Stay in the know on all smart updates of your favorite topics.
9. Road safety

This is the 9th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Casualties in traffic are main threats to the quality of the living environment. ‘Vision zero’ might change this.
Any human activity that annually causes 1.35 million deaths worldwide, more than 20 million serious injuries, damage of $1,600 billion and is a major cause of global warming would be banned immediately. Except for the use of the car. This post describes how changes in road design will improve safety.
The more public transport, the safer the traffic
Researchers from various universities in the US, Australia and Europe have studied the relationship between road pattern, other infrastructure features and road safety or its lack. They compared the road pattern in nearly 1,700 cities around the world with data on the number of accidents, injuries, and fatalities. Lead researcher Jason Thompsonconcluded: <em>It is quite clear that places with more public transport, especially rail, have fewer accidents</em>. Therefore, on roads too public transport must prioritized.
The growing risk of pedestrians and cyclists
Most accidents occur in developing and emerging countries. Road deaths in developed countries are declining. In the US from 55,000 in 1970 to 40,000 in 2017. The main reason is that cars always better protect their passengers. This decrease in fatalities does not apply to collisions between cars and pedestrians and cyclists, many of which are children. Their numbers are increasing significantly, in the US more than in any other developed country. In this country, the number of bicycle lanes has increased, but adjustments to the layout of the rest of the roads and to the speed of motorized traffic have lagged, exposing cyclists to the proximity of speeding or parking cars. SUVs appear to be 'killers'and their number is growing rapidly.
Safe cycling routes
In many American cities, paint is the primary material for the construction of bike lanes. Due to the proximity of car traffic, this type of cycle routes contributes to the increasing number of road deaths rather than increasing safety. The Canadian city of Vancouver, which doubled the number of bicycle lanes in five years to 11.9% of all downtown streets, has the ambition to upgrade 100% of its cycling infrastructure to an AAA level, which means safe and comfortable for all ages and abilities. Cycle paths must technically safe: at least 3 meters wide for two-way traffic; separated from other traffic, which would otherwise have to reduce speed to less than 30 km/h). In addition, users also need to feel safe.
Street design
Vision Zero Cities such as Oslo and Helsinki are committed to reducing road fatalities to zero over the next ten years. They are successful already now: There were no fatalities in either city in 2019. These and other cities use the Vision Zero Street Design Standard, a guide to planning, designing, and building streets that save lives.
Accidents are often the result of fast driving but are facilized by roads that allow and encourage fast driving. Therefore, a Vision Zero design meets three conditions:
• Discouraging speed through design.
• Stimulating walking, cycling and use of public transport.
• Ensure accessibility for all, regardless of age and physical ability (AAA).
The image above shows a street that meets these requirements. Here is an explanation of the numbers: (1) accessible sidewalks, (2) opportunity to rest, (3) protected cycle routes, (4) single lane roads, (5) lanes between road halves, (6) wide sidewalks, (7) public transport facilities, (8) protected pedestrian crossings, (9) loading and unloading bays, (10) adaptive traffic lights.
Enforcement
Strict rules regarding speed limits require compliance and law enforcement and neither are obvious. The Netherlands is a forerunner with respect to the infrastructure for bikes and pedestrians, but with respect to enforcement the country is negligent: on average, a driver of a passenger car is fined once every 20,000 kilometers for a speeding offense (2017 data). In addition, drivers use apps that warn of approaching speed traps. Given the risks of speeding and the frequency with which it happens, this remissing law enforcement approach is unacceptable.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
7. Accessibility

This is the 7th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. The question is whether motorized traffic must be banned from central parts of the city to improve the quality of the urban environment.
Most cities face a choice when it comes to accessibility of their central parts: Whether they renovate the road infrastructure or they face a growing and lasting conflict between car traffic and visitors, whose numbers will decrease further as a result of prioritizing cars. This post deals with the first option.
Changing priorities in the use of road space
The starting point for this renovation is choosing the best experience for both residents and visitors. Therefore, the use of road space in all parts of cities must be under scrutiny. This also applies the connecting roads between centers and the other parts of the city. The distribution of space between pedestrians, cyclists, cars, and public transport has to be reconsidered. A good example is the Ferdinand Bolstraat in Amsterdam. Cars have been banned, the sidewalks are widened, cyclists have their own lanes and the tram uses a switch track (photo below left), just as in Leidsestraat (photo above left).
Accessibility
The rule of thumb is that the larger a city and the better public transport is functioning, the more the accessibility by car of the central parts and the residential areas as well can be reduced. Visitors who rely on the use of a car then store their vehicle in a parking on the edge of the center, preferably near supermarkets or other places where voluminous purchases can be made. From these parking spaces they enter the central area on foot. Incidentally, it is worth considering opening the entire center to cars until 11 a.m. to pick up orders.
Cyclists can be allowed deeper penetration in the central urban area, but not unlimited. They leave their bicycles in (guarded) parking facilities too.
Public transport never stops more than 300 meters from the middle of the center, where comfortable waiting areas are offered, and information is available.
Separation of traffic flows
A separation of traffic flows is required for the entire urban area. The most central streets will be exclusively intended for pedestrians, emergency services and occasionally the tram. Bicycles are allowed in streets in the center, depending on their wideness.
Public transport has always priority at traffic lights. It ensures not only transfer-free accessibility of the urban center, but also connects the most important residential and work areas with a minimum number of transfer. The possible arrival of autonomous minibuses will radically improve the flexibility of public transport (photo above right).
Intra-urban walking and cycling routes
Pedestrians’ and cyclists’ safety and amenity are improved if the connections between the central and outlying parts of the city are accessible by separate routes too. In a city whose green space penetrates deep into the central area, these routes can partly run through nature. A good example is the cycle route from the center of Utrecht to Leidsche Rijn (photo bottom right). Pedestrians need an attractive route through the built-up area for reasons of social safety.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
KL Brouwerij ‘Leefomgeving van de toekomst’

Waar je woont en hoe je leeft, heeft invloed op je gezondheid. Hoe kunnen we de leefomgeving inrichten om de gezondheid van bewoners te bevorderen en gezondheidsachterstanden te verminderen? Tijdens deze KL Brouwerij gaan we samen op buurtsafari op het Marineterrein in Amsterdam.
Het Marineterrein is een prachtige leefomgeving, waar veel geëxperimenteerd wordt met creatieve innovaties die de leefomgeving en publieke ruimte van de toekomst voorbereiden. Op 28 september gaan we samen op safari over het terrein. We ervaren zelf hoe een aantal van deze experimenten onze leefomgeving verbeteren. Daarna vertelt Annick Mantoua, directeur van De Gezonde Stad over hoe zij samen met bewoners en de gemeente een initiatief hebben opgestart dat leidt tot aanpassingen in de fysieke leefomgeving en de bevordering van de gezondheid in de buurt.
We laten ons inspireren door de leefomgeving van de toekomst. We zoeken naar inspiratie voor wat er allemaal mogelijk is en zal zijn in de openbare ruimte, en ontwerpen vervolgens onze eigen ideeën. Kom ook!
De KL Brouwerij wordt georganiseerd door Kennisland. Een aantal keer per jaar laten we ons werk even voor wat het is en brouwen we samen nieuwe ideeën voor maatschappelijke uitdagingen. We brengen leven in de brouwerij door te ontdekken, smeden, broeden, fantaseren en borrelen. Dit doen we met partners, experts, ervaringsdeskundigen en betrokkenen bij het vraagstuk dat die middag centraal staat, en waar we meer over willen leren.
Deze KL Brouwerij vindt plaats op <strong>28 september van 16.30-18.30 uur</strong>. Meer informatie en aanmelden kan via onderstaande link. Via e-mail houden we je op de hoogte over het programma. Heb je vragen? Stuur dan een mailtje naar Faduma Mukhtar via fm@kl.nl.
What can Amsterdam learn from YIMBY Arnhem!

