conceivable that there is a project in the area for assisted living for (former) drug addicts or former homeless people. The Actieagenda Wonen “Samen werken aan goed wonen” (2021) provides examples of the new mantra 'the inclusive neighbourhood'. It is a hopeful story in a dossier in which misery predominates. The Majella Wonen project in Utrecht appealed to me: Two post-war apartment complexes have been converted into a place where former homeless people and 'regular' tenants have developed a close-knit community. It benefits everyone if the residents of these types of projects are accepted in the neighborhood and invited to participate.
Consultation between neighbours
It remains important that residents as early as possible discuss agreements about how the shared part of life can be made as pleasant as possible. This is best done through varying combinations of informal neighborhood representatives who discuss current affairs with their immediate neighbours. A Whatsapp group is indispensable.
Mixing income groups is also desirable, especially if the differences in housing and garden size are not too great. It does not work if the impression of a kind of 'gold coast' is created.
If functions are mixed and there are also offices and other forms of activity in a neighborhood, it is desirable that employees also integrate. This will almost happen automatically if there is a community center with catering.
Most of what is mentioned above, cannot be planned, but a dose of goodwill on the part of all those involved contributes to the best quality of living together.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
11. Nature inclusivity

This is the 11th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. In this post, I wonder whether nature itself can tackle the environmental problems that humans have caused.
Ecosystem services
According to environmental scientists, ecosystems are providers of services. They are divided into production services (such as clean drinking water, wood, and biomass), regulating services (such as pollination, soil fertility, water storage, cooling, and stress reduction) and cultural services (such as recreation, and natural beauty). In case of nature-inclusive solutions ecosystems are co-managed to restore the quality of life on the earth in the short term and to maintain it in the long term, insofar as that is still possible.
The green-blue infrastructure
The meaning of urban green can best be seen in conjunction with that of water, hence the term green-blue infrastructure. Its importance is at least fourfold: (1) it is the source of all life, (2) it contributes substantially to the capture and storage of CO2, (3) 'green' has a positive impact on well-being and health; (4) it improves water management. This post is mainly about the third aspect. The fourth will be discussed in the next post. 'Green' has many forms, from sidewalk gardens to trees in the street or vegetated facades to small and large parks (see collage above).
Improving air quality
Trees and plants help to filter the water itself. They have a significant role to play in managing water and air pollution. Conifers capture particulate matter. However, the extent to which this occurs is less than is necessary to have a significant impact on health. Particulate matter contributes to a wide range of ailments. Like infections of the respiratory system and cardiovascular disease, but also cancer and possibly diabetes.
Countering heat stress
Heat stress arises because of high temperature and humidity. The wind speed and the radiation temperature also play a role. When the crowns of trees cover 20% of the surface of an area, the air temperature decreases by 0.3oC during the day. However, this relatively small decrease already leads to a 10% reduction in deaths. Often 40% crown area over a larger area is considered as an optimum.
Reduce mental stress and improve mood
According to Arbo Nederland, 21% of the number of absenteeism days is stress-related, which means approximately a €3 billion damage. A short-term effect of contact with nature on stress, concentration and internal tranquility has been conclusively demonstrated. The impact of distributing greenery within the residential environment is larger than a concentrated facility, such as a park, has.
Strengthening immune function via microbiome
The total amount of greenery in and around the house influences the nature and quantity of the bacteria present. This green would have a positive effect on the intestinal flora of those who are in its vicinity and therefore also on their immune function. The empirical support for this mechanism is still rather limited.
Stimulate physical activity
The impact of physical activity on health has been widely demonstrated. The Health Council therefore advises adults to exercise at least 2½ hours a week. The presence of a green area of at least ¼ hectare at 300 meters from the home is resulting more physical activity of adults in such areas, but not to more activity as a whole.
Promoting social contact
Well-designed green areas near the living environment invite social contacts. For instance, placement of benches, overview of the surroundings and absence of traffic noise. The state of maintenance are important: people tend to avoid neglected and polluted areas of public space, no matter how green.
Noise reduction
Vegetation dampens noise to some extent, but it is more important that residents of houses with a green environment experience noise as less of a nuisance. It is assumed that this is due to a mechanism already discussed, namely the improvement of stress resistance because of the greenery present.
Biophilic construction
For years buildings made people sic. A growing number of architects want to enhance the effect of 'green' on human health by integrating it into the design of houses and buildings and the materials used. This is the case if it is ensured that trees and plants can be observed permanently. But also, analogies with natural forms in the design of a building
The 'Zandkasteel', the former headquarters of the Nederlandse Middenstandsbank in Amsterdam, designed by the architects Ton Alberts and Max van Huut, is organically designed both inside and outside, inspired by the anthroposophical ideas of Rudolf Steiner. The (internal) water features are storage for rainwater and the climate control is completely natural. The building has been repurposed for apartments, offices and restaurants.
Green gentrification
Worldwide, there is a direct correlation between the amount of greenery in a neighborhood and the income of its residents. Conversely, we see that poorer neighborhoods where new green elements are added fall victim to green gentrification over time and that wealthier housing seekers displace the original residents.
The challenge facing city councils is to develop green and fair districts where gentrification is halted and where poorer residents can stay. Greening in poor communities must therefore be accompanied by measures that respect the residential rights and aim at improving the socio-economic position of the residents.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Recap of Demo Days #16 – Mobility meets Energy

