Stay in the know on all smart updates of your favorite topics.
AMS Conference: Final call for submissions & keynote speaker announcement

We're thrilled to share another round of exciting updates on the AMS Conference (April 23-24, 2024). As a quick reminder, the submission deadline has been extended to November 14th, providing you with an opportunity to be a contributor to this multi-dimensional event celebrating urban innovation and sustainability. Submit your abstract, workshop, or special session here 👉 https://reinventingthecity24.dryfta.com/call-for-abstracts
🎙️ Meet our keynote speaker: Charles Montgomery
We are honored to introduce Charles Montgomery, an award-winning author and urbanist, named one of the 100 most influential urbanists in the world by Planetizen magazine in 2023. Charles Montgomery leads transformative experiments, research, and interventions globally to enhance human well-being in cities.
His acclaimed book, Happy City, Transforming Our Lives Through Urban Design, explores the intersection between urban design and the emerging science of happiness. His presentation at the AMS Conference, "Your city should be a trust machine," delves into the critical role of trust in human happiness and societal success. As the world grapples with a trust deficit, Charles Montgomery shares insights drawn from over a decade of using lessons from behavioral science and psychology to turn cities into better social machines.
🚀 Don't miss your chance to contribute to the future of cities! For more details about submissions and to submit your abstract, workshop, and/or special session, visit our conference website 👉 https://reinventingthecity24.dryfta.com/call-for-abstracts
23. Governance

This is the 23st episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Its topic is the way how the quality of the living environment benefits from good governance.
In 1339 Ambrogio Lorenzetti completed his famous series of six paintings in the town hall of the Italian city of Siena: The Allegory of Good and Bad Government. The image above refers to the characteristics of governance: Putting the interests of citizens first, renouncing self-interest, helpfulness, and justice. These characteristics still apply.
Rooted in the community
The starting point of urban policy is a long-term vision on the development of the city that is tailored to the needs and wishes of citizens, as they become manifest within and beyond the institutional channels of representative democracy. In policies that are rooted in the community, knowledge, experiences, and actions of those involved are also addressed. Each city has a pool of experts in every field; many are prepared to commit themselves to the future of their hometown.
Participation
Governance goes beyond elections, representative bodies, following proper procedures and enforcing the law. An essential feature is that citizens can trust that the government protects their interests and that their voices are heard. The municipality of Amsterdam has access to a broad range of instruments: co-design, Initiating a referendum, subsiding local initiatives, neighbourhood law, including the 'right to challenge' and neighbourhood budgets. I will deal with participation in the next post.
Two-way communication
Barcelona and Madrid both use technical means to give citizens a voice and to make this voice heard in policy. Barcelona developed the platform Decidem (which means 'We decide' in Catalan) and Madrid made available Decide Madrid ('Madrid decides'). Both platforms provide citizens with information about the policy, allow them to put topics on the policy agenda, start discussions, change policy proposals, and issue voting recommendations for the city council.
Madrid has developed its participatory electronic environment together with CONSUL, a Madrid-based company. CONSUL enables cities to organize citizen participation on the internet. The package is very extensive. The software and its use is free. Consul is in use in 130 cities and organizations in 33 countries and has reached some 90 million citizens worldwide.
City management
Each city offers a range of services and facilities, varying from the fire brigade, police, health services, municipal cleaning services to 'Call and repair' lines, enabling residents to report defects, vandalism, damage, or neglect. Nuisance has many sources: non-functioning bridges, traffic lights, behavior of fellow citizens, young and old, traffic, aircraft noise and neighbours. In many cases, the police are called upon, but they are too often unable or unwilling to intervene because other work is considered more urgent. This is detrimental to citizens' confidence in 'politics' and seriously detracts from the quality of the living environment.
Resilience
Cities encounter disasters and chronic problems that can take decades to resolve. Resilience is needed to cope and includes measures that reduce the consequences of chronic stress (e.g., communal violence) and - if possible - acute shocks (e.g., floods) and eliminate their occurrence through measures 'at the source.'
For an adequate approach to disasters, the fire brigade, police, and ambulances work together and involve citizens. This cooperation must be learned and built up through practice, improvisation and trust and is not created through a hierarchical chain of command.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
22. Nature, never far away