At the 22nd of September 2023 we celebrate the tenth YIMBY Harvest Festival at the Hoeve Klein Mariëndaal in Arnhem. What is YIMBY? YIMBY is the acronym for Yes-In-My-Back-Yard. YIMBY Arnhem! started in 2013 with the distribution of small scale food platforms, called YIMBY's, to the citizen of Arnhem. At the same time green education was offered to urban food growers to convert green enthusiasm into green harvest. During ten years hundreds of citizen in Arnhem joined the YIMBY social network of growing healthy, organic food in the city. The succes of YIMBY Arnhem! are the people supported by local government and local branches of green companies.
YIMBY is a culture of YES, positively stimulating social innovation for a healthier, greener and more social neighbourhood. The YIMBY experience demonstrates that changes do not start in The Hague, Brussels or Strasbourg. The change to a greener and more social Europe starts at home, in the backyard of people. We invited Frans Timmermans to the YIMBY Harvest Festival in Arnhem to share and to learn from ten years of YIMBY experience in the city of Arnhem. YIMBY Arnhem! shows that in due time small grassroots initiatives steadily grow and empower people to social inclusion and green cooperation.
6. Appropriate density
This article is part of the series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Read whether Increasing density of cities complies with the quality of the urban environment.
There is widespread agreement to use the available space more thoughtful than during the last decades. In the Nationale Omgevingsvisie (NOVI), the Dutch government has unambiguously expressed its preference for housing locations within existing built-up areas or in the vicinity of stations.
The need for density
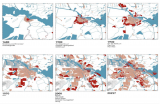
Frequently, references are made to ‘urban sprawl' in the USA to illustrate the disadvantages of low density. However, but The Netherlands is also familiar with extensive growth of the urban area. The maps above show the growth of the Amsterdam area. Between 1900 and 2000, the population of Amsterdam grew from 317,000 to 727,000 inhabitants. Its surface from 560 to 11,500 hectares.
The spread of urban activities over an ever-increasing surface and the associated traffic movements have led to vast monotonous areas, car dependence, expansion of the road network, increasing congestion, impoverishment of social life, air pollution, emissions of greenhouse gases and decline of nature.
A summary of 300 OECD research projects shows that compactness results in more efficient use of facilities, but that there are also disadvantages in terms of health and well-being, usually as results of air pollution and traffic.
Advantages of density
Denser development is generally associated with the availability of amenities within walking distance, creating support for better public transport accessibility, and leading to more efficient use of utilities. Moreover - corrected for the composition of the population - CO2 emissions in urban areas are at least 30% lower than in the suburbs. An advantage that disappears in case of high-rises.
No necessity to expand building outside urban areas
According to many urban planners, there is no reason to divert to locations outside the existing built-up area. They claim that there is sufficient space in every city for new residential locations, for instance disused office buildings and factory locations. Many new homes can also come available through the division of oversized single-family homes and the renovation and raising of older (porch) homes.
These arguments only hold if at the same time the nuisance by densification is limited. For example, by reducing car useto prevent the roads from becoming even more crowded and the streets even more filled with parked cars. I don't see that happening yet.
Competing claims on urban land use
There is another important objection to further densification and that is the fact that other forms of land use also appeal to available land within the urban space. For example, the expansion of industry, trade, research etcetera. preferably in the vicinity of living areas to reduce the length of trips.
The most important claim on the available space is the need to expand the city’s greenery. Research into the development of 'green' in Amsterdam and Brussels since 2010 shows that the open space ratio (OSR) in both cities has decreased. In Amsterdam this was 3.68 km2 (4.7%) and in Brussels 9.17 km2 (11.9%). This is in line with a recent study by Arcadis, which shows that the four major cities in the Netherlands score very poorly on healthy outdoor space, greenery, air quality, noise nuisance, heat stress and safety.
Inner- and outer-urban development revisited
The report therefore concludes that extension of the use of urban space for housing must be weighed up against other claims for the use of space, such as urban greening, urban agriculture, and the maintenance and expansion of business activities. At the same time, the objections to ecologically responsive building activities outside the already urbanized areas must be reconsidered. Three-quarters of the agricultural land is used for intensive livestock farming, not exactly creating valuable nature. I will come back to it later.
In the 'Dossier leefbaar wonen' (in Dutch)' I wrote extensively about the subject of providing affordable housing. You can download this e-book using the link below:
4. Informative plinths

This article is part of the series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Read how design, starting from street-level view contributes to the quality of the urban environment.
Plinths express the nature of activities inside
The visual quality, design and decoration of the plinth, the 'ground floor' of a building, contributes significantly to the quality of the streetscape and to the (commercial) success of the activities that take place at plinth level. This also applies, for example, if the activities of a workshop can be observed through the windows. Blank walls speed up visitors' pace, unless this wall has attractive art. Vacancy is disastrous.
A plinth displays the destination of a building or a part of it (photo bottom left). Fashion stores and suppliers of delicacies depend on its ability to attract buyers. There is nothing against allowing the plinth to expand slightly onto the street - think of beautiful displays of fresh vegetables - if a sufficiently wide barrier-free pedestrian route is maintained.
The total length of streets that must generate customers and visitors must not be too long in order to keeps vacancy to a minimum. This may mean that still profitable shops in streets where the number of vacancies is increasing must consider moving if revitalization of the street is infeasible. The space left behind can best be revamped into space for housing or offices to prevent further dilapidation.
Plinths of non-commercial destinations
The need for an attractive plinth also applies to non-commercial spaces. This may concern information centers, libraries, day care centers for children or the elderly, places where music groups rehearse, etcetera. Co-housing and co-working centers might also concentrate several activities in a semi-public print. In an apartment building, you might like to see an attractive portal through the glass, with stairs and elevators and a sitting area.
Residential plinths
Houses in the more central parts of the city can also have an attractive plinth. In practice, this happens often by placing plants and creating a seat on the sidewalk. The so-called Delft plinths are narrow, sometimes slightly raised additional sidewalks for plants, a bench, or stalling bicycles (photo bottom middle). The worst is if the plinth of a private house is mainly the garage door.
The aesthetics of the plinth
In many pre-war high streets, the plinth was designed as an integral part of the building. In the ‘60s and ‘70s, many retailers modernized their businesses and demolished entire ground floors. The walls of the upper floor, sometimes of several buildings at the same time, rested on a heavy steel beam and the new plinth was mainly made of glass (photo top left). Often a door to reach the upper floors is missing, complicating the premises’ residential function. Initially, these new fronts increased the attractivity of the ground floor. However, the effect on the streetscape has turned out to be negative. In Heerlen, artist and 'would be' urban planner Michel Huisman (the man behind the Maankwartier) is busy restoring old shopfronts together with volunteers and with the support of the municipality (photos top right). In Amsterdam, shopfronts are also being restored to their original appearance (photo bottom right).
Plinths policy
The sky is the limit for improving plinths, as can be seen in the book Street-Level Architecture, The Past, Present and Future of Interactive Frontages by Conrad Kicker and the *Superplinten Handbook</em> , commissioned by the municipality of Amsterdam.
In 2020, a plinth policy was introduced in the Strijp-S district in Eindhoven from a social-economic background. 20% of the available plinths is destined for starters, pioneers and 'placemakers'. Continuous coordination with the target group is important here. In The Hague, 100 former inner-city shops have now been transformed into workplaces for young and creative companies. Differentiating rents is part of the plinth policy too.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
3. Attractive streetscape