For the sixteenth edition of our Demo Days, we were finally able to meet offline again since the start of the pandemic. This meant: old-school post-its instead of filling online Miro boards. The Mobility & Energy Demo Day was hosted at one of our partners’ locations, namely Commandant’s Residence at the Marineterrein. From CO2 neutral transport to the Johan Cruijff ArenA to city logistics in the university quarter, in this article you’ll read all about mobility & energy projects our partners are working on.
About our Demo Days
The Demo Days are one of the tools we use to stimulate innovation and encourage connection between our partners and community. The purpose of the Demo Days is to present the progress of various innovation projects, ask for help, share dilemmas and involve more partners to take these projects to the next level. More information about the Demo Days can be found here.
Demo Day: Mobility & Energy
CO2 neutral transport to the Johan Cruijff ArenA in 2023 - Boen Groothof and Susanne van Gelder (municipality of Amsterdam)
How can we make CO2 neutral transport to any event in the Johan Cruijff ArenA possible by 2030? This is what the participants of the Mobility Challenge want to figure out. The participants voiced what their organisation wants to contribute to the challenge, and also expressed what they expect from each other. The next step is for all the parties to internally concretize their role within the challenge even further, to make CO2 neutral travelling to events in the Johan Cruijff ArenA possibly by 2030.
A sustainable energy system for business park De Vaart – Anke Delfos (municipality of Almere)
How to make the energy system of business park de Vaart in Almere more sustainable? This was the central question of the work session led by Anke Delfos. The participants concluded that a start could be made with the 'coalition of the willing' and identifying the front runners. The companies that are already enthusiastic can form a vanguard that can actively think along in the new developments. An analysis can be made of the measures that the companies are willing to take individually or collectively. This may lead to collaborations between organizations. The municipality will then also gain insight into which solutions will actually help to generate more energy and meet the increasing demand for energy. In a later phase, the vanguard can also inspire and motivate other companies to take action.
Measuring objectives for urban mobility - Susanne Balm (Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences), Marcel Ludeman (municipality of Amsterdam), Lisa van Velzen (Delft University of Technology)
The municipality of Amsterdam, Facility Services UvA-HvA and the HvA Lectureship City Logistics are working on a logistics research in the University Quarter of Amsterdam. This area is located in the city centre and is used by many stakeholders such as inhabitants, students, and visitors. The goal of the study is to design and evaluate logistical concepts for the University Quarter that are consistent with the objectives for liveability, accessibility and safety of this area. The question for the group: How can these objectives be operationalized and measured? The participants talked about the subjectivity of the objectives and how you can measure certain objectives, but also came up with concrete solutions. For example, providing information to stakeholders for more understanding and recognitions. One of the participants suggested a role-play to evaluate different solutions for smooth logistics in the area.
Want to join the next Demo Day?
Are you working on an innovative project that could use some input? Or are you preparing for an inspiring event that needs a spotlight? Our next Demo Day takes place on the 11th of October. If it fits within our themes (circular, mobility, energy and digital), sent a message to Sophie via sophie@amsterdamsmartcity.com or let us know in the comments. We are happy to talk with you to find out if it's a match!
Would you like to participate in the next Demo Day and share your thoughts on our partners’ innovative projects? As soon as the program for the next Demo Day is determined, we will share it on the platform and give you the opportunity to join as participant.
Curious to circular & digital projects? Read more about it in the recap of Demo Day Circular & Digital.
Photo: Myrthe Polman
Amsterdam Smart City tekent: samen maken we CO2 neutraal reizen naar evenementen de norm

