Stay in the know on all smart updates of your favorite topics.
21. Work, also in the neighbourhood

This is the 21th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Its topic is the combination of living and working in the same neighbourhood. This idea is currently high on the agenda of many city councils.
Benefits for the quality of the living environment
If there is also employment in or near the place where people live, several residents might walk to work. That will only apply to relatively few people, but urban planners think that bringing living and working closer together will also increase the liveliness of the neighborhood. But more reasons are mentioned: including cross-fertilization, sharing of spaces, the shared use of infrastructure (over time), a greater sense of security and less crime. Whether all these reasons are substantiated is doubtful.
In any case, mixed neighbourhoods contributes to widening the range of residential environments and there is certainly a group that finds this an attractive idea. The illustrations above show places were living and work will be mixed (clockwise): Deventer (Havenkwartier), The Hague (Blinckhorst), Leiden (Bioscience Park), Amersfoort (Oliemolenterrein), Amsterdam (Ravel) and Hilversum (Wybertjesfabriek).
Break with the past
Le Corbusier detested the geographical nearness of work and living. In his vision, all the daily necessities of residents of the vertical villages he had in mind had to be close to home, but the distance to work locations could not be great enough. Incidentally, very understandable because of the polluting nature of the industry in the first half of the 20th century. Nowadays, the latter is less valid. An estimated 30% of companies located on industrial sites have no negative environmental impact whatsoever. A location in a residential area therefore does not have to encounter any objections. The choice for an industrial site was mainly dictated because the land there is much cheaper. And that's where the shoe pinches. The most important reason to look for housing locations on industrial estates is the scarcity of residential locations within the municipality and consequently their high prices. Moreover, in recent decades the surface of industrial estates has grown faster than that of residential locations, at least until a couple of years ago.
Companies are still hesitating
Companies are generally reserved about the development of housing in their immediate vicinity. Apart from the realistic expectation that the price of land will rise, they fear that this will be at the expense of space that they think they will need to grow in the future. This fear is justified: In the Netherlands 4600 hectares of potential commercial sites disappeared between 2016 and 2021. Another concern is that future 'neighbors' will protest against the 'nuisance' that is inherent to industrial sites, among others because of the traffic they attract. The degree of 'nuisance' will mainly depend on the scale on which the mixing will take place. If this happens at block level, the risk is higher than in case of the establishment of residential neighborhoods in a commercial environment. But as said, there is no need to fear substantial nuisance from offices, laboratories, call centers and the like. Companies also see the advantages of mixing living and working, such as more security.
Searching for attractive combinations of living and working
Project developers see demand for mixed-use spaces rising and so do prices, which is an incentive for the construction of compact multifunctional buildings, in which functions are combined. To create sufficient space for business activity in the future, they advocate reserving 30% for business space in all residential locations. The municipality of Rotterdam counters this with a 'no net loss' policy regarding gross floor surface for commercial spaces.
Gradually, attractive examples of mixed living and working areas emerge. Park More (from Thomas More), the entrance area of the Leiden Bioscience Park, which will consist of homes, university facilities and a hotel (photo top right). The idea is that in the future there will also be room for the storage of rainwater, the cultivation of food and the production of the estate's own energy.
Another example, which can probably be followed in more places, is the transformation of the Havenkwartier Deventer into a mixed residential and working area, although part of the commercial activity has left and the buildings are being repurposed as industrial heritage (photo above left). The starting point is that, despite hundreds of new homes, the area will retain its industrial and commercial character, although some residents complain about the 'smoothening' of the area'. Living and working remains a challenging combination, partly depending on where the emphasis lies. In this respect, many eyes are focused on the substantiation of the plans of Amsterdam Havenstad.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Expeditie Muziek

Ik heb de laatste jaren honderden posts geschreven over stedelijke ontwikkeling, innovatie en organisatie. Vele daarvan hebben op deze website gestaan. Ik verschuif mijn schrijfactiviteiten geleidelijk naar het thema waarvan mijn hart sneller gaat kloppen, namelijk muziek. In mijn nieuwe Nederlandstalige blog 'Expeditie muziek' (zie de link hieronder) verken ik wekelijk een ander facet. Deze week is dat de geschiedenis van de blues, vorige week heb ik een top tien samengesteld van de in mijn ogen mooiste Nederlandstalige liedjes 'ooit'. Neem eens een kijkje.
20. Facilities within walking and cycling distance

This is the 20th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Its topic is to enable citizens having daily necessities in a walking and bicycling distance.
During the pandemic, lockdowns prevented people from leaving their homes or moving over a longer distance. Many citizens rediscovered their own neighbourhood. They visited the parks every day, the turnover of the local shops increased, and commuters suddenly had much more time. Despite all the concerns, the pandemic contributed to a revival of a village-like sociability.
Revival of the ‘whole neighbourhood’
Revival indeed, because until the 1960s, most residents of cities in Europe, the US, Canada, and Australia did not know better than their dally needs were available within a few minutes' walk. In the street where I was born, there were four butchers, four bakers, three greengrocers and four groceries, even though the street was not much longer than 500 meters. No single shop survived. My primary school was also on that street, and you had to be around the corner for the doctor. This type of quality of life went lost, in the USA in particular. However, urban planners never have forgotten this idea. In many cities, the pandemic has turned these memories into attainable goals, albeit still far removed from reality. Nevertheless, the idea of the 'whole neighborhood' gained traction in many cities. It fits into a more comprehensive planning concept, the 15-minute city.
Support for facilities
The idea is that residents can find all daily needs within an imaginary circle with an area of approximately 50 hectares. This implies a proportionate number of residents. A lower limit of 150 residents per hectare is often mentioned, considering a floor area of 40% for offices and small industry. The idea is further that most streets are car-free and provide plenty of opportunity for play and meeting.