This is the 22st episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Its topic is the way how the quality of the living environment benefits from reducing the contrast between urban and rural areas.
Photos from space show a sharp contrast between city and countryside. Urban areas are predominantly gray; rural areas turn green, yellow, and brown, but sharp contrasts are also visible within cities between densely built-up neighborhoods and parks. Even between neighborhoods there are sometimes sharp transitions.
The division between city and country
Large and medium-sized cities on the one hand and rural areas on the other are worlds apart in many respects and local government in municipalities would like to keep it that way. For a balanced development of urban and rural areas, it is much better if mutual cohesion is emphasized, that their development takes place from a single spatial vision and (administrative) organization and that there are smooth transitions between both. The biggest mistake one can made is regarding the contrast between city and country as a contradiction between city and nature. Where large-scale agriculture predominates in the rural area, the remaining nature has a hard time. Where nature-inclusive construction takes place in cities, biodiversity is visibly increasing.
The idea that urban and rural areas should interpenetrate each other is not new. At the time, in Amsterdam it was decided to retain several wedges and to build garden villages. Some of the images in the above collage show such smooth transitions between urban and rural areas: Eko Park, Sweden (top right), Abuja, Nigeria (bottom left), and Xion'an, China (bottom center). The latter two are designs by SOM, an international urban design agency that focuses on biophilic designs.
Pulling nature into the city
Marian Stuiver is program leader Green Cities of Wageningen Environmental Research at WUR. In her just-released book The Symbiotic City, she describes the need to re-embed cities in soil, water and living organisms. An interesting example is a design by two of her students, Piels and Çiftçi, for the urban expansion of Lelystad. The surrounding nature continues into the built-up area: soil and existing waterways are leading; buildings have been adapted accordingly. Passages for animals run between and under the houses (see photo collage, top left). Others speak of rewilding. In this context, there is no objection to a small part of the countryside being given a residential destination. Nature benefits!
Restoration of the rural area
The threat to nature does not come from urban expansion in the first place, but mainly from the expansion of the agricultural area. Don't just think immediately of the clearing of tropical rain woods to produce palm oil. About half of the Dutch land area is intended for cows. Usually, most of them are stabled and the land is mainly used to produce animal feed.
The development of large-scale industrialized agriculture has led to the disappearance of most small landscape features, one of the causes of declining biodiversity. Part of the Climate Agreement on 28 June 2019 was the intention to draw up the Aanvalsplan landschapselementen . Many over-fertilized meadows and fields that are intended to produce animal feed in the Netherlands were once valuable nature reserves. Today they value from a biodiversity point of view is restricted and they are a source of greenhouse gases. Nature restoration is therefore not primarily focusses at increasing the wooded area. Most of the land can continue to be used for agricultural and livestock farming, provided that it is operated in a nature-inclusive manner. The number of farmers will then increase rather than decrease.
Pulling the city into nature
There are no objections against densification of the city as long this respects the green area within the city. So-called vertical forests by no means make up for the loss of greenery. Moreover, space is needed for urban agriculture and horticulture (photo collage, top center), offices, crafts, and clean industry as part of the pursuit of complete districts. Nature in the Netherlands benefits if one to two percent of the land that is currently used to produce animal feed is used for housing, embedded in a green-blue infrastructure. Some expansion and densification also apply to villages, which as a result are once again developing support for the facilities, they saw disappearing in recent decades.
Finally, I mentioned earlier that nature is more than water, soils, plants, and trees. Biophilic architects also draw nature into the built environment by incorporating analogies with natural forms into the design and using natural processes for cooling and healthy air. The 'Zandkasteel' in Amsterdam is still an iconic example (photo collage, bottom right).
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Just.City.2023

KOM NAAR JUST.CITY.AMSTERDAM.2023
Amsterdam is al 750 jaar in beweging. De ontwikkelingen van de afgelopen jaren maken het een stad waarin niet voor iedereen plek is. Basisvoorzieningen zoals wonen, onderwijs, zorg, voedsel, de publieke ruimte en een leefbaar klimaat staan bijvoorbeeld steeds meer onder druk. We merken allemaal dat er zaken niet rechtvaardig zijn en daar willen wij, samen met jou, verandering in brengen.
Vanaf 16 november voert het Centre of Expertise Urban Governance and Social Innovation daarom officieel de naam Centre of Expertise Rechtvaardige Stad. Op die datum organiseren wij als lancering Just.City.Amsterdam.2023; een middag vol workshops, lezingen, gesprekken en persoonlijke ontmoetingen. Tijdens deze middag in Ru Paré Community willen we elkaar inspireren en aanzetten tot manieren om naar een rechtvaardige stad te kijken en er samen aan te werken. Jij bent van harte welkom!
We hebben schrijvers, dichters, onderzoekers, ondernemers, studenten, bestuurders en buurtorganisaties uit de stad gevraagd om een bijdrage te leveren aan ons programma. Met onder andere: Gökhan Aksoy, Abdelkader Benali, Joris Lechêne, Ria Braaf-Fränkel, Lucia Kula, Roberto Rocco, Arnt Mein.
Via onderstaande knop vind je meer informatie over de lancering en het aanmelden.
21. Work, also in the neighbourhood

This is the 21th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Its topic is the combination of living and working in the same neighbourhood. This idea is currently high on the agenda of many city councils.
Benefits for the quality of the living environment
If there is also employment in or near the place where people live, several residents might walk to work. That will only apply to relatively few people, but urban planners think that bringing living and working closer together will also increase the liveliness of the neighborhood. But more reasons are mentioned: including cross-fertilization, sharing of spaces, the shared use of infrastructure (over time), a greater sense of security and less crime. Whether all these reasons are substantiated is doubtful.
In any case, mixed neighbourhoods contributes to widening the range of residential environments and there is certainly a group that finds this an attractive idea. The illustrations above show places were living and work will be mixed (clockwise): Deventer (Havenkwartier), The Hague (Blinckhorst), Leiden (Bioscience Park), Amersfoort (Oliemolenterrein), Amsterdam (Ravel) and Hilversum (Wybertjesfabriek).
Break with the past
Le Corbusier detested the geographical nearness of work and living. In his vision, all the daily necessities of residents of the vertical villages he had in mind had to be close to home, but the distance to work locations could not be great enough. Incidentally, very understandable because of the polluting nature of the industry in the first half of the 20th century. Nowadays, the latter is less valid. An estimated 30% of companies located on industrial sites have no negative environmental impact whatsoever. A location in a residential area therefore does not have to encounter any objections. The choice for an industrial site was mainly dictated because the land there is much cheaper. And that's where the shoe pinches. The most important reason to look for housing locations on industrial estates is the scarcity of residential locations within the municipality and consequently their high prices. Moreover, in recent decades the surface of industrial estates has grown faster than that of residential locations, at least until a couple of years ago.
Companies are still hesitating
Companies are generally reserved about the development of housing in their immediate vicinity. Apart from the realistic expectation that the price of land will rise, they fear that this will be at the expense of space that they think they will need to grow in the future. This fear is justified: In the Netherlands 4600 hectares of potential commercial sites disappeared between 2016 and 2021. Another concern is that future 'neighbors' will protest against the 'nuisance' that is inherent to industrial sites, among others because of the traffic they attract. The degree of 'nuisance' will mainly depend on the scale on which the mixing will take place. If this happens at block level, the risk is higher than in case of the establishment of residential neighborhoods in a commercial environment. But as said, there is no need to fear substantial nuisance from offices, laboratories, call centers and the like. Companies also see the advantages of mixing living and working, such as more security.
Searching for attractive combinations of living and working
Project developers see demand for mixed-use spaces rising and so do prices, which is an incentive for the construction of compact multifunctional buildings, in which functions are combined. To create sufficient space for business activity in the future, they advocate reserving 30% for business space in all residential locations. The municipality of Rotterdam counters this with a 'no net loss' policy regarding gross floor surface for commercial spaces.
Gradually, attractive examples of mixed living and working areas emerge. Park More (from Thomas More), the entrance area of the Leiden Bioscience Park, which will consist of homes, university facilities and a hotel (photo top right). The idea is that in the future there will also be room for the storage of rainwater, the cultivation of food and the production of the estate's own energy.
Another example, which can probably be followed in more places, is the transformation of the Havenkwartier Deventer into a mixed residential and working area, although part of the commercial activity has left and the buildings are being repurposed as industrial heritage (photo above left). The starting point is that, despite hundreds of new homes, the area will retain its industrial and commercial character, although some residents complain about the 'smoothening' of the area'. Living and working remains a challenging combination, partly depending on where the emphasis lies. In this respect, many eyes are focused on the substantiation of the plans of Amsterdam Havenstad.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Expeditie Muziek