Het klimaat verandert en het wordt steeds drukker in Amsterdam. Jaarlijks komen er alleen al miljoenen bezoekers op Zuidoost af voor het grootste entertainment gebied van Nederland. We staan voor de opgave om de stad, waaronder Zuidoost, leefbaar, veilig en tegelijkertijd bereikbaar te houden. Verschillende partners slaan daarom nu de handen ineen om bezoekers van en naar evenementen in 2023 CO2 neutraal te laten reizen
De auto is op dit moment het meest gebruikte vervoersmiddel in Zuidoost. Amsterdam heeft ervoor gekozen om de privé auto minder ruimte te geven in de stad en de uitstoot van fossiele brandstof terug te dringen om de luchtkwaliteit in de stad te verbeteren en bij te dragen aan de klimaatdoelstellingen.
De transitie van mobiliteit vraagt om een samenwerking tussen (semi) publieke en private partijen en het verstevigen van duurzame alternatieven voor de privé auto. Op 11 mei hebben de gemeente Amsterdam, Johan Cruijff ArenA, Ajax, NS, GVB, Transdev, VRA en Amsterdam Smart City getekend voor een samenwerking rondom CO2 neutraal reizen. Het doel: in 2023 bezoekers CO2 neutraal te laten reizen van en naar één of meerdere evenementen in de Johan Cruijff ArenA. Zodat we samen leren hoe we CO2 neutraal reizen naar evenementen de norm maken
Op de Amsterdam Smart City Demodag op 14 juni zullen de bovenstaande organisaties bij elkaar komen in één van de werksessies, om verder na te denken over het proces. Wat hebben we nodig? Wat wordt de werkwijze? Wat kunnen de grootste hobbels zijn?
Ben je werkzaam bij één van onze partnerorganisaties en lijkt het je interessant om hierover mee te denken? Stuur een mail naar trisha@amsterdamsmartcity.com voor verdere informatie over deelname aan de werksessie.
22. Two '100 smart city missions'- Twice an ill-advised leap forward