This article is part of the series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Read how design, starting from the physical aspects of the streetscape en -pattern contributes to the quality of the urban environment. Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Streets and squares are appreciated best if there is cohesion between several elements, such as the block height, the number of floors, the type of houses, the building line and the colour. When some elements work together, others can vary. Uniformity without variation results in people avoiding a street.
Coherence and variation in balance
Variation creates liveliness and will extend the time visitors spend on a street. This principle is applied almost everywhere in the world. Walls are fitted with arches, pillars, porches, porches, pitched roofs, windowsills, canopies, balustrades, cornices, dormer windows, linear and vertical elements, see the bottom-centre image of a Paris’ building. At the same time, the attributes of separate buildings that provide variety are most effective against a coherent background. The Parisian avenues illustrate this too, because most edifices are built according to the same principles while the ornamentation of each facade differs. The attractive streetscape in Sicily (top right) and in the Alsace (bottom right) demonstrate an almost perfect balance between similarity and difference.
Use of colour
A good example are the painted houses in the Canadian settlement of Lunenburg, which was founded in the 18th century by German woodworkers and is a UNESCO world heritage site today (top centre). The nature of the construction and the type of buildings ensure cohesion; the colour provides the variation.
Street pattern
A manageable pattern of similarly important streets contributes to the spread of visitors and provides a level playing field for shops and restaurants. A mesh, which does not necessarily have to be rectangular, facilitates orientation. A rectangular street pattern is at the expense of the element of surprise and detracts from the feeling that there is something to discover. Squares will often be found at street intersections.
Landmarks
Understanding of the pattern of the streets is reinforced by providing intersections with landmarks, such as statues, fountains, or distinguishing buildings (photo, top right). These elements help visitors developing a mental map. Maps every here and there are more helpful than signposts. The fewer poles in the ground, the better.
Canals and moats
Canals and moats also contribute to the attractivity of the streetscape. They restore the human dimension in too wide streets, also in new parts of the city. The images on the left show a central street in Zaandam (top) and a 'waterway' in the Amsterdam Houthavens quarter (bottom). The edges of waterways should never be used as parking spaces. Definitely not in Amsterdam, because its unique streetscape.
2. Human density

This article is part of the series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Read how design, departing from the human dimension contributes to the quality of the urban environment. Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Human dimension means that residents nor visitors feel overwhelmed by the environment. An urban planner must avoid them thinking that it is all about other things, such as commerce, traffic, or the buildings themselves, which unfortunately often is the case indeed. Constructions by 'star architects' can be crowd pullers but usually also result into a disproportionate use of space. Cities therefore better tolerate only a limited number of such edifices. Alexander Herrebout (OTO Landscape) believes that space has a human dimension if you experience attention for you as a human being and that there are objects you can connect with. For many, this will be more often a historic building (church, town hall) than a modernist one.
Compactness (‘enclosure’)
Compact streets and squares give a sense of security. They encourage people to linger there, increasing the chance of unforeseen encounters. Sjoerd Soeters considers squares in the first place as a widening in the street pattern and therefore they are preferably no larger than 24 by 40 meters. A round or oval shape enhances the feeling of security. If the height of the surrounding buildings is also in line with this, there may be contact between residents and people on the street. Good examples are the square he designed in the Oostpoort shopping center in Amsterdam, but also a square in <em>The Point</em>, a new shopping center in Utah (US), resp. bottom left and bottom center and of course the Piazza der Campo in Siena.
If streets are too wide or narrow or buildings are too high?
Trees, for example a double row all around, will help if a street is too wide or a square is too big. Trees are also a source of reducing urban heat. The extent to which trees contribute to the sense of intimacy is expressed by comparing the images at the top left (Herring Cove Road, Halifax, Canada) and the top right (Course Mirabeau, Aix-en-Provence). A square or a street that is too wide can be further visually reduced by the construction of terraces, the placement of a pavilion or the presence of water features, such as on the Brusselplein, Leidsche Rijn (bottom right). Sometimes also by allowing destination traffic and public transport.
A street that is too narrow can be widened psychologically by designing sidewalks and a carriageway in the same level and shades, possibly separated by a narrow band, as illustrated in the image of the Sluisbuurt in Amsterdam (top center).
If case of high-rises, the human dimension can be respected by planting trees and by placing taller buildings back from the plinth to limit their visibility from the street. This is also illustrated by the image of the Sluisbuurt (top center).
Density
Compactness presupposes a certain density. In a very dense city center is only room for pedestrians and not for traffic, in some cases except for the tram. Though, these areas must be always accessible to emergency services. Waste removal, deliveries and parking must be solved differently, for example on the inner space of blocks or by introducing strict time slots. Every city also needs space for events such as concerts, fairs, etcetera. Accessibility is more important than a central location.
1. Lively streets and squares

This article is the first in the series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities.Read how lively places contribute to the quality of streets and squares. Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
The public space is like a stage. The Dutch architect and urban planner Sjoerd Soeters, known for the Amsterdam Houthavens, likes to say that. He meant that it is the inhabitants and visitors of cities who provide the liveliness, but that streets and squares must ensure that they come. This apparently worked out well on the Rue Sainte-Catherine in Bordeaux (photo above right).
Shopping facilities and catering
Research shows that the quality of the shopping facilities, also for 'fun shoppers', is still the main driver to visit the center of cities. A varied catering offer follows in second place (photo bottom left). A welcome addition are spaces with a non-commercial purpose, such as museums, galleries, art lending, information centers of municipalities or companies, etcetera.
Sidewalks
Sidewalks use to be too narrow, due to the perceived need to accommodate motorized traffic. A sidewalk in central parts of the city must be at least 20 feet wide, such as that of Fillmore Street, San Francisco (top left photo). In that case, sufficient space is offered for greenery, free passage for passers-by and tables or chairs, billboards, and street vendors, who make a welcome contribution to the liveliness of the street.
Opportunity to rest
Places that invite you to linger increase the attractiveness of the area and the chance of unforeseen encounters (collision spaces). These can be terraces, but also non-commercial places such as tree-lined squares with benches, games, buskers (acoustic), an ice cream cart etcetera. One of the most famous examples is the Spanish Steps in Rome. Such spaces usually arise 'by themselves', but they can also be designed as such, for instance, squares in Barcelona and Shanghai (photos bottom center and bottom right). By no means it is certain that they will also be used as such.
Minimize traffic noise
In the more centrally located parts of a city, a certain level of sound is part of the experience, but traffic noise is a source of nuisance and drives away visitors. Through traffic is not compatible with all other (inner) urban functions; destination traffic must be reduced, channeled and its speed limited. Noise at events must also be reduced to an acceptable level for visitors, residents, and passers-by, knowing that events attract many people, but can also repel others as well.
Places with a different character
In an atmospheric city center you will find quiet places and others where it is bustling at the same time. Those quiet places can be small parks with playgrounds and benches to rest, but also publicly accessible courtyards of residential blocks.
Exploiting iconic places
Most cities have places with special characteristics. These are often historic or modern buildings, monuments, fountains etcetera. Sometimes it is a well-known square, such as the Vrijthof in Maastricht. Sometimes it is also the boulevard along a river or special viewpoints (photo top middle) that both city dwellers and visitors like to include in their route and where they linger for a while.
Art
All parts of a city with a central function should be amply supplied with art. For this purpose, also (temporarily) empty shops can be used, which also serve as an information center. Think of art objects on the street (possibly replica’s) and fascinating paintings on blind walls, which number must be limited by the way. In the evening, light art can be imagined on the facades of buildings surrounding streets and squares.
New series: 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities
This article is the introduction to the series 25 building blocks for better streets, neighbourhoods and cities, which you can read every Tuesday and Friday starting next week. The link below refers to an overview of all upcoming posts.
It often strikes me how much people agree about the quality of the living environment. Many, especially younger ones, prefer a house built in the '30s. Older neighbourhoods almost always score higher than modern ones, due to the alleged lack of atmosphere, sociability, and intimacy in the latter. Urban planners, architects and politicians would like to change this, and they are doing so. Slowly.
In urban planning a breeze of fresh air comes in.
How cities in Europe currently look stems largely from the ideas of Le Corbusier through his role in the Congrès Internationaux d'Architecture Moderne (CIAM). The Dutch architect and urban planner Cornelis van Eesteren was also a prominent representative. The influence of the Congress is visible in the spacious post-war residential areas with their long rows of single-family houses and medium-rise buildings. The underlying idea was to design a functional city in which living, working, shopping and recreation all have their own separated places.
Slowly, the voice of a new generation of urban planners in which Jane Jacobs and Jan Gehl (pictures above) play a prominent role became louder. They detest post-war urban expansion and advocate mixing urban functions. 70 years after the publication of her book The Death and Life of Great American Cities, Planetizen magazine predicated urban activist Jane Jacobs as the most influential urban planner ever, even though she never studied this field. Jan Gehl, who did, follows in second place. By the way, Anne Hidalgo, the mayor of Paris, is in 7th place; not because of what she studied but of what she put into practice.
Many others, including representatives of New Urbanism, play an important role in further developing the ideas of Jacobs and Gehl. For instance, they put back on the agenda the return to the 15-minute city. ‘New urbanists’ also top the list: Andres Duany, the author of Suburban Nation at four and Jeff Speck, who authored Walkable City, at ten.
The concept of high-quality living environment
Many contemporary ideas about urban development come together in the concept of high-quality living environment. A compact definition of this concept is improving human well-being in a condensing city. I have collected and clustered references to characteristics of high-quality living environments in many recent publications into 25 building blocks. Each block deals with one aspect of the quality of the living environment, or in other words the creation of better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Consider this a tribute to the mission of the Amsterdam Smart City community, of which I was a curator for several years.
I hope you get inspired and support the use of these building blocks.
GEMINI: Greening European Mobility through cascading innovation INItiatives