Ik heb de laatste jaren honderden posts geschreven over stedelijke ontwikkeling, innovatie en organisatie. Vele daarvan hebben op deze website gestaan. Ik verschuif mijn schrijfactiviteiten geleidelijk naar het thema waarvan mijn hart sneller gaat kloppen, namelijk muziek. In mijn nieuwe Nederlandstalige blog 'Expeditie muziek' (zie de link hieronder) verken ik wekelijk een ander facet. Deze week is dat de geschiedenis van de blues, vorige week heb ik een top tien samengesteld van de in mijn ogen mooiste Nederlandstalige liedjes 'ooit'. Neem eens een kijkje.
19. Safe living environment

This is the 19th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. This post is about increasing the independent mobility of children and the elderly, which is limited due to the dangers that traffic entails.
For safety reasons, most urban children under the age of ten are taken to school. The same goes for most other destinations nearby. It hampers children’s independent mobility, which is important for their development.
Car-free routes for pedestrians and cyclists
For security reasons, car-free connections between homes and schools, community centers, bus stops and other facilities are mandatory (photo’s top left and bottom right). Car routes, in their turn, head to neighborhood parking spaces or underground parking garages. Except for a limited number of parking spaces for disabled people.
Design rules
Model-wise, the design of a residential area consists of quadrants of approximately 200 x 200 meters in which connections are primarily intended for pedestrians and cyclists. There are routes for motorized traffic between the quadrants and there are parking facilities and bus stops at the edges. Inhabitants might decide that cars may enter the pedestrian area at walking pace to load and unload to disappear immediately afterwards. The routes for pedestrians and cyclists connect directly with the shops and other destinations in the neighborhood, based on the idea of the 15-minute city. Shops 'ideally' serve 9 to 16 quadrants. In practice, this mode will have many variations because of terrain characteristics, building types and aesthetic considerations.
Examples
The number of neighborhoods where cars can only park on the outskirts is growing. A classic example is 'ecological paradise' Vauban were 50 'Baugruppen' (housing cooperatives) have provided affordable housing (photo bottom middle ). Car-free too is the former site of the Gemeentelijk waterleidingbedrijf municipal water supply company in Amsterdam - (photo bottom left). Here almost all homes have a garden, roof terrace or spacious balcony. The Merwede district in Utrecht (top middle) will have 12,000 inhabitants and for only 30% room for parking is available, and even then only on the edge of the district. Shared cars, on the other hand, will be widely available. The space between the houses is intended for pedestrians, cyclists and children playing.
More emphasis on collective green
Due to the separation of traffic types and the absence of nuisance caused by car, there are no obligatory streets, but wide foot- and cycle paths. Instead there are large lawns for playing and picnicking, vegetable gardens and playgrounds. Further space savings will be achieved by limiting the depth of the front and back gardens. Instead, large collective space appears between the residential blocks; remember the Rivierenwijk in Utrecht that I mentioned in the former post (top right). Behind the buildings, there is room for small backyards, storage sheds and possibly parking space.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Ethics and other digital dilemmas

Our we spending more time than offline? Get off your screen and join us as we discuss ‘addiction by design’ and other digital dilemmas. Meet the experts on ethics and responsible technologies. During this event we will learn about how digital applications have evolved, how they have shaped our society, and how we can make them more humane. Don't miss this opportunity to network with fellow apps-for-good developers.
Next Thursday November 2nd, we will be discussing the bitter truths of ethics in web & app development. As a designer, coder or business developer, how can we keep our apps responsible? How can we create healthier relationships between app users (and makers)? What does our digital and social society look like in the next 15 years? The goal of this event is to showcase, discover and foster apps for good.
AGENDA:
- 17:00 Welcome drinks - Welcome drinks to break the ice and network a bit with fellow attendees.
- 17:30 Opening and Welcome - Pinch / Appsterdam
- 17:45 Kick-off Speaker - Mike Lee - Mayor of Appsterdam. Mike will be revisiting his 2013 flagship talk “Ethics Made Easy”. How does this talk still hold up ten years later? What has changed, what principles should app makers consider going forward?
- 18:10 Ethical Expert: Douwe Schmidt - Public Tech Gemeente Amsterdam. Douwe us a co-found of the Tada - 6 values that guide the responsible use of data and the responsible design of technology in the city based on inclusivity, with control, human centric, legitimate and controlled, open and transparent & from everyone, for everyone.
- 18:30 Food is served
- 19:00 TDB
- 19:20 Emiel Poot - De Jonge Strateeg & Appsterdammer - Emiel will delve into the balance between our human nature and todays digital landscape. We all have a fundamental need for social connection, but how have our instincts adapted to digital relationships, communication, and sense of belonging? Join us as we navigate the fascinating synergy between our wired brains and the virtual networks that have reshaped the very essence of human interaction.
- 19:45 - Closing and networking drinks.
Kom 10 november naar de FoodCLIC visie workshop: Samen de route uitstippelen naar een gezonde, duurzame en toegankelijke voedselomgeving voor iedereen in de MRA.