The 22nd and penultimate episode in the *Better cities: The contribution of digital technology-*series will discuss two ambitious ‘smart city’plans of two governments and the associated risks.
Recently, the European Commission launched a 100-city plan, the EU Mission on Climate-Neutral and Smart Cities. One hundred European cities that aspire to be climate neutral by 2030 (you read that correctly) can register and count on supplemental funding. I immediately thought of another 100-city plan, India's Smart City Mission. In 2015, Prime Minister Modi announced that in six years 100 Indian cities would become 'smart'. The official term of the project has now ended, and I will examine below whether this goal has been achieved, I discuss the two plans and then explain why I call both of them a leap forward. At the end I will make a few suggestions for how the European mission can still learn from the Indian one.
India's Smart City Mission
The problem
In India, 377 million people live in cities. In 15 years, 200 million will have been added. Already, traffic in Indian cities has come to a complete standstill, each year more than 600,000 people die from air pollution, half of the urban areas have no drinking water connection, waste collection is poor and only 3% of sewage is treated. The rest is discharged into surface water, which is also the main source of drinking water.
The mission
The Smart City Mission was intended to implement substantial improvements on all these problems in 100 cities, which together comprise 30% of the population. In the improvements digital technology had to play an important role.
The 100 cities were selected because of favorable prospects and the quality of the plans, which usually consisted of a long series of projects.
Governance
The regular city governing bodies were deemed incompetent to lead the projects. That is why management boards (‘special purpose vehicles’) have been appointed, operating under company law and led by a CEO, supported by international consultancy firms. All rights and duties of the City Council regarding the execution of the mission were delegated to the appointed boards, including the power to collect taxes! Not surprisingly, this decision has been challenged in many places. Several cities have withdrawn from 'the mission' for this reason.
Financing
To implement their projects, each city would receive $150 million over five consecutive years. This money should be seen as seed capital to be supplemented from additional sources such as public-private partnerships, commercial bank lending, external financing, loans, and foreign investment.
Area-oriented and pan-urban approach
The plans contain two components: an area-oriented and a pan-urban approach. The first aims at adapting, retrofitting or new construction and should relate to a wide range of 'smart services'. For example high-speed internet, waste facilities, parking facilities, energy-efficient buildings, but also replacement of slums by high-rise buildings. The slick 'architectural impressions' that circulated at the beginning of the planning period (see above) mainly concern the area-oriented approach.
The pan-urban approach includes at least one 'smart' facility for a larger part of the city. The choice is often made to improve the transport infrastructure, for example the construction of new roads and highways and the purchase of electric buses. No fewer than 70 cities have built a 'smart' control center based on the example of Rio de Janeiro, which I believe was rather premature.
Progress
Now that the official term of 'the mission' has ended, a first inventory can be made, although observers complain about a lack of transparency about the results. About half of all the 5000 projects that have been started have not (yet) been completed and a significant part of the government funds have not yet been disbursed. This could still happen in the coming years. This is also because attracting external resources has lagged behind expectations. These funds came mainly from governments, and large technology companies. This has had an impact on the implementation of the plans.
The slow progress of most projects is partly because most of the population was barely aware of the mission and that city councils were not always cooperative either.
Impact
It was foreseen that half of the available resources would go to area-oriented projects; this eventually became 75-80%. As a result, on average only 4% of the inhabitants of the cities involved have benefited from 'the mission' and even then it is not clear what the benefits exactly entail. The city of New Delhi covers an area of almost 1500 km2, while the area concerned is only 2.2 km2: So you're not even going to have 100 smart cities. You're going to have 100 smart enclaves within cities around the country, said Shivani Chaudhry, director of the Housing and Land Rights Network.
It soon became clear that the mission would be no more than a drop in the ocean. Instead of $150 million, it would take $10 billion per city, $1000 billion in total, to address all ambitions, according to an official calculation. Deloitte was a little more modest, calculating the need for $150 billion in public money and $120 billion from private sources.
Type of projects
The many topics eligible for funding have resulted in a wide variety of projects. Only one city has put the quality of the environment first. Most cities have initiated projects in the areas of clean energy, improving electricity supply, reducing air pollution, construction of new roads, purchasing electric buses, waste disposal and sanitation. What is also lacking, is a focus on human rights, gender, and the interests of the poorest population groups.
In some places, it has been decided to clear slums and relocate residents to high-rise buildings on the outskirts of the city. Indian master architect Doshi warns that the urban vision behind the smart city plans will destroy the informality and diversity that is the cornerstone of the country's rural and urban society. He challenges planners to shift the emphasis to rural areas and to create sufficient choices and opportunities there.
The European Mission on Climate-neutral and Smart Cities
The problem
Cities produce more than 70% of the world's greenhouse gas emissions and use more than 65% of total energy. In addition, cities in Europe only cover 4% of the total surface area and accommodate 75% of the population. The ecological footprint of the urban population is more than twice what it is entitled to, assuming a proportional distribution of the earth's resources.
The mission
On November 25, 2021, the European Commission called on European cities to express their interest in a new European mission on Climate-neutral and smart cities. The mission aims to have 100 climate-neutral and smart cities by 2030, which will act as a model for all other European cities.
The sectors involved in this transformation process are the built environment, energy production and distribution, transport, waste management, industrial processes and product use, agriculture, forestry, and other land uses and large-scale deployment of digital technology. That is why the European Commission talks of a green and digital twin, or a simultaneous green and digital transformation.
Governance
Reaching the stated goal requires a new way of working and the participation of the urban population, hence the motto 100 climate neutral cities by 2030 - by and for the citizens.