Opportunity for social contacts
In a 'whole neighbourhood', residents find opportunity for shopping and meeting from morning to evening. There is a supermarket, a bakery, a butcher, a greengrocer's shop, a drugstore, a handful of cafes and restaurants, a fitness center, a primary school, a medical center, craft workshops, offices, green spaces and a wide variety of houses. Here, people who work at home drink their morning coffee, employees meet colleagues and freelancers work at a café table during the quiet hours. Housemen and women do their daily shopping or work out in the gym, have a chat, and drink a cup of tea. People meet for lunch, dinner and socializing on the terrace or in the cafes, until closing time. A good example is the Oostpoort in Amsterdam, albeit one of the larger ones with a station and a few tram lines.
Planning model
On the map above, the boundaries of the neighborhoods with an area of approximately 50 hectares are shown in the form of circles. The circular neighborhood is a model. This principle can already play a role on the drawing board in new neighborhoods to be built. In existing neighbourhoods, drawing circles is mainly a matter of considering local data. The center of the circle will then often be placed where there are already some shops. Shops outside the intended central area can be helped to move to this area. Spaces between existing homes can be reserved for small-scale businesses, schools, small parks, communal gardens and play facilities. Once the contours have been established, densification can be implemented by choosing housing designs that align to the character of the neighbourhood. Towards the outside of the imaginary circle, the building density will decrease, except at public transport stops or where circles border the water, often an ideal place for higher buildings.
If a thoroughfare passes through the center of the circle, this street can be developed into a city street, including a public transport route. Facilities are then realized around a small square in the center of the circle and the surrounding streets.
Incidentally, space between the circles can be used for through traffic, parks, and facilities that transcend districts, for instance a swimming pool or a sports hall or an underground parking garage. Mostly, neighborhoods will merge seamlessly into each other.
It will take time before this dream comes true.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
19. Safe living environment

This is the 19th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. This post is about increasing the independent mobility of children and the elderly, which is limited due to the dangers that traffic entails.
For safety reasons, most urban children under the age of ten are taken to school. The same goes for most other destinations nearby. It hampers children’s independent mobility, which is important for their development.
Car-free routes for pedestrians and cyclists
For security reasons, car-free connections between homes and schools, community centers, bus stops and other facilities are mandatory (photo’s top left and bottom right). Car routes, in their turn, head to neighborhood parking spaces or underground parking garages. Except for a limited number of parking spaces for disabled people.
Design rules
Model-wise, the design of a residential area consists of quadrants of approximately 200 x 200 meters in which connections are primarily intended for pedestrians and cyclists. There are routes for motorized traffic between the quadrants and there are parking facilities and bus stops at the edges. Inhabitants might decide that cars may enter the pedestrian area at walking pace to load and unload to disappear immediately afterwards. The routes for pedestrians and cyclists connect directly with the shops and other destinations in the neighborhood, based on the idea of the 15-minute city. Shops 'ideally' serve 9 to 16 quadrants. In practice, this mode will have many variations because of terrain characteristics, building types and aesthetic considerations.
Examples
The number of neighborhoods where cars can only park on the outskirts is growing. A classic example is 'ecological paradise' Vauban were 50 'Baugruppen' (housing cooperatives) have provided affordable housing (photo bottom middle ). Car-free too is the former site of the Gemeentelijk waterleidingbedrijf municipal water supply company in Amsterdam - (photo bottom left). Here almost all homes have a garden, roof terrace or spacious balcony. The Merwede district in Utrecht (top middle) will have 12,000 inhabitants and for only 30% room for parking is available, and even then only on the edge of the district. Shared cars, on the other hand, will be widely available. The space between the houses is intended for pedestrians, cyclists and children playing.
More emphasis on collective green
Due to the separation of traffic types and the absence of nuisance caused by car, there are no obligatory streets, but wide foot- and cycle paths. Instead there are large lawns for playing and picnicking, vegetable gardens and playgrounds. Further space savings will be achieved by limiting the depth of the front and back gardens. Instead, large collective space appears between the residential blocks; remember the Rivierenwijk in Utrecht that I mentioned in the former post (top right). Behind the buildings, there is room for small backyards, storage sheds and possibly parking space.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
18. Space for sporting and playing in a green environment

This is the 18th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. This message is about the limited possibilities for children to play in a green environment because of the sacrifices that are made to offer space for cars and private gardens
Almost all residential areas in the Netherlands offer too little opportunity for children to play. This post deals with this topic and also with changing the classic street pattern to make way for routes for pedestrians and cyclists.
Everything previously mentioned about the value of a green space applies to the living environment. The rule 3 : 30 : 300 is often used as an ideal: Three trees must be visible from every house, the canopy cover of the neighborhood is 30% and within an average distance of 300 meters there is a quarter of a hectare of green space, whether or not divided over a number of smaller parcels.
Functions of 'green' in neighbourhoods
The green space in the living environment must be more than a grass cover. Instead, it creates a park-like environment where people meet, it is accompanied by water features and can store water in case of superfluent rain, it limits the temperature and forms the basis for play areas for children.
Legally, communal, and private green areas are different entities; in practice, hybrid forms are becoming common. For example, a communal (inner) garden that can be closed off in the evening or public green that is cadastral property of the residents but intended for public use. In that case the residents live in a park-like environment which they might maintain and use together. Het Rivierdistrict in Utrecht is an example of this.