FoodCLIC is een Europees onderzoeksproject waarin onderzoek gedaan wordt naar voedselsysteemtransformatie in stadsregio's. Het project richt zich op de plekken waar productie en consumptie samen komen, oftewel de voedselomgeving van de Metropool Regio Amsterdam. Voedsel Verbindt is als een van de praktijk partners aangesloten bij dit project en wilt daarom graag ook jouw stem vertegenwoordigd hebben binnen het onderzoek. Samen met de Vrije Universiteit, Food Council MRA en de Gemeente Amsterdam werken we samen om tot mooie inzichten te komen.
FoodCLIC kenmerkt zich doordat we ons bezig gaan houden met actie-onderzoek. In de vorm van real-life interventies. Voor verandering moeten we namelijk gewoon iets gaan doen, op zoek naar de oplossingen dus!
Datum en tijd:
vrijdag 10 november van 09.30 tot 16.30 (borrel tot 17.30 uur. )
Inclusief lokale lunch.
De locatie is:
Cultureel centrum NoLIMIT, Geldershoofd 80, 1103 BG, Amsterdam
Programma
09:30: Inloop & registratie
09:45: Start van de bijeenkomst
10:30: Workshop 1 - Regionale visie op de voedselomgeving in 2050
12:00: Voedseltours door de wijk
12:30: Pauze (Lunch) - Lokale voedselinitiatieven op je bord
13:30: Workshop 2 - Het voedselsysteem begrijpen
15:00: Pauze
15:30: Workshop 3 - Uitkomsten en doelstellingen formuleren
16:30: Borrel
Registreer jezelf via de onderstaande link:
Voel je vrij om contact op te nemen via ruben.smolders@voedselverbindt.nl
17. A sociable inclusive neighborhood

This is the 17th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. This post is about the contributions of sociability and inclusivity to the quality of the living environment.
Almost everyone who is going to move looks forward with some trepidation to who the neighbors will be. This post is about similarities and differences between residents as the basis for a sociable end inclusive neighborhood.
"Our kind of people"
The question 'what do you hope your neighbors are' is often answered spontaneously with 'our kind of people'. There is a practical side to this: a family with children hopes for a family with playmates of about the same age. But also, that the neighbors are not too noisy, that they are in for a pleasant contact or for making practical arrangements, bearing in mind the principle 'a good neighbor is better than a distant friend'. A person with poor understanding often interprets 'our kind of people' as people with the same income, religion, ethnic or cultural background. That doesn't have to be the case. On the other hand, nothing is wrong if people with similar identities seeking each other's proximity on a small scale.
All kinds of people
A certain homogeneity among the immediate neighbours, say those in the same building block, can go hand in hand with a greater variety at the neighbourhood level in terms of lifestyle, ethnic or cultural background, age, and capacity. This variety is a prerequisite for the growth of inclusiveness. Not everyone will interact with everyone, but diversity in ideas, interests and capacities can come in handy when organizing joint activities at neighborhood and district level.
Variation in living and living arrangements
The presence of a variety in lifestyles and living arrangements can be inspiring. For example, cohousing projects sometimes have facilities such as a fitness center or a restaurant that are accessible to other residents in the neighbourhood. The same applies to a cohabitation project for the elderly. But it is also conceivable that there is a project in the area for assisted living for (former) drug addicts or former homeless people. The Actieagenda Wonen “Samen werken aan goed wonen” (2021) provides examples of the new mantra 'the inclusive neighbourhood'. It is a hopeful story in a dossier in which misery predominates. The Majella Wonen project in Utrecht appealed to me: Two post-war apartment complexes have been converted into a place where former homeless people and 'regular' tenants have developed a close-knit community. It benefits everyone if the residents of these types of projects are accepted in the neighborhood and invited to participate.
Consultation between neighbours
It remains important that residents as early as possible discuss agreements about how the shared part of life can be made as pleasant as possible. This is best done through varying combinations of informal neighborhood representatives who discuss current affairs with their immediate neighbours. A Whatsapp group is indispensable.
Mixing income groups is also desirable, especially if the differences in housing and garden size are not too great. It does not work if the impression of a kind of 'gold coast' is created.
If functions are mixed and there are also offices and other forms of activity in a neighborhood, it is desirable that employees also integrate. This will almost happen automatically if there is a community center with catering.
Most of what is mentioned above, cannot be planned, but a dose of goodwill on the part of all those involved contributes to the best quality of living together.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Harnessing Bio-Based Construction to Beat Carbon Budgets and Preserve Our Planet
The construction sector is projected to exceed its carbon budget by 2026 using current construction practices.
But by constructing half of new residential buildings with bio-based materials, we can actually reduce CO2 emissions by 18% by 2030. That’s according to Metabolic's latest research, made possible through funding from Built by Nature. And if we consider carbon sequestration, we can even reduce the impact of the residential construction sector by 52%.
However, if solely focusing on carbon, we must be mindful not to shift the burden to other planetary boundaries. In our research, we discuss topics such as sustainable wood supply, climate change risks, and land use change. Based on our findings, we propose six steps to consider to realize a sustainable biobased construction sector.
Amsterdam Donut Dag