According to the plan's authors, the main obstacle to climate transition is not a lack of climate-friendly and smart technology, but the inability to implement it. The current fragmented form of governance cannot bring about an ambitious climate transition. Crucial to the success of the mission is the involvement of citizens in their various roles as political actors, users, producers, consumers, or owners of buildings and means of transport.
Funding
The additional investment to achieve the mission is estimated at €96 billion for 100 European cities by 2030, with a net positive economic benefit to society of €25 billion that will increase further in the period thereafter. The European Commission will provide €360 million in seed funding.
The overwhelming amount of funding will have to come from banks, private equity, institutional investors, and from the public sector at the local, regional and national level.
What went wrong with the Indian Mission and its follow-up
The gap between ambitions and reality
Almost all comments on 'the mission' emphasize that three necessary conditions were not met from the start, namely a widely accepted governance model, adequate funding, and involvement of the population and local government. There was an unbridgeable gap between ambitions and available resources, with the contribution of external capital being grossly overestimated.
The biggest problem, however, is the gap between the mission's ambitions and the nature of the problems that India it faces: Cities are bursting at the seams because of the millions of poor people who flock to cities every year in search of work and a place to live that find them only in the growing slums. The priorities for which the country must find a solution are therefore: improving life in rural areas, improving housing in the cities, ensuring safe drinking water, waste disposal, sanitation, and purification of wastewater, good (bus) transport and less polluting car traffic. Urgently needed is a sustainable development model that addresses ecological problems, makes urbanization manageable, controls pollution and will use resources efficiently.
Leap forward
The 'Mission' is a leap forward, which does not tackle these problems at the root, but instead seeks a solution in 'smartification'. Policymakers were captivated by the promises made by IBM and other technology companies that ICT is the basis for solving most urban problems. A view that I objected in the third episode of this series. IC solutions have been concentrated in enclaves where businesses and prosperous citizens are welcomed. The Government of India Special Rapporteur on Housing therefore notes that the proposals submitted had a predominant focus on technology rather than prioritizing affordable housing and doubts the correctness of this choice.
Instead of emphasizing the role of digital technology, the focus should have been on equitable, inclusive, and sustainable living areas for all. Not the area-oriented but the pan-urban approach should have prevailed.
Follow-up
Several authors suggest future actions consistent with the above comments:
• Setting a longer time horizon, which is much more in line with the problems as they are felt locally.
• Decentralization, coupled with strengthening local government in combination with citizen participation.
• A more limited number of large-scale pan-urban projects. These projects should have an immediate impact on all 4000 Indian cities and the surrounding countryside.
• More attention for nature and the environment instead of cutting down trees to widen motorways.
• Training programs in the field of urbanization, partly to align urban development with Indian culture.
The European mission revisited
Leap forward
Europe and India are incomparable in many ways, but I do see similarities between the two missions.
With the proclamation of the 'mission', the Indian government wanted to show the ultimate – perhaps desperate – act of determination to confront the country's overwhelming problems. I therefore called this mission a flight forward in which the image of the 'smart city' was used as a catalyst. However, the country’s problems are out of proportion to this, and the other means employed.
It is plausible that the European Union Commission also wanted to take an ultimate act. After the publication of the ambitious European Green Deal, each national governments seems to be drawing its own plan. The ‘100 cities mission’ is perhaps intended as a 'booster', but here too the feasibility of this strategy is doubtful.
Smart and green
The European Union cherishes the image of a 'green and digital twin', a simultaneous green and digital transformation. Both the Government of India and the European Commission consider digital technology an integral part of developing climate neutral cities. I hope to have made it clear in the previous 21 episodes of this series that digital technology will certainly contribute. However, the reduction of greenhouse gases and digitization should not be seen as an extension of each other. Making a city climate neutral requires way more than (digital) technology. Moreover, suitable technology is still partly under development. It is often forgotten that technology is one of the causes of global warming. Using the image of green and smart twins will fuel the tension between the two, just like it happened in India. In that case, it remains to be seen where the priority will lie. In India it was 'smart'.
Funding
Funding of the Indian mission fell short; much is still unclear about funding of the European mission. It is highly questionable whether European states, already faced with strong opposition to the costs of 'climate', will be willing to channel extra resources to cities.
Governance
The European mission wants to be by and for the citizens. But the goal has already been established, namely becoming climate neutral by 2030. A new 'bottom-up' governmental approach would have been to investigate whether there are cities where a sufficiently large part of the population agrees with becoming climate neutral earlier than in 2050 and how much sooner that could be and next, leave it to these cities themselves to figure-out how to do this.
Can Europe still prevent its mission from failing like India's? I propose to look for in the same direction as India seems to be doing now:
• Opt for one unambiguous goal: Reducing greenhouse gases significantly earlier than 2050.
• Challenge a limited number of cities each to form a broad coalition of local stakeholders that share this ambition.
• Make extra resources available, but also ask the cities themselves to make part of the necessary investments.
• Stimulate universities and industry to provide a European response to Big Tech and to make connections with the 'European Green Deal'.
My e-book Smart City Tales contains several descriptions of intended and alleged smart cities, including the much-discussed Saudi Arabian Neom. The Dutch version is here.
Do you have the ultimate solution for a safe cycle path?
In the Netherlands, people like to cycle a lot. However, bicycle paths are not always safe due to the great variety of cyclists, such as cargo bikes and e-bikes, racing cyclists and bicycle delivery drivers. The Amsterdam Bike City (ABC) Innovation Lab from the Municipality of Amsterdam is looking for the best solution for the variety of speeds on the cycle path, to do something about this problem. The ten best submissions may present their solution to a jury of leading professionals.
Do you have the best idea to improve safety on bicycle paths? If so, you will win € 2,000 and have a chance of winning € 45,000 to implement your idea. Take that chance!
More information:
Transformatie verkeerssysteem Berlijn? Geert Kloppenburg legt uit hoe simpel het is!