Play at the neighborhood level
Children want wide sidewalks and a place (at least 20 x 10 m2) close to home that is suitable for (fantasy) games and where there may also be attractive play equipment. The importance of playground equipment should not be overestimated. For many children, the ideal playground consists of heaps of coarse sand, water, climbing trees and pallets. To the local residents It undoubtedly looks messier than a field full of seesaw chickens. Good playground equipment is of course safe and encourages creative action. They can also be used for more than one purpose. You can climb on it, slide off it, play hide and seek and more. Of the simple devices, (saucer) swings and climbing frames are favorites.
A somewhat larger playground to play football and practice other sports is highly regarded. Such a space attracts many children from the surrounding streets and leads to the children playing with each other in varying combinations.
Squares
Most squares are large bare plains, which you prefer to walk around. Every neighborhood should have a square of considerable size as a place where various forms of play and exercise are concentrated. In the middle there is room for a multifunctional space - tastefully tiled or equipped with (artificial) grass - for ball games, events, music performances, markets and possibly movable benches. Ideally, the central part is somewhat lower, so that there is a slope to sit on, climb and slide down. On the edge there is room for countless activities, such as different forms of ball games, a rough part, with climbing trees, meeting places, spaces to hide, space to barbecue and walls to paint, but also catering and one or more terraces. Lighting is desirable in the evening, possibly (coloured) mood lighting. There is an opportunity for unexpected and unforeseen activities, such as a food car that comes by regularly, street musicians that come to visit, changing fairground attractions and a salsa band that comes to rehearse every week.
Such a square can possibly be integrated into a park that, apart from its value as a green space, already offers opportunities for children to play. Adding explicit game elements makes parks even more attractive.
Connecting car-free routes
Safe walking and cycling routes connect playgrounds, parks, and homes. They offer excellent opportunities to use bicycles, especially where they are connected to those of other neighbourhoods.
By seeing facilities for different age groups in conjunction, networks and nodes are created for distinctive target groups. The children's network mainly includes play areas close to home, connected via safe paths to playgrounds in the vicinity. Facilities especially for teenagers are best located somewhat secluded, but not isolated. Essentially, they want to fit in. The teenage network also includes places where there is something to eat, but also various facilities for sports and at a certain age it includes the entire municipality.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
17. A sociable inclusive neighborhood

This is the 17th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. This post is about the contributions of sociability and inclusivity to the quality of the living environment.
Almost everyone who is going to move looks forward with some trepidation to who the neighbors will be. This post is about similarities and differences between residents as the basis for a sociable end inclusive neighborhood.
"Our kind of people"
The question 'what do you hope your neighbors are' is often answered spontaneously with 'our kind of people'. There is a practical side to this: a family with children hopes for a family with playmates of about the same age. But also, that the neighbors are not too noisy, that they are in for a pleasant contact or for making practical arrangements, bearing in mind the principle 'a good neighbor is better than a distant friend'. A person with poor understanding often interprets 'our kind of people' as people with the same income, religion, ethnic or cultural background. That doesn't have to be the case. On the other hand, nothing is wrong if people with similar identities seeking each other's proximity on a small scale.
All kinds of people
A certain homogeneity among the immediate neighbours, say those in the same building block, can go hand in hand with a greater variety at the neighbourhood level in terms of lifestyle, ethnic or cultural background, age, and capacity. This variety is a prerequisite for the growth of inclusiveness. Not everyone will interact with everyone, but diversity in ideas, interests and capacities can come in handy when organizing joint activities at neighborhood and district level.
Variation in living and living arrangements
The presence of a variety in lifestyles and living arrangements can be inspiring. For example, cohousing projects sometimes have facilities such as a fitness center or a restaurant that are accessible to other residents in the neighbourhood. The same applies to a cohabitation project for the elderly. But it is also conceivable that there is a project in the area for assisted living for (former) drug addicts or former homeless people. The Actieagenda Wonen “Samen werken aan goed wonen” (2021) provides examples of the new mantra 'the inclusive neighbourhood'. It is a hopeful story in a dossier in which misery predominates. The Majella Wonen project in Utrecht appealed to me: Two post-war apartment complexes have been converted into a place where former homeless people and 'regular' tenants have developed a close-knit community. It benefits everyone if the residents of these types of projects are accepted in the neighborhood and invited to participate.
Consultation between neighbours
It remains important that residents as early as possible discuss agreements about how the shared part of life can be made as pleasant as possible. This is best done through varying combinations of informal neighborhood representatives who discuss current affairs with their immediate neighbours. A Whatsapp group is indispensable.
Mixing income groups is also desirable, especially if the differences in housing and garden size are not too great. It does not work if the impression of a kind of 'gold coast' is created.
If functions are mixed and there are also offices and other forms of activity in a neighborhood, it is desirable that employees also integrate. This will almost happen automatically if there is a community center with catering.
Most of what is mentioned above, cannot be planned, but a dose of goodwill on the part of all those involved contributes to the best quality of living together.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Harnessing Bio-Based Construction to Beat Carbon Budgets and Preserve Our Planet
The construction sector is projected to exceed its carbon budget by 2026 using current construction practices.
But by constructing half of new residential buildings with bio-based materials, we can actually reduce CO2 emissions by 18% by 2030. That’s according to Metabolic's latest research, made possible through funding from Built by Nature. And if we consider carbon sequestration, we can even reduce the impact of the residential construction sector by 52%.
However, if solely focusing on carbon, we must be mindful not to shift the burden to other planetary boundaries. In our research, we discuss topics such as sustainable wood supply, climate change risks, and land use change. Based on our findings, we propose six steps to consider to realize a sustainable biobased construction sector.
16. A pleasant (family) home

This is the 16th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. This post is about one of the most important contributions to the quality of the living environment, a pleasant (family)home.