Groter dan ooit: Amsterdam Donut Dag 13 november - schrijf je nu in!**
De langverwachte Amsterdam Donut Dag staat bijna voor de deur! Op 13 november duiken we in de wereld van de Donut Economie en laten we zien hoe de gezamenlijke inspanning van pioniers Amsterdam tegen 2025 dichter bij de Donut brengt.
Dit jaar is extra bijzonder, want het markeert de allereerste Wereldwijde Donut Dag onder het motto 'Lokale Actie, Mondiale Connectie.' Wereldwijd organiseren meer dan 30 groepen en netwerken lokale Donut Festivals!
Verspreid over Amsterdam vinden op maandag 13 november in totaal 15 Donut-sessies plaats. Hier laten we samen zien dat de Donut Economie geen theoretisch model is, maar een praktische benadering. Verwacht geen vage beloftes, maar concrete voorbeelden van initiatieven binnen de stad, zowel groot als klein.
's Avonds komen we samen in Pakhuis de Zwijger om samen met pioniers en elkaar te dromen en te visualiseren hoe Amsterdam eruit zou kunnen zien in 2025. Mis deze geweldige kans niet! Ben jij erbij?
16. A pleasant (family) home

This is the 16th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. This post is about one of the most important contributions to the quality of the living environment, a pleasant (family)home.
It is generally assumed that parents with children prefer a single-family home. New construction of this kind of dwelling units in urban areas will be limited due to the scarcity of land. Moreover, there are potentially enough ground-access homes in the Netherlands. Hundreds of thousands have been built in recent decades, while families with children, for whom this type of housing was intended, only use 25% of the available housing stock. In addition, many ground-access homes will become available in the coming years, if the elderly can move on to more suitable housing.
The stacked house of your dreams
It is expected that urban buildings will mainly be built in stacks. Stacked living in higher densities than is currently the case can contribute to the preservation of green space and create economic support for facilities at neighbourhood level. In view of the differing wishes of those who will be using stacked housing, a wide variation of the range is necessary. The main question that arises is what does a stacked house look like that is also attractive for families with children?
Area developer BPD (Bouwfonds Property Development) studied the housing needs of urban families based on desk research, surveys and group discussions with parents and children who already live in the city and formulated guidelines for the design of 'child-friendly' homes based on this.
Another source of ideas for attractive stacked construction was the competition to design the most child-friendly apartment in Rotterdam. The winning design would be realized. An analysis of the entries shows that flexible floor plans stand head and shoulders above other wishes. This wish was mentioned no less than 104×. Other remarkably common wishes are collective outdoor space [68×], each child their own place/play area [55×], bicycle shed [43×], roof garden [40×], vertical street [28×], peace and privacy [27× ], extra storage space [26×], excess [22×] and a spacious entrance [17×].
Flexible layout
One of the most expressed wishes is a flexible layout. Family circumstances change regularly and then residents want to be able to 'translate' to the layout without having to move. That is why a fixed 'wet unit' is often provided and wall and door systems as well as floor coverings are movable. It even happens that non-load-bearing partition walls between apartments can be moved.
Phased transition from public to private space
One of the objections to stacked living is the presence of anonymous spaces, such as galleries, stairwells, storerooms, and elevators. Sometimes children use these as a play area for lack of anything better. To put an end to this kind of no man's land, clusters of 10 – 15 residential units with a shared stairwell are created. This solution appeals to what Oscar Newman calls a defensible space, which mainly concerns social control, surveillance, territoriality, image, management, and sense of ownership. These 'neighborhoods' then form a transition zone between the own apartment, the rest of the building and the outside world, in which the residents feel familiar. Adults indicate that the use of shared cars should also be organized in these types of clusters.
Variation
Once, as the housing market becomes less overburdened, home seekers will have more options. These relate to the nature of the house (ground floor or stacked) and - related thereto - the price, the location (central or more peripheral) and the nature of the apartment itself. But also, on the presence of communal facilities in general and for children in particular.
Many families with children prefer that their neighbors are in the same phase of life and that the children are of a similar age. In addition, they prefer an apartment on the ground floor or lower floors that preferably consists of two floors.
Communal facilities
Communal facilities vary in nature and size. Such facilities contain much more than a stairwell, lift and bicycle storage. This includes washing and drying rooms, hobby rooms, opportunities for indoor and outdoor play, including a football cage on the roof and inner gardens. Houses intended for cohousing will also have a communal lounge area and even a catering facility.
However, the communal facilities lead to a considerable increase in costs. That is why motivated resident groups are looking for other solutions.
Building collectively or cooperatively
The need for new buildings will increasingly be met by cooperative or collective construction. Many municipalities encourage this, but these are complicated processes, the result of which is usually a home that better meets the needs at a relatively low price and where people have got to know the co-residents well in advance.
With cooperative construction, the intended residents own the entire building and rent a housing unit, which also makes this form of housing accessible to lower incomes. With collective building, there is an association of owners, and everyone owns their own apartment.
Indoor and outdoor space for each residential unit
Apartments must have sufficient indoor and outdoor space. The size of the interior space will differ depending on price, location and need and the nature of the shared facilities. If the latter are limited, it is usually assumed that 40 - 60 m2 for a single-person household, 60 - 100 m2 for two persons and 80 - 120 m2 for a three-person household. For each resident more about 15 to 20 m2 extra. Children over 8 have their own space. In addition, more and more requirements are being set for the presence, size, and safety of a balcony, preferably (partly) covered. The smallest children must be able to play there, and the family must be able to use it as a dining area. There must also be some protection against the wind.
Residents of family apartments also want their apartment to have a spacious hall, which can also be used as a play area, plenty of storage space and good sound insulation.
'The Babylon' in Rotterdam
De Babel is the winning entry of the competition mentioned before to design the ideal family-friendly stacked home (see title image). The building contains 24 family homes. All apartments are connected on the outside by stairs and wide galleries. As a result, there are opportunities for meeting and playing on all floors. The building is a kind of box construction that tapers from wide to narrow. The resulting terraces are a combination of communal and private spaces. Due to the stacked design, each house has its own shape and layout. The living areas vary between approximately 80 m2 and 155 m2 and a penthouse of 190 m2. Dimensions and layouts of the houses are flexible. Prices range from €400,000 – €1,145,000 including a parking space (price level 2021).
As promised, the building has now been completed, albeit in a considerably 'skimmed-down' form compared to the 'playful' design (left), no doubt for cost reasons. The enclosed stairs that were originally planned have been replaced by external steel structures that will not please everyone. Anyway, it is an attractive edifice.
14. Liveability
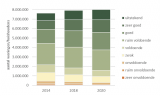
The picture shows the average development of the liveability per household in residential neighborhoods in the Netherlands from 2014 (source: Leefbaarheid in Nederland, 2020)
This is the 14th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. This post discusses how to improve the liveability of neighbourhoods. Liveability is defined as the extent to which the living environment meets the requirements and wishes set by residents.
Differences in liveability between Dutch neighbourhoods
From the image above can be concluded that more than half of all households live in neighborhoods to be qualified as at least 'good'. On the other hand, about 1 million households live in neighborhoods where liveability is weak or even less.
These differences are mainly caused by nuisance, insecurity, and lack of social cohesion. Locally, the quality of the houses stays behind.
The neighborhoods with a weak or poorer liveability are mainly located in the large cities. Besides the fact that many residents are unemployed and have financial problems, there is also a relatively high concentration of (mental) health problems, loneliness, abuse of alcohol and drugs and crime. However, many people with similar problems also live outside these neighbourhoods, spread across the entire city.
Integration through differentiation: limited success
The Netherlands look back on a 75 years period in which urban renewal was high on the agenda of the national and municipal government. Over the years, housing different income groups within each neighbourhood has played a major role in policy. To achieve this goal, part of the housing stock was demolished to be replaced by more expensive houses. This also happened if the structural condition of the houses involved gave no reason to demolishment.
Most studies show that the differentiation of the housing stock has rarely had a positive impact on social cohesion in a neighborhood and often even a negative one. The problems, on the other hand, were spread over a wider area.
Ensuring a liveable existence of the poor
Reinout Kleinhans justly states: <em>Poor neighborhoods are the location of deprivation, but by no means always the cause of it.</em> A twofold focus is therefore required: First and foremost, tackling poverty and a structural improvement of the quality of life of people in disadvantaged positions, and furthermore an integrated neighborhood-oriented approach in places where many disadvantaged people live together.
I have already listed measures to improve the quality of life of disadvantaged groups in an earlier post that dealt with social security. I will therefore focus here on the characteristics of an integrated neighbourhood-oriented approach.
• Strengthening of the remaining social cohesion in neighborhoods by supporting bottom-up initiatives that result in new connections and feed feelings of hope and recognition.
• Improvement of the quality of the housing stock and public space where necessary to stimulate mobility within the neighborhood, instead of attracting 'import' from outside.
• Allowing residents to continue living in their own neighborhood in the event of necessary improvements in the housing stock.
• Abstaining from large-scale demolition to make room for better-off residents from outside the neighborhood if there are sufficient candidates from within.
• In new neighborhoods, strive for social, cultural, and ethnic diversity at neighborhood level so that children and adults can meet each other. On 'block level', being 'among us' can contribute to feeling at home, liveability, and self-confidence.
• Curative approach to nuisance-causing residents and repressive approach to subversive crime through the prominent presence of community police officers who operate right into the capillaries of neighbourhoods, without inciting aggression.
• Offering small-scale assisted living programs to people for whom independent living is still too much of a task. This also applies to housing-first for the homeless.
• Strengthening the possibilities for identification and proudness of inhabitants by establishing top-quality play and park facilities, a multifunctional cultural center with a cross-district function and the choice of beautiful architecture.
• Improving the involvement of residents of neighbourhoods by trusting them and giving them actual say, laid down in neighborhood law.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Live podcast-opname over afbouw: ‘Voer voor Verandering’