Context
At the heart of the GEMINI Project lies a commitment to fostering innovation and to accelerate the transition towards climate neutrality in mobility solutions.
Goal 11 of the UN Sustainable Development Goals advocates for access to safe, affordable, and sustainable transport systems. Nowadays, transport plays a significant role on air pollution and is one of the major sources of greenhouse gas emissions and is the only sector in the EU with increased Green House Gas (GHG) emissions compared to 1990.
The promotion of sustainable and innovative mobility solutions can help towards reducing GHG and carbon footprints, improving air quality, and achieving climate goals.
Project brief
The GEMINI Project (2023-2026 “Greening European Mobility through cascading innovation Initiatives” is a Horizon Europe funded project with 43 partners led by the Urban Electric Mobility Initiative (UEMI).
To accelerate the transition towards climate neutrality, GEMINI aims to foster widespread adoption of sustainable shared mobility solutions. To achieve this, the project will develop and test innovative business models for New Mobility Services (NMS) such as shared connected automated vehicles and shared mobility public transport through public-private partnerships. The NMS business models will be demonstrated in ten European Cities (Amsterdam, Copenhagen, Helsinki, Munich, Leuven, Ljubljana, Paris-Saclay, Porto and Turin).
Additionally, GEMINI will create digital tools and platforms that accommodate various mobility services, promoting collaboration and integration within the mobility sector. The project will actively engage stakeholders in the co-creation process, introducing Mobility as a Commons (MaaC) and incentivizing behavioural shifts and user acceptance of these new mobility options.
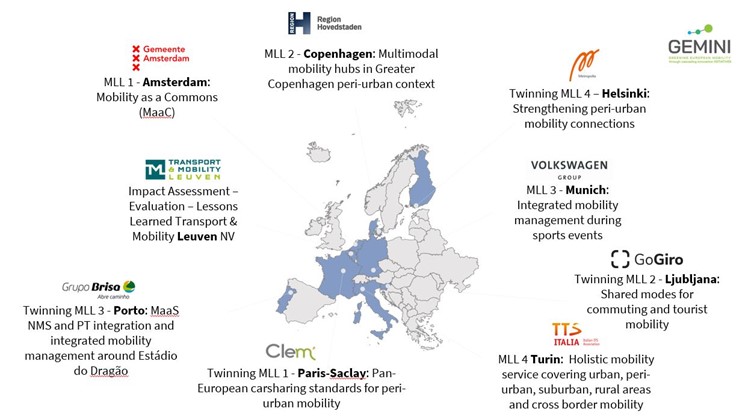
Furthermore, GEMINI will formulate policy recommendations to enable the scaling up and replication of successful mobility solutions. By aligning with Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans (SUMPs) and urban mobility planning frameworks, the project aims to contribute to a comprehensive policy package that guides and incentivizes future mobility innovations. The GEMINI project envisions fostering sustainable, accessible, and affordable shared mobility solutions that contribute to a safer and more environmentally friendly urban mobility landscape.
Objectives
- Develop and test sustainable business models for New Mobility Services (NMS) to increase shared mobility solutions (MaaS and MaaC) for various user groups, including enterprises, families, and tourists.
- Create digital enablers, including collaboration platforms and multimodal MaaS solutions, to integrate and facilitate a wide range of mobility services.
- Actively involve stakeholders in the co-creation of new mobility options and integrate Social Innovation practices to incentivize behavioural changes and user acceptance.
- Formulate policy recommendations to support the scaling up and replicability of successful mobility solutions, contributing to the development and implementation of SUMPs and urban mobility planning frameworks.
Cenex NL key contributions
The team plays a vital role in developing policy recommendations and technology roadmaps to accelerate the deployment of innovative mobility services. Through collaboration with local authorities in twinning cities, these roadmaps will align with the fast-track deployment of shared mobility trends in the short and medium term. Additionally, Cenex NL will contribute to the development of the Handbook consolidating the project’s learnings and offering practical guidance to cities and citizens across Europe.
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 101103801.
Professionals in romanian local public administration. Smart city managers
City Managers Association in Romania (AAPRO) was founded in 2010, as a follow-up of a pilot project called “Public Administrator – a success factor for an efficient management at local level” carry out by the Central Unit for the Public Administration Reform (a structure within the Romanian Ministry of Administration and Interior Affairs).
AAPRO is commited to form a national, relevant, elite and professional Body of City Managers, who must have a clear image on the background of this career and become responsible for their professional conduct and self-improvement.
The initiative to introduce the City manager position at each local level in Romania targets an higher lever of professionalism at counties, municipalities, cities and communes staff.
The romanian equivalent of the city manager can be hired upon the Mayor’s proposal or the one of the local council (wich must give the final aproval anyway), after a transparent selection process. His main responsibilities are to coordinate some of the public administration affairs and services (on an agreed agenda) and to do other specific tasks delegated by the Mayor / President of County Council, all of these concluded in a management contract, based on clear management objectives and performance criteria.
The City Manager is one common thing among the efficient and successful local governments
all over the world. Adopting him in the romanian administration was a step from public adminsitration to public management, focusing on delivery good qaulity services for the citizens. The Public Administrator, as we call it here, is not another birocrat, but a strategist, a visonary, balancing day-to-day (organizational) problem solving with planning and shaping the future, acording to the adopted local strategy and the community aspirations.
At the local level, the elected body and the technical staff, coordinated by the Mayor or the President of County Council and the Public Administrator, must first find aut and understand what people want, need and hope, then come up with a strategy, an action plan, seek for solutions, means and resources, involve the local actors such as bussines community and civil society, and communicate at any moment what has been done so far, and what is is comming.
In this picture, the City manager has a leading role, he is an communicator, technology facilitator, and can be, if the Mayor delegates him, even budget chief authorizing officer. Currently, in Romania activate more than 700 Public Administrators (the number varies from month to monyh), as follows :
- Out of 41 counties, 34 ocupied positions and 7 vacancies
- Out of 103 municipies, 56 ocupied positions and 37 vacancies
- Out of 216 cities, 60 ocupied positions and 65 vacancies
- Out of 2850 communes, 550 ocupied positions and 350 vacancies
Those above figures makes 459 vacancies in total, with the observation that, in many cases, we are talking about small comunes with scarce Romanian City Managers Association (AAPRO) conducted a survey among its members that identified the needs for training, building local capacities on climate protection, urban regeneration, structural changes and energy policies, concept of smart city and creatively intelligent communities.
Establishing appropriate training structures for the now and future City Managers is essential for supporting the development of the cities and climate strategies (it aims to encourage cities and municipalities to take concrete actions for climate protection in Romania), urban regeneration and structural changes, concept of smart city and creatively intelligent communities.
This project focuses on the competences that the city managers must have in order to achieve a multiplication effect through their contribution. The nationwide implementation of a systematic local energy management using the City Managers can thus make an important step to tapp existing saving potentials in different regions and to establish a sustainable portfolio management.
We hope that, with your support, that the outcomes of this important project, can be forwarded on an extended scale to the local institutions (schools, hospitals, etc) and communities, as good practices, improving the energy efficiency status and reducing the energy poverty, urban regeneration and structural changes, concept of smart city and creatively intelligent communities.
The pilot group will be composed of 50 to 80 city managers upon their self enrollment and applying few clear selection parameters : level of municipality, experience, english language, etc. The target group will be afterward authorized to further train other city managers and employees of the local municipalities. This core team is expected to disseminate the information and to act as an experts group in our Association.
As Romania has (at this moment) a deficit of at least 250 city managers, the learning and workshops center will be powerful tool, a public management academy and a testing facility for the ones applying for this position.
Slotevent Summerschool over publieke platformen