It is generally assumed that parents with children prefer a single-family home. New construction of this kind of dwelling units in urban areas will be limited due to the scarcity of land. Moreover, there are potentially enough ground-access homes in the Netherlands. Hundreds of thousands have been built in recent decades, while families with children, for whom this type of housing was intended, only use 25% of the available housing stock. In addition, many ground-access homes will become available in the coming years, if the elderly can move on to more suitable housing.
The stacked house of your dreams
It is expected that urban buildings will mainly be built in stacks. Stacked living in higher densities than is currently the case can contribute to the preservation of green space and create economic support for facilities at neighbourhood level. In view of the differing wishes of those who will be using stacked housing, a wide variation of the range is necessary. The main question that arises is what does a stacked house look like that is also attractive for families with children?
Area developer BPD (Bouwfonds Property Development) studied the housing needs of urban families based on desk research, surveys and group discussions with parents and children who already live in the city and formulated guidelines for the design of 'child-friendly' homes based on this.
Another source of ideas for attractive stacked construction was the competition to design the most child-friendly apartment in Rotterdam. The winning design would be realized. An analysis of the entries shows that flexible floor plans stand head and shoulders above other wishes. This wish was mentioned no less than 104×. Other remarkably common wishes are collective outdoor space [68×], each child their own place/play area [55×], bicycle shed [43×], roof garden [40×], vertical street [28×], peace and privacy [27× ], extra storage space [26×], excess [22×] and a spacious entrance [17×].
Flexible layout
One of the most expressed wishes is a flexible layout. Family circumstances change regularly and then residents want to be able to 'translate' to the layout without having to move. That is why a fixed 'wet unit' is often provided and wall and door systems as well as floor coverings are movable. It even happens that non-load-bearing partition walls between apartments can be moved.
Phased transition from public to private space
One of the objections to stacked living is the presence of anonymous spaces, such as galleries, stairwells, storerooms, and elevators. Sometimes children use these as a play area for lack of anything better. To put an end to this kind of no man's land, clusters of 10 – 15 residential units with a shared stairwell are created. This solution appeals to what Oscar Newman calls a defensible space, which mainly concerns social control, surveillance, territoriality, image, management, and sense of ownership. These 'neighborhoods' then form a transition zone between the own apartment, the rest of the building and the outside world, in which the residents feel familiar. Adults indicate that the use of shared cars should also be organized in these types of clusters.
Variation
Once, as the housing market becomes less overburdened, home seekers will have more options. These relate to the nature of the house (ground floor or stacked) and - related thereto - the price, the location (central or more peripheral) and the nature of the apartment itself. But also, on the presence of communal facilities in general and for children in particular.
Many families with children prefer that their neighbors are in the same phase of life and that the children are of a similar age. In addition, they prefer an apartment on the ground floor or lower floors that preferably consists of two floors.
Communal facilities
Communal facilities vary in nature and size. Such facilities contain much more than a stairwell, lift and bicycle storage. This includes washing and drying rooms, hobby rooms, opportunities for indoor and outdoor play, including a football cage on the roof and inner gardens. Houses intended for cohousing will also have a communal lounge area and even a catering facility.
However, the communal facilities lead to a considerable increase in costs. That is why motivated resident groups are looking for other solutions.
Building collectively or cooperatively
The need for new buildings will increasingly be met by cooperative or collective construction. Many municipalities encourage this, but these are complicated processes, the result of which is usually a home that better meets the needs at a relatively low price and where people have got to know the co-residents well in advance.
With cooperative construction, the intended residents own the entire building and rent a housing unit, which also makes this form of housing accessible to lower incomes. With collective building, there is an association of owners, and everyone owns their own apartment.
Indoor and outdoor space for each residential unit
Apartments must have sufficient indoor and outdoor space. The size of the interior space will differ depending on price, location and need and the nature of the shared facilities. If the latter are limited, it is usually assumed that 40 - 60 m2 for a single-person household, 60 - 100 m2 for two persons and 80 - 120 m2 for a three-person household. For each resident more about 15 to 20 m2 extra. Children over 8 have their own space. In addition, more and more requirements are being set for the presence, size, and safety of a balcony, preferably (partly) covered. The smallest children must be able to play there, and the family must be able to use it as a dining area. There must also be some protection against the wind.
Residents of family apartments also want their apartment to have a spacious hall, which can also be used as a play area, plenty of storage space and good sound insulation.
'The Babylon' in Rotterdam
De Babel is the winning entry of the competition mentioned before to design the ideal family-friendly stacked home (see title image). The building contains 24 family homes. All apartments are connected on the outside by stairs and wide galleries. As a result, there are opportunities for meeting and playing on all floors. The building is a kind of box construction that tapers from wide to narrow. The resulting terraces are a combination of communal and private spaces. Due to the stacked design, each house has its own shape and layout. The living areas vary between approximately 80 m2 and 155 m2 and a penthouse of 190 m2. Dimensions and layouts of the houses are flexible. Prices range from €400,000 – €1,145,000 including a parking space (price level 2021).
As promised, the building has now been completed, albeit in a considerably 'skimmed-down' form compared to the 'playful' design (left), no doubt for cost reasons. The enclosed stairs that were originally planned have been replaced by external steel structures that will not please everyone. Anyway, it is an attractive edifice.
15. Affordable housing

This is the 15th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. This post is about one of the most serious threats to the quality of the living environment, namely the scarcity of housing, which is also unaffordable for many.
In many countries, adequate housing has become scarcer and too expensive for an increasing number of people. Unfortunately, government policy plays an important role in this. But good policy can also bring about a change. That's what this post is about.