Dinsdag 7 november organiseert DRIFT in Theater Walhalla te Rotterdam haar allereerste interactieve podcast-avond over afbouw. Waar moeten we mee stoppen voor een beter Nederland? En hoe?
Wouter Mulders gaat in gesprek met stopstrateeg Marije van den Berg en aspirant-Minister van Afbraak Derk Loorbach. Stel je vragen live in de podcast en praat – zodra de microfoon weer uit is – onder het genot van een drankje na met andere transitiemakers. Koop hier je kaartje!
De DRIFT podcast ‘Voer voor verandering‘ gaat het vierde seizoen in. In dit nieuwe seizoen gaan we aan de slag met de vraag: als goede afbouw zo belangrijk is voor een groener en eerlijker Nederland, waarom zien we er dan zo weinig van? In vijf afleveringen, duiken we die vraag in door middel van muziek, verhalen en gesprekken met (oud-)burgemeesters, activisten, een rouw- en verliestherapeut en allerlei andere experts en ervaringsdeskundigen.
Omdat we meer willen doen dan alleen (uit)zenden, gaan we dinsdagavond 7 november een live podcast opnemen, waarin we het gesprek aan gaan met ons (luisteraars)netwerk over afbouw. Daar kun jij bij zijn!
Het programma ziet er als volgt:
- 18:30 – deuren open
- 19:00 – start van de avond met inleiding
- 19:45 – live opname met Wouter Mulders, Marije van den Berg en Derk Loorbach
- 20:30 – afsluiting
- 21:00 – napraten en gelegenheid tot drankje
De avond zal plaatsvinden in Theater Walhalla’s ‘Kleine Walhalla’, Sumatraweg 9-11 op Katendrecht in Rotterdam.
Kaartjes kosten € 12 en zijn te koop via deze link.
13. Social safety