🚀 Hoe veranderen publieke platformen de overheid? Een thema dat ons allemaal raakt! Platformen veroveren de wereld. Uber, Marktplaats en AirBNB kennen we allemaal.
Op 30 aug zal het slotevent plaatsvinden van de Summerschool.
Deze middag staat, geheel toepasselijk, in het teken van de veranderende overheid. De 20e Summerschool gaat namelijk over de vraag: Hoe veranderen publieke platformen de overheid, welke toekomstscenario’s kunnen we daarover schetsen en hoe disruptief zijn deze?
Ontdek het antwoord op deze prikkelende vraag tijdens het spectaculaire slotevent ter ere van de 20e summerschool van het @Kennislab voor Urbanisme! 🌟 We nodigen iedereen uit die ooit heeft deelgenomen aan een summerschool of dit graag wil doen.
Deze Summerschool wordt georganiseerd door 'Kennislab voor Urbanisme' en de 'Future City Foundation' in opdracht van de Provincie Zuid-Holland in Den Haag.
Wanneer:
Op 30 augustus van 12.30 tot 17.00 uur
Locatie:
Provinciehuis van de Provincie Zuid-Holland, Zuid Hollandplein 1, 2596 AW Den Haag
📅 Zet 30 augustus alvast in je agenda, want van 12.30 tot 17.00 uur staat een middag vol inspiratie en innovatie op het programma.
📢Bekijk hier het programma van de middag https://lnkd.in/etuMCCU5
📢of geef je direct op via https://lnkd.in/erHMed74
*Dit event is gratis toegankelijk
Smart City tips for an innovative summer in Amsterdam

Whether you’re a visitor exploring Amsterdam, or a local opting for a staycation this summer, boredom is not on the agenda. There are some great things to do and see if you’re interested in innovation and sustainability. Delve into my curated list of smart city summer tips with exhibitions, activities and experiences from our partners and community. Zigzag across the city and discover the city from a different perspective!
1. Discover the city as a living place at the Landscape festival: ‘Met andere ogen’ (with other eyes)
Nature is a source of beauty and comfort, of relaxation and well-being, but it is now also in crisis. Diversity is declining and habitats are disappearing. In the ecological recovery lying ahead, the city plays a remarkable role: not only as a hotspot for biodiversity, but also as a meeting place where we can forge links between human and other life. Waag Futurelab invites you to set your sights on the Amsterdam Science Park and discover the city as a living place, together with artists, local residents and scientists. Take a walk along the walking route across the Amsterdam Science Park past all the installations and interventions.
From June until September 2023. Pick up a map at Café-Restaurant Polder (address: Science Park 201). Costs: free.
2. Take an architectural summer walk through new city areas
Arcam, the centre for architecture in Amsterdam, organises a series of architectural walks through neighbourhoods in development: Houthaven, Sloterdijk, Zuidas, Centrumeiland and Elzenhagen-Zuid. On Sundays from June to September, you can join a summer walk, led by an enthusiastic city expert, to visit and learn more about newly (to be) transformed areas of Amsterdam.
Every Sunday (from June to September) from different pick-up points. Costs: € 15,00 per person.
3. Fix your broken stuff at Repair Café Oud Noord
Give your broken belongings a second chance at the Repair Café in De Ceuvel (Metabolic Lab). Whether it's electronics, textiles, furniture, or bikes, the dedicated team at the Repair Café is there to assist with even the most challenging repairs. Join this community-driven initiative on the first Wednesday of each month! While the repairs are free, donations for used materials are warmly appreciated.
Every first Wednesday of the month (next up August 2, from 18:00-20:00) at De Ceuvel, Metabolic Lab. Costs: Free.
4. Green up your city with the NK Tegelwippen (‘National Tile Removal Championship’)
In the Netherlands, it's common to see apartment buildings, offices, and homes surrounded by tiles. This might be low-maintenance, but they're not particularly beautiful and do absolutely nothing to help the environment. We’re increasingly facing problems such as heat stress and flooding, and all those stone tiles in urbanised areas do not cool down on a hot day or let water through when it rains. Join the National Tile Removal Championship this summer! Remove tiles (for example in your garden) and replace them with plants and flowers for a greener city.
From March 21st till October 31st, more information via the website of NK Tegelwippen.
5. Learn more about our energy addition at the Energy Junkies exhibition
Our dependence on fossil fuels and the effects of our energy consumption on climate change are the focus of NEMO’s new exhibition for adults: Energy Junkies. NEMO invites you to explore the decisions that will determine our future. How would you transform our energy addiction into a healthy habit? Create your own carbon diet, choose the right medicines from the climate pharmacy and dream about a world where we are cured of our energy addiction. Visit Energy Junkies at NEMO’s Studio, the off-site location for adults on the Marineterrein in Amsterdam.
Energy Junkies is open from Wednesday – Sunday, from 12:00 – 17:30 until October 29. Costs: € 7,50
6. Visit the Maker Market
Meet passionate and innovative makers from all over the world at The Maker Market! Here you will find handmade products produced with love and craftsmanship. The event focuses on sustainable production processes and Fair Trade. Engage with the makers, hear their stories, and witness their creative processes. This way, you can discover products with a good story.
On Saturday July 28 (11:00-17:00), Sunday July 28 (12:00-17:00), Saturday August 26 (11:00-17:00) and Sunday August 27 (12:00-17:00) at the Passage. Costs: Free.
7. Book a tour at Mediametic
Get a glimpse behind the scenes at Mediametic! During their weekly tour on Friday, you’ll get the chance to peek inside their labs, in which they explore the possibilities of bio-materials for design, science and art. You’ll also visit the Clean lab, where Mediametic is currently focusing on the use of waste materials, as a source for new material. You get an introduction in the Aroma lab, their open perfume workshop and scent library where scent is explored as an artistic medium. And you will get to see the Plant lab, where herbs and edible flowers are grown for the restaurant in a sustainable way.
On Friday’s at 16:00, Mediametic. Costs: € 4,50 incl. a drink.
8. Keep your head cool! At Waag Open
It's getting hot in here! Since 1923, the KNMI (The Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute) measured 28 heat waves and almost half them occurred in the past 20 years. If this trend continues, the number of 'tropical' days (days above 30 degrees) will have doubled by 2050. But what are the consequences of these heat waves in people's homes? In countless Dutch (rental) homes, bedrooms heat up considerably in summer. And that can lead to physical and mental complaints: heat stress. During Waag Open: Keep your head cool, Lisanne Corpel (researcher at the Hogeschool van Amsterdam) shares her knowledge on measuring heat and the phenomenon of heat stress.
Thursday August 3 from 19:30-21:30 at Waag, Nieuwmarkt 4. Costs: € 7,50 incl. a drink.
As you explore these smart city summer tips in Amsterdam, let the innovative initiatives inspire you to make positive changes in your own life. Be sure to check out our platform for more exciting events and experiences. Do you have any other tips for inspiring smart city activities not to be missed this summer? Share them with the community in the comments!
Anders kijken en anders doen in de Metropool van Morgen