As in many other developed countries, for a large part of the 20th century, the Dutch government considered it as its task to provide lower and middle classes with good and affordable housing. Housing associations ensured the implementation of this policy. Add to this well-equipped neighborhood shopping centers, ample medical, social, educational and transportation facilities and a diverse population. When the housing shortage eased in the 1970s, the nation was happier than ever. That didn't take long.
The emergence of market thinking in housing policy
During the last decades of the 20th century, the concern for housing largely shifted to the market. Parallel to this, housing corporations had to sell part of their housing stock. Mortgages were in easy reach and various tax facilities, such as the 'jubelton' and the mortgage interest deduction, brought an owner-occupied home within reach of many. In contrast, the waiting time for affordable rental housing increased to more than 10 years and rental housing in the liberalized zone became increasingly scarce and expensive. In Germany and Austria, providing good housing has remained a high priority for the government and waiting times are much shorter. The photo at the top left part shows the famous housing project Alt Erla in Vienna. Bottom shows left six affordable homes on the surface of one former home in an American suburb and top right is the 'Kolenkit', a social housing project in Amsterdam.
The explosive rise in housing costs
In order to adapt housing cost to the available budget, many people look for a house quite far away from the place where they work. Something that in turn has a negative effect on the travel costs and the time involved. Others settle in a neighborhood where the quality of life is moderate to poor or rent a too expensive house. More than a million households spend much more than the maximum desirable percentage of income (40%) on housing, utilities, and transport.
Between 2012 and 2022, the average price of a home in the Netherlands rose from €233,000 to €380,000. In Amsterdam, the price doubled from €280,000 to €560,000. Living in the city is becoming a privilege of the wealthier part of the population.
It is often assumed that around 900,000 housing units will be needed in the Netherlands by 2030, of which 80% is intended for single-person households.
An approaching change?
It seems that there is a shift going on, at least in policy thinking. The aim is to build an average of 100,000 homes per year in the coming years and to shorten the lead time between planning and realization. Achieving these intentions is uncartain because construction is being seriously delayed by the nitrogen crisis. The slow pace of new construction has once again drawn attention to the possibility of using existing houses and buildings for a significant proportion of these new housing units. More so as it is estimated that 80% of demand comes from single-person households.
The existing housing stock offers large potential for the creation of new living spaces. This potential has been investigated by, among others, the Kooperative Architecten Werkplaats in Groningen, resulting in the report <em>Ruimte zat in de stad</em>. The research focuses on 1800 post-war neighbourhoods, built between 1950 and 1980 with 1.8 million homes, 720,000 of which are social rental homes. The conclusion is that the division and expansion of these homes can yield 221,000 new units in the coming years. Eligible for this are single-family houses, which can be divided into two, and porch apartment blocks, which can be divided into more units per floor. Dividing up existing ground-access homes and homes in apartment blocks is technically not difficult and the costs are manageable. This applies even more if the adjustments are carried out in combination with making the relevant homes climate neutral. In addition, huge savings are made on increasingly expensive materials.
Even more interesting is to combine compaction with topping. This means the addition of one or two extra floors, so that a lift can also be added to the existing apartments. In construction terms, such an operation can be carried out by using light materials and installing an extra foundation. A project group at Delft University of Technology has designed a prototype that can be used for all 847,000 post-war porch houses, all of which need major maintenance. This prototype also ensures that the buildings in which these homes are located become energy-neutral and include facilities for socializing and play. Hence the extra wide galleries, with stairs between the floors and common areas in the plinth (image below right).
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
13. Social safety

This is the 13th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. This post discusses the way cities can secure public space, distinguishing symptom control and a more fundamental approach.
Scope of crime
According to the World Health Organization, the risk of being confronted with physical violence significantly detracts from the quality of life. In 2000, homicides worldwide resulted in half a million deaths, nearly twice the number of people who died in a war that year, but less than 40% of fatalities on roads. Many murders are related to drug trafficking. The number of murders in the European Union that year was about 5200. Between 2008 and 2016, car thefts dropped by 36% and robberies by 24%. Both trends leveled off after 2010. However, police-recorded sexual violence in the EU shows an increase of 26% between 2013 and 2016.
Monitoring
Social safety is a precondition for the viability of public space. This applies to who works there, who lives there and who visits it. Frequently chosen solutions are the installation of cameras. Not bad, although streets without cameras run the risk of becoming less safe. Moreover, miscreants know well how to disguise their identity.
In Stratumseind, the illustrious nightlife center of Eindhoven, extensive experiments with CCTV cameras and sensors and, in addition, atmospheric lighting and scents have been executed (photo below right researcher Rinus Kanters in the control room). The city regards this experiment as a 'living lab' and it has continuously been evaluated. The results so far are that no clear connection has been found between this technology and the number of incidents, the feeling of safety among visitors has increased and the police are more quickly on the scene in the event of incidents.
Intensive use
Further conditions are intensive use. The more people on the street, the greater the social security, except for theft. Also 'eyes on the street', apartments in the space above the plinths help. More generally, transparency is of value. Transparent plinths of apartment buildings contribute to it (photo left: the Kleiburgflat, Amsterdam)
Lighting
Lighting is an important issue. It is not even so much about the fierceness of it, which entails other objections, but about the uniformity (photo above right). A particularly wrong idea is to equip lights with motion sensors, so that they only come on when a passer-by approaches. This is at the expense of the ability to keep an overview. There is no objection to slightly dimming the lighting when streets are less busy.
A decent existence
The ultimate policy to reduce crime and improve security is:
• Providing training, guidance and 'social employment', such as the 'Melkert jobs' from the 1990s, to bridge the distance to the labor market.