This is the 13th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. This post discusses the way cities can secure public space, distinguishing symptom control and a more fundamental approach.
Scope of crime
According to the World Health Organization, the risk of being confronted with physical violence significantly detracts from the quality of life. In 2000, homicides worldwide resulted in half a million deaths, nearly twice the number of people who died in a war that year, but less than 40% of fatalities on roads. Many murders are related to drug trafficking. The number of murders in the European Union that year was about 5200. Between 2008 and 2016, car thefts dropped by 36% and robberies by 24%. Both trends leveled off after 2010. However, police-recorded sexual violence in the EU shows an increase of 26% between 2013 and 2016.
Monitoring
Social safety is a precondition for the viability of public space. This applies to who works there, who lives there and who visits it. Frequently chosen solutions are the installation of cameras. Not bad, although streets without cameras run the risk of becoming less safe. Moreover, miscreants know well how to disguise their identity.
In Stratumseind, the illustrious nightlife center of Eindhoven, extensive experiments with CCTV cameras and sensors and, in addition, atmospheric lighting and scents have been executed (photo below right researcher Rinus Kanters in the control room). The city regards this experiment as a 'living lab' and it has continuously been evaluated. The results so far are that no clear connection has been found between this technology and the number of incidents, the feeling of safety among visitors has increased and the police are more quickly on the scene in the event of incidents.
Intensive use
Further conditions are intensive use. The more people on the street, the greater the social security, except for theft. Also 'eyes on the street', apartments in the space above the plinths help. More generally, transparency is of value. Transparent plinths of apartment buildings contribute to it (photo left: the Kleiburgflat, Amsterdam)
Lighting
Lighting is an important issue. It is not even so much about the fierceness of it, which entails other objections, but about the uniformity (photo above right). A particularly wrong idea is to equip lights with motion sensors, so that they only come on when a passer-by approaches. This is at the expense of the ability to keep an overview. There is no objection to slightly dimming the lighting when streets are less busy.
A decent existence
The ultimate policy to reduce crime and improve security is:
• Providing training, guidance and 'social employment', such as the 'Melkert jobs' from the 1990s, to bridge the distance to the labor market.
• Creating guaranteed jobs in the public sector for all. Not only to improve the quality of life of the unemployed, but also to perform numerous tasks that are currently left undone.
• Allocating a decent income to all adults, as long as paid work still falls short. Experiments with basic income show that this increases resilience, self-confidence and the chance of paid work.
• Providing temporary professional (psychological) assistance and guidance with household, and financial management and training on the way to full integration in society.
• The more intensively residents of a neighborhood interact with each other and keep an eye on each other's possessions, the less crime will have a chance. Social control has always been a powerful weapon against crime.
• In anticipation of permanent housing, shelter the homeless to prevent drug-related crimes and give high priority to combating violence and burglary.
It would be naive to think that less inequality and improvements in income, jobs and housing for the poorest groups will eliminate crime altogether. Greed, thrill-seeking, boredom, membership in wrong groups, wrong connections, imitation, mental illness, and alcohol and drugs abuse are not necessarily related to poverty and require judicial action.
Effective prevention and policing
• protection against the relatively small group of repeat-offenders, who are responsible for most crimes, especially violent crimes.
• Close cooperation between residents and the police at neighborhood level
• Police presence on bicycles (better than in cars),
• Detailed knowledge of the police and judiciary of and communication with youth groups that incidentally causes problems
• Sensible and proportionate use of digital resources to track down criminals.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Vote your favourite innovative idea to the AmSIA stage!

Which innovative idea will make it to the stage during the finale of the Amsterdam Science & Innovation Award 2023? This Innovation Award is the Amsterdam competition for research based innovative ideas that contribute to a better world. Check out the website and watch the pre-finalists one-minute videos in which they present their innovative ideas and vote for your favorite! During the finale on 21 November, the jury will award € 10,000 to the three best ideas in the categories of Society, Health and Environment & Climate.
Piss Soap Workshop at W139 (Amsterdam)

Dear Community,
This Saturday at w139 from 14:00-17:00 I will be facilitating a workshop on how to make your own soap with waste, including your golden biofluid.
Throughout the entire Piss Soap workshop, the basics of ecodeviance will be presented and exemplified throughout the process of saponification. We will review the possibility for local and tangible regenerative design, circular ecology and how to tackle the climate crisis while providing cleaning products. The workshop will present the full process of saponification and the steps required to transform domestic waste into usable soap. We will mix the various ingredients and create a circular process informed by waste management. The participants will have the opportunity to create intimate and personal outcomes from their own (bio) wastes. At the end of the workshop, everybody will come back home with 750g of soap to cure at home. After the 3 months needed to its complete maturation, the soap will be ready to be used for washing.
It is all free of charge, feel free to register by sending an email to piss.soaps@gmail.com
12. Water Management