In een korte video (3min) geeft Geert Kloppenburg zijn visie geeft over hoe 7 wegen het Berlijnse verkeerssysteem transformeren middels een goedkoop en snel uitvoerbaar plan.
Bekijk de video hier en wordt abonnee van het youtube kanaal voor meer video's!
Laat je feedback achter in de comments of stuur een email naar: eline@geertkloppenburg.nl
Helsinki and Amsterdam invite motorists to ‘code the streets’

Helsinki and Amsterdam are inviting motorists to take part in a study that aims to offer the most socially responsible driving routes in each city.
Code the Streets – an EU-sponsored mobility initiative which will run throughout October and November – asks drivers to test new functions in the traffic navigation app TomTomAmiGO and Mercedes-Benz’ navigation planner, to better understand how to route motorists in a more environmentally aware way.
This includes suggestions on avoiding roads close to schools, residential areas, and parts of the city with high pollution.
The initiative is a collaboration between the City of Amsterdam, City of Helsinki, Aalto University, Amsterdam Institute for Advanced Metropolitan Solutions (AMS Institute), Forum Virium Helsinki, Technical University Delft and The Future Mobility Network, and is funded by TomTom, Mercedes-Benz and EIT Urban Mobility.
Read the full story here: https://cities-today.com/helsinki-and-amsterdam-invite-motorists-to-code-the-streets/
Toekomst van het spoor: Nog meer bouwen?

In deze podcast, praktische voorbeelden uit de Rotterdamse haven en Groningen. Een vernieuwend herontwerp van spoor aanvraag richting infra groeifonds van Dijsselbloem ipv alle traditionele aanvragen voor extra spoor.
Luister naar ProRail innovatiemanager Karel van Gils: https://bit.ly/Karelgils
Redesign of public space in your own area possible?

Would this simple redesign of the public space in the suburbs of Utrecht, be an option in your area? In a special serie of short videos, Geert Kloppenburg visit suburbs of the large cities in the Randstad in Holland. Here is part 1 Utrecht. Curious what you think of the idea and feel free to share!
Watch the video here:
https://youtu.be/l_l5PRhzfVU
Podcast met Rijksbouwmeester Floris Alkemade

‘Andere ontwerpprincipes voor een mobiliteitsysteem zijn noodzakelijk.’ Deze podcast met Floris van Alkemade over de kunst van verandering is nog altijd actueel (deze zomer te gast bij Zomergasten VPRO).
‘Vergrijzing kan een enorme maatschappelijke potentie hebben’
Geert Kloppenburg en Alexander van Altena spreken met rijksbouwmeester Floris Alkemade over waarom verandering eigenlijk helemaal niet radicaal is. Wat gebeurt er als je met andere ontwerpprincipes naar mobiliteit gaat kijken? En hoe kunnen we buitenwijken inrichten voor de mobiliteit van de toekomst?
Vervoer in 2050: zo duurzaam mogelijk