• Creating guaranteed jobs in the public sector for all. Not only to improve the quality of life of the unemployed, but also to perform numerous tasks that are currently left undone.
• Allocating a decent income to all adults, as long as paid work still falls short. Experiments with basic income show that this increases resilience, self-confidence and the chance of paid work.
• Providing temporary professional (psychological) assistance and guidance with household, and financial management and training on the way to full integration in society.
• The more intensively residents of a neighborhood interact with each other and keep an eye on each other's possessions, the less crime will have a chance. Social control has always been a powerful weapon against crime.
• In anticipation of permanent housing, shelter the homeless to prevent drug-related crimes and give high priority to combating violence and burglary.
It would be naive to think that less inequality and improvements in income, jobs and housing for the poorest groups will eliminate crime altogether. Greed, thrill-seeking, boredom, membership in wrong groups, wrong connections, imitation, mental illness, and alcohol and drugs abuse are not necessarily related to poverty and require judicial action.
Effective prevention and policing
• protection against the relatively small group of repeat-offenders, who are responsible for most crimes, especially violent crimes.
• Close cooperation between residents and the police at neighborhood level
• Police presence on bicycles (better than in cars),
• Detailed knowledge of the police and judiciary of and communication with youth groups that incidentally causes problems
• Sensible and proportionate use of digital resources to track down criminals.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
12. Water Management

This is the 12th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. This post deals with the question of how nature itself can help to deal with excessive rainfall and subsequently flooding of brooks and rivers, although these disasters are partially human-made.
Until now, flooding has mainly been combated with technical measures such as the construction of dykes and dams. There are many disadvantages associated with this approach and its effectiveness decreases. Nature-inclusive measures, on the other hand, are on the rise. The Netherlands is at the forefront of creating space for rivers to flood, where this is possible without too many problems.
Sponge areas
An important principle is to retain water before it ends up in rivers, canals, and sewers. The so-called sponge city approach can be incorporated into the fabric of new neighbourhoods and it creates sustainable, attractive places too. A combination of small and large parks, green roofs, wadis, but also private gardens will increase the water storage capacity and prevents the sewer system from becoming overloaded and flooding streets and houses. Steps are being taken in many places in the world; [China is leading the way](https://www\.dropbox\.com/s/47zxvl3kgbeeasa/Tale of two cities.pdf?dl=0) (photo top right). However, the intensity of the precipitation is increasing. In 2023, 75 cm of rain fell in Beijing in a few days. Under such conditions, local measures fall short. Instead, nature-inclusive measures must be applied throughout the river basin.
Retention basins
In new housing estates, water basins are constructed to collect a lot of water. Their stepped slopes make them pleasant places to stay in times of normal water level. The pictures on the left are from Freiburg (above) and Stockholm (below). The top center photo shows the construction of a retention basin in Lois Angeles.
Wadis
Wadis are artificial small-scale streams in a green bed with a high water-absorbing capacity. In the event of heavy rainfall, they collect, retain and discharge considerably more water than the sewer system (bottom center photo). Green strips, for example between sidewalks, cycle paths and roads also serve this purpose (photo bottom right: climate-adaptive streets in Arnhem).
Green roofs, roof gardens and soils
Green roofs look good, they absorb a lot of CO2 and retain water. The stone-covered urban environment is reducing the water-retaining capacity of the soil. Sufficiently large interspaces between paving stones, filled with crushed stone, ensure better permeability of streets and sidewalks. The same applies to half-open paving stones in parking lots.
Refrain from building in flood-prone areas
Up to the present day, flood-prone parts of cities are used for various purposes, often because the risk is underestimated or the pressure on space is very great. London's Housing and Climate Crises are on a Collision Course is the eloquent title of an article about the rapidly growing risk of flooding in London.
Hackney Wick is one of 32 growth centers set to help alleviate London's chronic housing shortage, which has already been repeatedly flooded by heavy rainfall. However, the construction of new homes continues. Measures to limit the flood damage at ground floor level include tiled walls and floors, water-inhibiting steel exterior doors, aluminum interior doors, kitchen appliances at chest height, closable sewers, and power supply at roof-level. Instead, floating neighbourhoods should be considered.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
11. Nature inclusivity

This is the 11th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. In this post, I wonder whether nature itself can tackle the environmental problems that humans have caused.
Ecosystem services
According to environmental scientists, ecosystems are providers of services. They are divided into production services (such as clean drinking water, wood, and biomass), regulating services (such as pollination, soil fertility, water storage, cooling, and stress reduction) and cultural services (such as recreation, and natural beauty). In case of nature-inclusive solutions ecosystems are co-managed to restore the quality of life on the earth in the short term and to maintain it in the long term, insofar as that is still possible.
The green-blue infrastructure
The meaning of urban green can best be seen in conjunction with that of water, hence the term green-blue infrastructure. Its importance is at least fourfold: (1) it is the source of all life, (2) it contributes substantially to the capture and storage of CO2, (3) 'green' has a positive impact on well-being and health; (4) it improves water management. This post is mainly about the third aspect. The fourth will be discussed in the next post. 'Green' has many forms, from sidewalk gardens to trees in the street or vegetated facades to small and large parks (see collage above).
Improving air quality
Trees and plants help to filter the water itself. They have a significant role to play in managing water and air pollution. Conifers capture particulate matter. However, the extent to which this occurs is less than is necessary to have a significant impact on health. Particulate matter contributes to a wide range of ailments. Like infections of the respiratory system and cardiovascular disease, but also cancer and possibly diabetes.
Countering heat stress
Heat stress arises because of high temperature and humidity. The wind speed and the radiation temperature also play a role. When the crowns of trees cover 20% of the surface of an area, the air temperature decreases by 0.3oC during the day. However, this relatively small decrease already leads to a 10% reduction in deaths. Often 40% crown area over a larger area is considered as an optimum.