Dringende oproep van Femke Halsema tijdens zesde State of the Region.
Van grenzen aan de groei en zonnepanelen voor iedereen tot talenten werven op een nieuwe manier en een nieuw perspectief op nieuwkomers: als we brede welvaart echt een kans willen geven, moeten we anders kijken en anders doen. En daarvoor is vertrouwen cruciaal, zegt Femke Halsema in haar oproep. Welkom bij de 6e editie van State of the Region, in de Meervaart Amsterdam.
Duurzaamheid. Wonen. De energietransitie. Als presentatoren Tex de Wit en Janine Abbring via de Mentimeter het publiek vragen naar de grootste uitdaging voor de Metropool Amsterdam verschijnt er een gevarieerde woordwolk op het scherm. Armoedebestrijding wordt genoemd, minder vergaderen en bereikbaarheid.
Ook noemen veel mensen brede welvaart. “En dat is vandaag een belangrijk thema”, zegt Abbring. “In eerdere State of the Regions lag de focus meer op cijfers, op economische welvaart. Nu richten we ons ook op minder materiële zaken.”
Dat zien we terug in een paar filmpjes. Pallas Achterberg, Challenge Officer bij Alliander roept daarin op beter te luisteren, tot samenwerken op een andere manier, een samenwerking waarin we ons eigen belang ondergeschikt maken aan het gemeenschappelijke belang. We zien een kinderarts die zich afvraagt waarom we ons niet veel meer richten op preventie. We zien ondernemers die bij het werven van talent verder kijken dan alleen het cv en ondernemers die zonnepanelen betaalbaar maken voor iedereen.
Geen lege term
Het zijn de concrete voorbeelden die nauw aansluiten bij de jaarlijkse State of the Region, de speech van Femke Halsema tijdens het gelijknamige evenement. Ze is burgemeester van Amsterdam, maar vandaag vooral voorzitter van de Metropoolregio Amsterdam én van Amsterdam Economic Board. Die organiseren dit evenement samen met de gemeente Amsterdam, amsterdam&partners en ROM InWest.
Halsema herhaalt de oproep die vandaag centraal staat: anders kijken en anders doen. “We moeten fundamentele keuzes maken om ervoor te zorgen dat brede welvaart geen lege term wordt. Dat we het werkelijk gaan uitvoeren. Wij doen nu deze oproep. En ik hoop dat we die samen met inwoners, bedrijven, maatschappelijke instellingen en u in de zaal werkelijkheid kunnen laten worden.”
Bijzondere samenwerking
De Board-voorzitter is net terug uit Hatay, de Turkse provincie die zo zwaar werd getroffen door de aardbeving. Door slechte samenwerkingen lukt het de regio niet goed om de enorme schades te herstellen. Het leven ligt er stil. In Nederland zit die samenwerking in ons bloed. De eerste Nederlandse dijk liep langs het Gooi, via Diemen en Amsterdam naar het IJ en was het gevolg van een bijzondere samenwerking tussen boeren, vissers, de graaf en inwoners.
“Die samenwerking vraagt nog wel onze aandacht. Ons verdienmodel is aan vernieuwing toe. Economische groei zal hand in hand moeten gaan met sociaal-maatschappelijke vooruitgang. Onze huidige voorspoed bereikt nog lang niet iedereen. Inkomensverschillen zijn groot, er is te veel uitstoot van fijnstof, er zijn te weinig arbeidskrachten en er is een tekort aan woningen.”
De Metropool als meent
Toch ziet Halsema geen reden voor pessimisme. Met dank aan grote en kleine bedrijven die in de Metropool hun uitvalsbasis hebben verdienen we hier 20 procent van het bruto binnenlands product. De voorzieningen en kennisinstellingen zijn van hoog niveau. En we zijn een veerkrachtige regio.
Vertrouwen is volgens Halsema de kern van onze toekomstige samenwerking. “We kunnen niet met elkaar blijven concurreren, we moeten elkaar versterken. We moeten onze Metropool zien als de meent van vroeger, een gemeenschappelijke weidegrond waar we samen verantwoordelijk voor zijn. Als jij die niet goed gebruikt, heeft dat gevolgen voor de andere gebruikers. De Metropool is te lang beschouwd als onbeheerde, woeste grond waar geen samenwerking voor nodig is.”
Halsema haalt econoom en nobelprijswinnaar Elinor Ostrom aan, die pleitte voor goede instituties voor gemeenschappelijk beheer. “We beheren goederen die we moeten laten floreren voor het welvaren van de gehele gemeenschap, zegt zij. Dat betekent dat we altijd het belang van de ander hebben mee te wegen, ook dat van mensen in de rest van Nederland en de wereld en ook dat van toekomstige generaties.”
‘Een mega radicale transformatie’
Anders kijken en anders doen klinkt misschien eenvoudig, maar vraagt van iedereen in de Metropool Amsterdam een nieuwe manier van denken en doen. Op het podium gaat Femke Halsema hierover in gesprek met Ingo UytdenHaage, co-CEO van Adyen, architect Thomas Rau en onderzoeken en community builder Soraya Shawki. Wat vinden zij van de oproep anders te kijken en anders te doen?
Wat Thomas Rau, architect, ondernemer, innovator betreft gaat de oproep niet ver genoeg. “Het is nog niet radicaal genoeg. We hebben het over 2050, maar ik vind dat we een duidelijk beeld moeten hebben van waar we over zeven jaar als Metropool willen staan. Daarbij moeten we niet doen wat mogelijk is, maar wat nodig is: een mega radicale transformatie. En dat is niet altijd comfortabel.”
Expats
Ingo Uytdenhaage , co-CEO van Adyen is wat positiever. “Bedrijven kijken vaak al verder dan alleen maar naar geld verdienen. Wij kijken ook naar onze impact op de regio, op de stad.” Die impact van Adyen is bijvoorbeeld dat er veel expats voor hen werken, zegt Abbring, en die hebben ook allemaal woonruimte nodig. Uytdenhaage ziet dat anders. “Ik noem ze geen expats, het zijn jongeren van begin 30 die een lokaal contract hebben en dezelfde uitdagingen hebben als andere jonge Amsterdammers. En ze willen ook helemaal niet allemaal in de stad wonen.” Hij krijgt bijval van Halsema: “We hebben internationale arbeidskrachten nodig voor het werk dat er ligt. We kunnen de tekorten niet oplossen met eigen inwoners.”
Soraya Shawki, researcher/community bouwer Open Embassy die nieuwkomers wegwijs maakt in de Nederlandse samenleving. Zij had graag een concretere oproep gezien. “Er is bijvoorbeeld nog veel systemische ongelijkheid. Er zijn heel veel mensen hier die pas na vijf jaar mogen werken. Dat zijn allemaal mensen die in de zorg en techniek aan de slag kunnen gaan.” Onlangs sprak ze een Iraanse wiskundelerares die Nederlands en Engels spreekt. “De gemeente vond dat ze zo snel mogelijk aan de slag moest gaan en stuurde een vacature voor een kassamedewerker door. Er ligt hier ook een rol voor werkgevers, om trajecten voor nieuwkomers beschikbaar te maken.”
Lessen aan nieuwkomers
Adyen is daar bijvoorbeeld al mee bezig en geeft programmeerlessen aan nieuwkomers. Ook laat het bedrijf in speciale lessen op scholen zien hoe technologie werkt, om zo de interesse van jongeren voor techniek te wekken. Wat Halsema betreft is het een goed voorbeeld van hoe bedrijven in de afgelopen jaren een andere taakopvatting hebben gekregen. “Waar ze voorheen misschien doneerden aan culturele instellingen, zie je nu dat ze veel meer investeren in de lokale economie en met jongeren en inwoners praten.”
Volgens Shawki mag dat nog wel wat verder gaan, bij overheden én bedrijven. “Participatie is vaak nog een vinkje op een lijstje, het is niet ingebed waardoor er bij bedrijven en overheden weinig kennis is over wat er precies nodig is. En dat terwijl mensen letterlijk expert zijn over hun eigen ervaringen. Wij hebben bijvoorbeeld expertpools van mensen die ervaring hebben met de nieuwe Wet inburgering.”
Nieuwe ontmoetingen
Soraya Shawki en Ingo UytdenHaage kenden elkaar tot vandaag nog niet, terwijl er wel wat overlap zit in hun werkzaamheden. Anders kijken en anders doen gaat ook over dit soort ontmoetingen, stelt interviewer Abbring vast. “De toekomst ligt altijd in de mensen die je niet kent”, bevestigt Rau. “In gesprekken met mensen die je niet kent. Dus ga het gesprek aan. Wij zijn de oplossing.”
En Halsema besluit: “De Metropoolregio was te lang een soort noodzakelijk kwaad, maar volgens mij moeten we het omdraaien. Alle grote onderwerpen moeten we op regionaal niveau met elkaar bespreken. We moeten wantrouwen inruilen voor vertrouwen. Alleen zo kunnen we radicale stappen zetten.”
Wil je direct aan de slag? Op Anders kijken, anders doen vind je inspirerende interviews en mooie voorbeelden. Je kunt er je eigen initiatieven en manier van werken onder de loep nemen. Past die wel bij de Metropool van Morgen? Ook kun je je er inschrijven voor de werkateliers die we na de zomer gaan organiseren.
Voor het hoofdprogramma waren er twee side-events:
State of the Youth
De Young on Board is in gesprek gegaan over het betrekken van jongeren bij het vormgeven van de toekomst van de Metropoolregio Amsterdam. Het thema participatie bleek na dit weekend relevanter dan ooit. Hoe zorgen we voor brede maatschappelijke betrokkenheid en hoe zorgen we ervoor dat jongeren weer vertrouwen krijgen in de politiek èn hun stemrecht?
Paula Smith (docent-onderzoeker Social Work bij InHolland) gaf ons een stoomcursus over jongerenparticipatie. Ze ging daarbij niet alleen in op de verschillen tussen jongeren en de rest van het electoraat, maar ook over de verschillen tussen jongeren. De belangrijkste boodschap van Paula is dat we jongerenparticipatie moeten gaan verankeren in (beleid)structuren. Als je jongeren nu betrekt creëer je namelijk geëngageerde burgers voor later.
Vervolgens zijn we met Younes Douari (Represent Jezelf) en Kimberley Snijders (voorzitter van De Nationale Jeugdraad) en Paula Smith in gesprek gegaan. Zij deelden hun ervaringen over wat er in de praktijk werkt om jongeren te betrekken in het maatschappelijke debat en bij het vormgeven van beleid. We hebben daarbij een aantal belangrijke lessen opgehaald, namelijk:
Betrek jongeren op tijd, en gebruik ze niet als windowdressing.
Maak gebruik van sociale structuren in wijken en dorpen en ga naar jongeren toe
Durf het aan om het resultaat echt uit handen te geven
Economische Verkenningen
Het andere side event was volledig gewijd aan de Economische Verkenningen MRA 2023.
Waag Open: houd je hoofd koel