Gaan we straks met de hyperloop op vakantie, stappen we in een personendrone, of is de (elektrische) fiets hét vervoersmiddel van de toekomst? In vier artikelen zoekt NEMO Kennislink-redacteur Roel van der Heijden op welke transportmanieren we moeten inzetten. Sparen we het milieu of willen we zo snel mogelijk overal ter wereld zijn? Sommige keuzes gaan ten koste van elkaar, maar niet altijd. We definiëren steeds een nieuwe einddoel. Het eerste deel is: hoe maken we vervoer zo duurzaam mogelijk?
De (elektrische) fiets is in dit toekomstscenario doorgebroken als hét vervoersmiddel voor alle afstanden onder de pakweg twintig kilometer. Hij blijkt niet te verslaan als het om duurzaamheid gaat. Ga je iets verder dan pak je de elektrische auto of trein. Voor de echt lange reizen gebruiken mensen het vliegtuig op grotendeels synthetische brandstoffen uit duurzame stroom.
Klinkt dit scenario verrassend ‘gewoon’? De fiets, de auto en het vliegtuig als de vervoersmiddelen van de toekomst? Waar zijn de drones en hyperloops? Uit een rondgang van NEMO Kennislink bij een aantal duurzaamheids- en vervoersonderzoekers blijkt dat we het daar wat betreft duurzaamheid niet van moeten hebben.
Lees het artikel hier. In vervolgdelen nemen we op een vergelijkbare manier de snelheid, betaalbaarheid en het delen van vervoer onder de loep.
(foto Petar Milošević via CC BY-SA 4.0)
Urban Mobility: Cycling transitions in two major European cities

After approximately 15 podcast interviews with experts from around the world, it's time for researcher/advisor/podcastmaker Geert Kloppenburg to look back at the best practices. He started 2,5 years ago with the idea to just contact people in the cities who are actually implementing changes in the streets at this moment. He has discovered so many great best practices that he would like to share.
Geert visited different cities around the world to interview experts on cycling and mobility and noticed an explosion in cycling. And when Corona came, the use of bicycles grew even more.
In this interview Geert looks back on 15 podcast and video interviews on the transformation of different cities.
Watch the 9 minute video and let us know what you think.
Note from ASC: What are your thoughts after watching 👀? Let us know bellow.
De groene Olympische Spelen in Tokyo

In 2020 zouden de ‘Olympic Green Games of Tokyo’ hebben plaatsgevonden, maar corona gooide roet in het eten. De Japanse overheid is er op gebrand om de Spelen in 2021 door te laten gaan met de ambitie om de groenste spelen ooit te organiseren. De Japanse inwoners zien het echter niet zo zitten dat er vanuit alle hoeken van de aardbol toeristen verschijnen. Dit leidde bij de Hedgehog Company tot de vraag:
‘Hoeveel CO2-emissie scheelt het als deze bezoekers lekker voor de buis naar de meerkamp kijken i.p.v. gemiddeld 9000 km af te reizen om te zien hoe een atleet zo ver mogelijk kan springen?’
Op basis van gegevens van de spelen in Rio in 2016 is uitgerekend hoeveel CO2-emissie vrij komt door de vliegreizen van buitenlandse bezoekers die naar het land kwamen met als hoofdreden de Olympische Spelen. Op basis van de gemiddelde afstand en de emissiefactor voor reizigers die gebruik maken van het vliegtuig, levert dit een totale CO2-emissie van meer 300 duizend ton CO2. Dit betekent dat er omgerekend 14 miljoen volgroeide bomen moeten zijn om hiervoor te compenseren. Dus, we kunnen de Japanse overheid adviseren om naar de inwoners te luisteren. Dit maakt de Olympische Spelen niet alleen beter bestendig tegen de pandemie maar ook echt ‘een stukje groener’.
De volledige blogpost kun je hier vinden, inclusief berekeningen en bronnen: https://bit.ly/33abAQh
The impact of COVID-19-lockdown on EV charging

With the lockdown, traffic in the Netherlands largely came to a halt. Electric vehicles were no exception. What are the consequences for the use of public charging infrastructure? And how has the charging behaviour of electric drivers changed? Rick Wolbertus, researcher of the Future Charging project at the Hogeschool van Amsterdam (AUAS), about an initial analysis of the changed use of public charging points. 'Working from home not only makes a difference in traffic jams, it especially had a positive impact on peak loads on the electricity grid.'