Reduce mental stress and improve mood
According to Arbo Nederland, 21% of the number of absenteeism days is stress-related, which means approximately a €3 billion damage. A short-term effect of contact with nature on stress, concentration and internal tranquility has been conclusively demonstrated. The impact of distributing greenery within the residential environment is larger than a concentrated facility, such as a park, has.
Strengthening immune function via microbiome
The total amount of greenery in and around the house influences the nature and quantity of the bacteria present. This green would have a positive effect on the intestinal flora of those who are in its vicinity and therefore also on their immune function. The empirical support for this mechanism is still rather limited.
Stimulate physical activity
The impact of physical activity on health has been widely demonstrated. The Health Council therefore advises adults to exercise at least 2½ hours a week. The presence of a green area of at least ¼ hectare at 300 meters from the home is resulting more physical activity of adults in such areas, but not to more activity as a whole.
Promoting social contact
Well-designed green areas near the living environment invite social contacts. For instance, placement of benches, overview of the surroundings and absence of traffic noise. The state of maintenance are important: people tend to avoid neglected and polluted areas of public space, no matter how green.
Noise reduction
Vegetation dampens noise to some extent, but it is more important that residents of houses with a green environment experience noise as less of a nuisance. It is assumed that this is due to a mechanism already discussed, namely the improvement of stress resistance because of the greenery present.
Biophilic construction
For years buildings made people sic. A growing number of architects want to enhance the effect of 'green' on human health by integrating it into the design of houses and buildings and the materials used. This is the case if it is ensured that trees and plants can be observed permanently. But also, analogies with natural forms in the design of a building
The 'Zandkasteel', the former headquarters of the Nederlandse Middenstandsbank in Amsterdam, designed by the architects Ton Alberts and Max van Huut, is organically designed both inside and outside, inspired by the anthroposophical ideas of Rudolf Steiner. The (internal) water features are storage for rainwater and the climate control is completely natural. The building has been repurposed for apartments, offices and restaurants.
Green gentrification
Worldwide, there is a direct correlation between the amount of greenery in a neighborhood and the income of its residents. Conversely, we see that poorer neighborhoods where new green elements are added fall victim to green gentrification over time and that wealthier housing seekers displace the original residents.
The challenge facing city councils is to develop green and fair districts where gentrification is halted and where poorer residents can stay. Greening in poor communities must therefore be accompanied by measures that respect the residential rights and aim at improving the socio-economic position of the residents.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
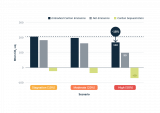
10. Health
Most important causes of death worldwide (Source: The Lancelet, le Monde)
This is the 10th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. In this post, I mainly focus on health problems which are directly related to the quality of the living environment
Are cities healthy places?
According to the WHO's Global Burden of Diseases Study, 4.2 million deaths worldwide each year are caused by particulate matter. The regional differences are significant. Urban health depends on the part of the world and the part of the city where you are living. More than 26 million people in the United States have asthma and breathing problems as a result. African-American residents in the US die of asthma three times as often as whites. They live in segregated communities with poor housing, close to heavy industry, transportation centers and other sources of air pollution.
Globally, the increasing prosperity of city dwellers is causing more and more lifestyle-related health problems. Heart disease, and violence (often drug-related) has overtaken infectious diseases as the first cause of death in wealthy parts of the world.
The Netherlands
Very recently, Arcadis published a report on 'the healthy city'. This report compares 20 Dutch cities based on many criteria, divided over five domains. The four major cities score negatively on many aspects. In particular: healthy outdoor space, greenery, air quality, noise nuisance, heat stress and safety. Medium-sized cities such as Groningen, Emmen, Almere, Amersfoort, Nijmegen, and Apeldoorn, on the other hand, are among the healthiest cities.
In Amsterdam, the level of particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) in 2018 exceeded World Health Organization standards in many streets. The GGD of Amsterdam estimates that 4.5% of the loss of healthy years is the result of exposure to dirty air.
Collaborative measuring air quality
In various cities, groups of concerned citizens have started measuring the quality of the air themselves. A professional example is the AiREAS project in Eindhoven. An innovative measuring system has been developed together with knowledge institutions and the government. Sensors are distributed over the area of the city and the system provides real-time information. The AiREAS group regularly discusses the results with other citizens and with the city government. The measurement of the quality of the air is supplemented by medical examination. This research has confirmed that citizens in the vicinity of the main roads and the airport have an increased risk of mortality, reduced lung function and asthma.
The AiREAS project is linked to similar initiatives in other European cities. Occasionally the data is exchanged. That resulted in, among other things, this shocking video.
Future?
Could the future not be that we are busy doing the obvious things for our health, such as walking, cycling, eating good food and having fun and that thanks to wearables, symptoms of diseases are watched early and permanently in the background, without us being aware of it? The local health center will monitor and analyze the data of all patients using artificial intelligence and advise to consult the doctor if necessary. An easily accessible health center in one's own neighborhood remains indispensable.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
9. Road safety

This is the 9th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Casualties in traffic are main threats to the quality of the living environment. ‘Vision zero’ might change this.
Any human activity that annually causes 1.35 million deaths worldwide, more than 20 million serious injuries, damage of $1,600 billion and is a major cause of global warming would be banned immediately. Except for the use of the car. This post describes how changes in road design will improve safety.