It's getting hot in here! De zomers worden steeds heter in Nederland. Sinds 1923 zijn er 28 hittegolven gemeten, waarvan bijna de helft de afgelopen 20 jaar plaatsvonden. Het KNMI verwacht dat door de klimaatverandering onze zomers in de toekomst alleen maar warmer zullen worden. Als we op deze voet doorgaan, zal in 2050 het aantal ‘tropische’ dagen (dagen waarop het meer dan 30 graden is) zijn verdubbeld.
Maar wat zijn de gevolgen van deze hittegolven bij mensen thuis? In talloze Nederlandse (huur)woningen warmen de slaapkamers 's zomers flink op. En dat kan leiden tot fysieke en mentale klachten: hittestress. Maar wat is dat eigenlijk?
Lisanne Corpel, onderzoeker aan de Hogeschool van Amsterdam (HvA), deelt haar kennis over het meten van hitte en het fenomeen hittestress. Ze deed een onderzoek naar hitte rondom de Nieuwmarkt in Amsterdam met onder meer bewoners van verzorgingshuis Flesseman.
Tijdens deze zomeravond gaan we samen op zoek naar oplossingen om het hoofd (en huis) koel te houden. Heb jij goede hitte-hacks of kun je zelf wel wat tips gebruiken? Kom dan naar deze zomereditie van Waag Open!
Programma
19:30 - 19:45 uur: Welkom door Sylke van Duijnen & introductie burgerwetenschap
19:45 - 20:00 uur: Lisanne Corpel (HvA) over hittestress: wat is het en hoe meet je het?
20:00 - 21:00 uur: Zelf hitte meten: op pad met sensoren in de buurt
21:00 - 21:30 uur: Data-analyse & borrel
Over burgerwetenschap
In burgerwetenschap (ook wel citizen sensing genoemd) kunnen burgers aan de hand van open source tools zelf hun leefomgeving meten en leren ze de data te interpreteren. Dit is waardevol omdat:
- Je als burger eigenaarschap over je data hebt
- Je gedeelde kennis creëert met experts en instanties
- Je handelingsperspectief wordt versterkt
Op deze manier wordt de informatiepositie van burgers versterkt, en staan ze sterker in het gesprek met bijvoorbeeld beleidsmakers. Ook krijgen ze handvatten aangereikt om zelf hun kwaliteit van leven te verbeteren. Denk aan de luchtkwaliteit in je straat, geluidoverlast van verkeer, de waterkwaliteit van je favoriete zwemplek óf de hitte in je huis!
Deze zomer onderzoekt Waag Futurelab, samen met de Hogeschool van Amsterdam, TU Delft en VPRO hoe warm het precies binnen wordt. Dit doen we in het project Thermo-staat waarbij bewoners zelf de hitte meten.
Waag Open
Elke eerste donderdagavond van de maand opent Waag haar deuren! Kom langs om te discussiëren en te doen. Want we gaan niet alleen in discussie over maatschappelijke thema's en de toekomst - je leert daarnaast ook altijd iets praktisch.
Iets dat je altijd al hebt willen uitproberen, zoals de 3D-printer in het FabLab, of juist iets dat je nooit had verwacht, zoals uitpluizen hoe DNA in elkaar zit in ons biotech-lab. Waag Open vindt plaats in (een van) de maakplaatsen op de eerste en tweede verdieping van het historische Waaggebouw op de Nieuwmarkt.
Toegankelijkheid
Omdat het Waag-gebouw een beschermd monumentaal pand is, is het helaas niet voorzien van een lift. Dit evenement vindt plaats in de Makersguild op de eerste verdieping van het Waag-gebouw.
Mocht je krap bij kas zitten en wel graag aan dit evenement willen deelnemen, neem dan contact op met tanja [@] waag [punt] org.
Bijeenkomst eindresultaten onderzoek Boundary Spanners in actie