Image: Ralph Hutter / Unsplash
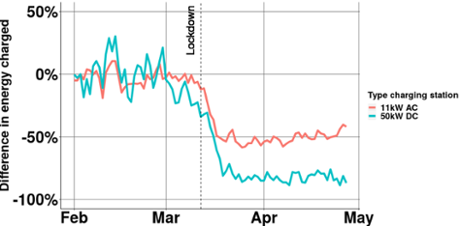
After the lockdown on March 12 2020, there was a lot less driving. Of course, this also applies to electric vehicles. In the Netherlands, about 50% less car driving and that is also reflected in the number of kWh that is charged at public charging stations. It is striking that the use of fast chargers fell faster than the use of level 2 stations. Level 2 stations were used about half as much while the use of fast charging stations (in the city) became about 80% less. The reference date for these numbers is the 3rd of February (February 1st is a Saturday).
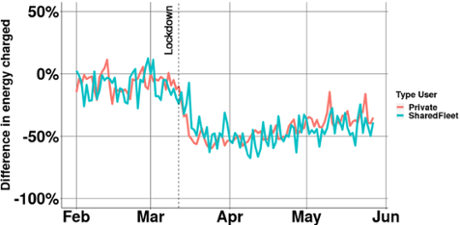
In the second figure, we compare shared cars with regular users. It is striking that shared cars keep pace with private use in the number of kWh charged. Although these cars are used by several people, there seems to be no additional fear of getting infected in shared cars.
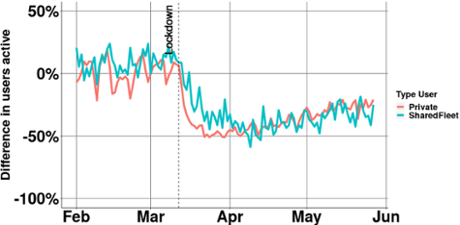
The third figure also shows that slowly traffic levels are returning back to normal. In particular, the number of different users is slowly returning to the pre-corona level. At the end of May, there were only 20% fewer users than before the lockdown. For the total energy that is charged, so the number of kilometers driven, we see that this is falling slightly behind. Compared to mid-March, there is already 10% more loading at the end of April.
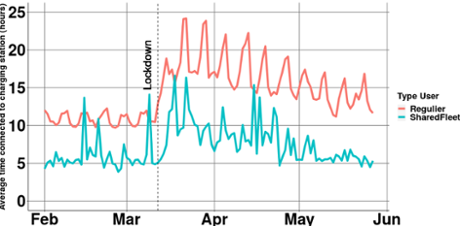
In terms of charging behavior, we also see a change, especially in the average time that a car is connected. For regular users, this average was around 10 hours, but in corona time it jumped to 15 hours, with some outliers on weekends. This was to be expected and is still relatively low compared to the decreased number of kilometers driven. In addition, the downward trend has started again. It is also positive that the connection time for shared cars is almost back to normal. It is clearly visible
It is also striking that the that time when EV drivers charge has changed since the lockdown. Especially the peak in the evenings has become a lot less. At the same time, more is charged especially during the day. So EV drivers go for (electric) rides to the super or hardware store, but commuter traffic has decreased a lot. In addition, all traffic is spread out during rush hours. Even after the lockdown eased after May 11, this trend is still visible. The trend towards more working from home therefore also has a significant (positive) impact on energy demand, especially during peak hours. Working from home therefore saves both traffic jams and peak loads on the electricity grid.
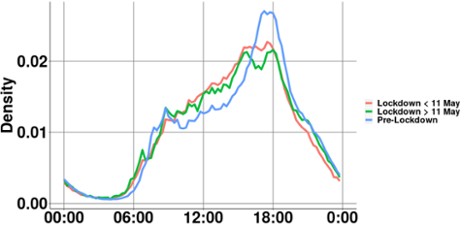
In conclusion, we see that electric transport is hit as hard by the corona crisis as transport in general. It is striking that fast chargers are used less than regular charging stations. Fast charging often shows in previous research in addition to regular charging, to cover longer distances in one day. The sharp fall in the need for fast charging can indicate a significantly reduced daily driving distance for many drivers such as taxis. Cars will stay connected to the charging station longer than before, but less than might be expected. The trend towards charging behavior before the corona crisis seems to have started again.
More information?
Project page Future Charging
Centre of Expertise Urban Technology
Research on Energy Transition
Social: Twitter, LinkedIn en Facebook
Metropolitan Mobility Podcast with Karen Vancluysen (Polis Network)

How can local governments deal with (technological) innovations? Listen to the #podcast with Karen Vancluysen of POLIS Network: https://bit.ly/mobilitypod
Stay up to date
Get notified about new updates, opportunities or events that match your interests.