This is the 12th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. This post deals with the question of how nature itself can help to deal with excessive rainfall and subsequently flooding of brooks and rivers, although these disasters are partially human-made.
Until now, flooding has mainly been combated with technical measures such as the construction of dykes and dams. There are many disadvantages associated with this approach and its effectiveness decreases. Nature-inclusive measures, on the other hand, are on the rise. The Netherlands is at the forefront of creating space for rivers to flood, where this is possible without too many problems.
Sponge areas
An important principle is to retain water before it ends up in rivers, canals, and sewers. The so-called sponge city approach can be incorporated into the fabric of new neighbourhoods and it creates sustainable, attractive places too. A combination of small and large parks, green roofs, wadis, but also private gardens will increase the water storage capacity and prevents the sewer system from becoming overloaded and flooding streets and houses. Steps are being taken in many places in the world; [China is leading the way](https://www\.dropbox\.com/s/47zxvl3kgbeeasa/Tale of two cities.pdf?dl=0) (photo top right). However, the intensity of the precipitation is increasing. In 2023, 75 cm of rain fell in Beijing in a few days. Under such conditions, local measures fall short. Instead, nature-inclusive measures must be applied throughout the river basin.
Retention basins
In new housing estates, water basins are constructed to collect a lot of water. Their stepped slopes make them pleasant places to stay in times of normal water level. The pictures on the left are from Freiburg (above) and Stockholm (below). The top center photo shows the construction of a retention basin in Lois Angeles.
Wadis
Wadis are artificial small-scale streams in a green bed with a high water-absorbing capacity. In the event of heavy rainfall, they collect, retain and discharge considerably more water than the sewer system (bottom center photo). Green strips, for example between sidewalks, cycle paths and roads also serve this purpose (photo bottom right: climate-adaptive streets in Arnhem).
Green roofs, roof gardens and soils
Green roofs look good, they absorb a lot of CO2 and retain water. The stone-covered urban environment is reducing the water-retaining capacity of the soil. Sufficiently large interspaces between paving stones, filled with crushed stone, ensure better permeability of streets and sidewalks. The same applies to half-open paving stones in parking lots.
Refrain from building in flood-prone areas
Up to the present day, flood-prone parts of cities are used for various purposes, often because the risk is underestimated or the pressure on space is very great. London's Housing and Climate Crises are on a Collision Course is the eloquent title of an article about the rapidly growing risk of flooding in London.
Hackney Wick is one of 32 growth centers set to help alleviate London's chronic housing shortage, which has already been repeatedly flooded by heavy rainfall. However, the construction of new homes continues. Measures to limit the flood damage at ground floor level include tiled walls and floors, water-inhibiting steel exterior doors, aluminum interior doors, kitchen appliances at chest height, closable sewers, and power supply at roof-level. Instead, floating neighbourhoods should be considered.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
11. Nature inclusivity

This is the 11th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. In this post, I wonder whether nature itself can tackle the environmental problems that humans have caused.
Ecosystem services
According to environmental scientists, ecosystems are providers of services. They are divided into production services (such as clean drinking water, wood, and biomass), regulating services (such as pollination, soil fertility, water storage, cooling, and stress reduction) and cultural services (such as recreation, and natural beauty). In case of nature-inclusive solutions ecosystems are co-managed to restore the quality of life on the earth in the short term and to maintain it in the long term, insofar as that is still possible.
The green-blue infrastructure
The meaning of urban green can best be seen in conjunction with that of water, hence the term green-blue infrastructure. Its importance is at least fourfold: (1) it is the source of all life, (2) it contributes substantially to the capture and storage of CO2, (3) 'green' has a positive impact on well-being and health; (4) it improves water management. This post is mainly about the third aspect. The fourth will be discussed in the next post. 'Green' has many forms, from sidewalk gardens to trees in the street or vegetated facades to small and large parks (see collage above).
Improving air quality
Trees and plants help to filter the water itself. They have a significant role to play in managing water and air pollution. Conifers capture particulate matter. However, the extent to which this occurs is less than is necessary to have a significant impact on health. Particulate matter contributes to a wide range of ailments. Like infections of the respiratory system and cardiovascular disease, but also cancer and possibly diabetes.
Countering heat stress
Heat stress arises because of high temperature and humidity. The wind speed and the radiation temperature also play a role. When the crowns of trees cover 20% of the surface of an area, the air temperature decreases by 0.3oC during the day. However, this relatively small decrease already leads to a 10% reduction in deaths. Often 40% crown area over a larger area is considered as an optimum.
Reduce mental stress and improve mood
According to Arbo Nederland, 21% of the number of absenteeism days is stress-related, which means approximately a €3 billion damage. A short-term effect of contact with nature on stress, concentration and internal tranquility has been conclusively demonstrated. The impact of distributing greenery within the residential environment is larger than a concentrated facility, such as a park, has.
Strengthening immune function via microbiome
The total amount of greenery in and around the house influences the nature and quantity of the bacteria present. This green would have a positive effect on the intestinal flora of those who are in its vicinity and therefore also on their immune function. The empirical support for this mechanism is still rather limited.
Stimulate physical activity
The impact of physical activity on health has been widely demonstrated. The Health Council therefore advises adults to exercise at least 2½ hours a week. The presence of a green area of at least ¼ hectare at 300 meters from the home is resulting more physical activity of adults in such areas, but not to more activity as a whole.
Promoting social contact
Well-designed green areas near the living environment invite social contacts. For instance, placement of benches, overview of the surroundings and absence of traffic noise. The state of maintenance are important: people tend to avoid neglected and polluted areas of public space, no matter how green.
Noise reduction
Vegetation dampens noise to some extent, but it is more important that residents of houses with a green environment experience noise as less of a nuisance. It is assumed that this is due to a mechanism already discussed, namely the improvement of stress resistance because of the greenery present.
Biophilic construction
For years buildings made people sic. A growing number of architects want to enhance the effect of 'green' on human health by integrating it into the design of houses and buildings and the materials used. This is the case if it is ensured that trees and plants can be observed permanently. But also, analogies with natural forms in the design of a building
The 'Zandkasteel', the former headquarters of the Nederlandse Middenstandsbank in Amsterdam, designed by the architects Ton Alberts and Max van Huut, is organically designed both inside and outside, inspired by the anthroposophical ideas of Rudolf Steiner. The (internal) water features are storage for rainwater and the climate control is completely natural. The building has been repurposed for apartments, offices and restaurants.
Green gentrification
Worldwide, there is a direct correlation between the amount of greenery in a neighborhood and the income of its residents. Conversely, we see that poorer neighborhoods where new green elements are added fall victim to green gentrification over time and that wealthier housing seekers displace the original residents.
The challenge facing city councils is to develop green and fair districts where gentrification is halted and where poorer residents can stay. Greening in poor communities must therefore be accompanied by measures that respect the residential rights and aim at improving the socio-economic position of the residents.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Stay up to date
Get notified about new updates, opportunities or events that match your interests.