Werk jij aan grootstedelijke vraagstukken en kom je daarbij steeds grenzen tegen tussen verschillende domeinen? Ben jij op zoek naar manieren om effectiever met die grenzen om te gaan? Kom dan op 28 september naar de slotbijeenkomst van het onderzoek ‘Boundary spanners in actie’.
Tijdens deze unieke en creatieve middag gaan we aan de slag met nieuwe inzichten uit dit onderzoek en ontdek je een nieuw handelingsrepertoire om je effectiviteit als boundary spanner te vergroten.
In het netwerk van Amsterdam Smart City werken ook veel mensen die deze rol van Boundary spanner hebben, in het vormgeven van projecten en intiatieven en tussen de partners. Boundary spanners zijn essentieel bij het overbruggen van domeingrenzen bij grootstedelijke vraagstukken zoals leefbaarheid, veiligheid, gebiedsontwikkeling, armoede enzovoort. Zij helpen om de verschillen te overbruggen die samenwerking moeilijk maken, zoals verschillen in sociale waarden en omgangsvormen die personen of groepen aanhangen, taal- en procedureverschillen tussen expertises, afdelingen en organisaties, of de effecten van de budgettaire inrichting op de machtsverhoudingen.
De afgelopen twee jaar volgden we tijdens het onderzoek ‘Boundary spanners in actie’ vijf verschillende project- en programmateams van professionals die in Amsterdam en Den Haag aan grootstedelijke vraagstukken werken. In deze slotbijeenkomst delen we de uitkomsten van dit onderzoek in de vorm van nieuwe inzichten en nieuwe handelingsmogelijkheden voor de boundary spanners, waarmee zij (nog) beter in staat zijn om grenzen te overbruggen bij het werken aan grootstedelijke vraagstukken.
Urban Swimming - the data and stories behind Amsterdam's favorite waterfront.

Hello fellow architects & future city makers - Join me tonight at Arcam's Architectencafé Summer edition where I’ll be demonstrating how data is keeping our waterfront more livable and more accessible for Amsterdammers.
I’ll be presenting the crazy stories behind the data we collected from the innovation district Marineterrein
RSVP:https://arcam.nl/events/barcam-architectencafe-2/
The is the second edition of Barcam:
Thursday, July 6 from 6:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m
Entry is free and drinks are reasonably priced!
Transition Day 2023: Mobility Justice - Power structures and engaging your target group

While our mobility system and its options are continuously expanding, there’s a growing number of people who feel excluded from the mobility system and experience a lack of access to services like public transport and shared mobility options. The concept of Mobility Poverty shows there are a variety of reasons for this exclusion, ranging from economic and geographical reasons, to falling behind on digital skills. If we want to move towards ‘Mobility Justice’, we would need a detailed image of the groups experiencing this exclusion and we would need a variety of actors to come up with -and implement- creative solutions to this emerging problem.
For the past months, Chris de Veer and I have been busy setting up a regional coalition and program on this subject. Because it’s becoming clear we’re discussing a problem we, a pool of mobility specialists, are not experiencing ourselves, we decided to critically look at what parties have a seat at the table. During the Amsterdam Smart City Transition Day on June 6th, we gathered input and reflections on the power structures in play and considerations when involving your target group in decision making.
Understanding power relations and structures when working on transitions
When designing solutions and innovative policies, it’s important to understand and be aware of the power structures in play. Our partner Kennisland is concerned with the topic and introduced this discussion within our network during on of our ‘Kennissessies’ earlier this year. Together with this session’s participants, we used their method to evaluate which parties have been involved in the initial phase of our Mobility Justice challenge.
It became clear that it had been mostly governmental parties which were involved in exploring the topic and initiating the design of a cooperation program. While this is of importance for practical matters like funding and political support, the group should have been diversified when we started exploring the problem and its solutions. The (target) group we’re talking about is currently lacking the power to help design both the collaboration process itself and the initiatives that should help fight Mobility Poverty.
Considerations when engaging with your target group
There was a general consensus in the group that we should now make more of an effort to engage with our target group. But how exactly? The group discussed different existing forms of involving a target group in decision making and advised us on matters to consider, namely;
- Decide in what stage(s) of the process collaboration or input is needed. Exploring the problem will require a completely different conversation and method compared to the stage of co-designing solutions.
- Be very clear about what you’ll use the outcomes for. If you decide to gather input from - and collaborate with your target group, you’ll need to actually incorporate the outcomes within your process. This is necessary to maintain the groups trust and validate their efforts.
- Besides defining problems and exploring its solutions, evaluation of the initiatives that follow will be equally important. Special efforts need to be put into place to keep the dialogue going with the target group during and after testing initiatives.
Next steps: Harnessing the power of community centres
When discussing potential next steps for the group, one of the session’s participants reminded us of the power of community centres. She mentioned an example in her own neighbourhood, where a group of neighbours initiated a sharing vehicle for elderly/disabled people. This example illustrated how local communities know best what specific problems or needs are at play, and how to set up solutions in a quick manner.
This conversation inspired us to now look for relevant local initiatives and community centres in the Amsterdam region. With their help, we hope to better understand problems related to Mobility Poverty and what specific solutions people need within their local context.
A call to the community
I’m now wondering if there is anyone in our Amsterdam Smart City community who could link us to local initiatives and community centres in the Amsterdam region? Mobility-related topics are a plus, but this is certainly not necessarily. Any advice or tips to share? Send me an email at pelle@amsterdamsmartcity.com. This summer, we’ll design the continuation of this project.
De Nationale Wetenschapsagenda: de toekomst van AI

Kunstmatige Intelligentie is een hot topic. Zowel de voor- en nadelen worden in maatschappelijk debat besproken. Zo kunnen studenten tegenwoordig een werkstuk laten schrijven door ChatGPT. Beantwoordt Siri in een handomdraai je vragen, maar luistert stiekem ook met jouw gesprekken mee. Intelligente robots kunnen een oplossing zijn voor het tekort aan personeel in de zorg of in de glastuinbouw. Maar kunnen mensen en robots ook goed samenwerken?
De komende jaren wordt er veel onderzoek gedaan naar kunstmatige intelligentie. Dit onderzoek geeft vorm aan technologie en heeft invloed op de manier waarop deze technologie een plek krijgt in onze maatschappij. Daarom is het belangrijk om mee te denken over waar dat onderzoek over moet gaan.
Welke thema’s zou jij wetenschappers willen meegeven? Wat is jouw toekomstvisie over kunstmatige intelligentie? En welke onderzoeksrichtingen moeten onderzoekers volgens jou juist vermijden?
Denk mee met de Nationale Wetenschapsagenda en kom op donderdag 22 juni naar RuParé Community om samen met anderen na te denken over maatschappelijke thema’s waaraan wetenschappers aandacht moeten besteden.
Programma
19:00 - 19:30 uur: Inloop
19:30 - 20:00 uur: Introductie kunstmatige Intelligentie door onderzoekswetenschapper Jurriaan van Diggelen
20:00 - 21:00 uur: interactief programma, waar we ingaan op de volgende aspecten:
- Welke zorgen of ideeën heb je?
- En wat is ervoor nodig om daar wel of dan wel niet te komen?
- Waar zou het onderzoek gedaan door wetenschappers op moeten letten?
Over Jurriaan van Diggelen
Van Diggelen is onderzoekswetenschapper bij TNO. Hij zal specifiek ingaan op de ontwikkelingen uit het veld van Artificial Intelligence (AI). Aan de hand van enkele voorbeelden licht hij in grote lijnen de ontwikkelingen van de huidige tijd toe en welke effecten dit heeft of kan hebben op onze samenleving.
De uitkomsten van de dag zullen als input dienen voor de Nationale Wetenschapsagenda. Deze agenda bepaalt de richting waar het wetenschappelijk onderzoek in Nederland over gaat. Voor de agenda is het belangrijk dat deze gebaseerd is op belang vanuit de samenleving. En wie kan dat nou beter bepalen dan jij?
Stay up to date
Get notified about new updates, opportunities or events that match your interests.