The more public transport, the safer the traffic
Researchers from various universities in the US, Australia and Europe have studied the relationship between road pattern, other infrastructure features and road safety or its lack. They compared the road pattern in nearly 1,700 cities around the world with data on the number of accidents, injuries, and fatalities. Lead researcher Jason Thompsonconcluded: <em>It is quite clear that places with more public transport, especially rail, have fewer accidents</em>. Therefore, on roads too public transport must prioritized.
The growing risk of pedestrians and cyclists
Most accidents occur in developing and emerging countries. Road deaths in developed countries are declining. In the US from 55,000 in 1970 to 40,000 in 2017. The main reason is that cars always better protect their passengers. This decrease in fatalities does not apply to collisions between cars and pedestrians and cyclists, many of which are children. Their numbers are increasing significantly, in the US more than in any other developed country. In this country, the number of bicycle lanes has increased, but adjustments to the layout of the rest of the roads and to the speed of motorized traffic have lagged, exposing cyclists to the proximity of speeding or parking cars. SUVs appear to be 'killers'and their number is growing rapidly.
Safe cycling routes
In many American cities, paint is the primary material for the construction of bike lanes. Due to the proximity of car traffic, this type of cycle routes contributes to the increasing number of road deaths rather than increasing safety. The Canadian city of Vancouver, which doubled the number of bicycle lanes in five years to 11.9% of all downtown streets, has the ambition to upgrade 100% of its cycling infrastructure to an AAA level, which means safe and comfortable for all ages and abilities. Cycle paths must technically safe: at least 3 meters wide for two-way traffic; separated from other traffic, which would otherwise have to reduce speed to less than 30 km/h). In addition, users also need to feel safe.
Street design
Vision Zero Cities such as Oslo and Helsinki are committed to reducing road fatalities to zero over the next ten years. They are successful already now: There were no fatalities in either city in 2019. These and other cities use the Vision Zero Street Design Standard, a guide to planning, designing, and building streets that save lives.
Accidents are often the result of fast driving but are facilized by roads that allow and encourage fast driving. Therefore, a Vision Zero design meets three conditions:
• Discouraging speed through design.
• Stimulating walking, cycling and use of public transport.
• Ensure accessibility for all, regardless of age and physical ability (AAA).
The image above shows a street that meets these requirements. Here is an explanation of the numbers: (1) accessible sidewalks, (2) opportunity to rest, (3) protected cycle routes, (4) single lane roads, (5) lanes between road halves, (6) wide sidewalks, (7) public transport facilities, (8) protected pedestrian crossings, (9) loading and unloading bays, (10) adaptive traffic lights.
Enforcement
Strict rules regarding speed limits require compliance and law enforcement and neither are obvious. The Netherlands is a forerunner with respect to the infrastructure for bikes and pedestrians, but with respect to enforcement the country is negligent: on average, a driver of a passenger car is fined once every 20,000 kilometers for a speeding offense (2017 data). In addition, drivers use apps that warn of approaching speed traps. Given the risks of speeding and the frequency with which it happens, this remissing law enforcement approach is unacceptable.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
De stad van de toekomst bouwen ze in Almere in Minecraft

Met een spetterende kick-off door Justin Edwards, Director of Learning Programmes van Microsoft, zijn 200 studenten van hogeschool Windesheim Flevoland vandaag in teams gestart met het in Minecraft bouwen van het nog te realiseren stadsdeel Pampus. Bijzonder omdat Almere als tweede stad na London start met een Minecraft challenge voor de realisatie van een nieuwbouwopgave. Het winnende studententeam van Windesheim mag haar concept van 7 – 9 november presenteren in het Holland paviljoen tijdens de Smartcity Expo World Congres in Barcelona.
De komende anderhalf jaar biedt Almere honderden jongeren tussen de 8 en 21 jaar op deze unieke manier de kans om zelf op de stoel van de architect te zitten en zo mee te denken over grote maatschappelijke vraagstukken. Basisschoolleerlingen en studenten bouwen op hun eigen niveau aan een virtueel Almere Pampus. Dit als plek waar zij in de toekomst zelf willen wonen. Dit stadsdeel bouwen ze met een speciale versie van Minecraft Education Edition.
Wethouder Maaike Veeningen van Almere (Economische ontwikkeling, hoger onderwijs): ‘we dagen leerlingen tot 21 jaar uit om met oplossingen te komen voor vraagstukken op het gebied van duurzaam, energiezuinig en inclusief bouwen. Op deze manier leren zij bijvoorbeeld over het gebruik van Artificial Intelligence (AI), Virtual Reality (VR) en robotisering bij het ontwikkelen van een nieuw stadsdeel. Zo betrekken we onze toekomstige inwoners bij het bouwen aan de ideale stad van de toekomst.’
Toekomstige leefomgeving
Het toekomstige Almere Pampus wordt in het zuidwesten van Almere gebouwd, met meer dan 30.000 woningen en 16.000 arbeidsplaatsen. Projectdirecteur Almere Pampus en senior stedenbouwkundige bij de gemeente Almere Paola Huijding over de Minecraft Challenge: “Deze leerlingen zijn misschien de toekomstige bewoners van Pampus. Hiermee bouwen we aan woon- en werkplekken omringd door water en groen. Het is daarom zo mooi dat juist de toekomstige generatie nu meedenkt over hun leefomgeving.”
Digitaalvaardig
De speciale editie van Minecraft die de studenteams gebruiken is ontwikkeld door Iamprogrez. Het gebruik ervan moet op een speelse en laagdrempelige manier bijdragen aan een digitaal vaardige samenleving. Scholieren krijgen zo inzicht in de banen van de toekomst. Ook kunnen zij in een buddysysteem ouderen meenemen in hun digitale kennis en vaardigheden.
Fleur van Beem, Executive Director bij VodafoneZiggo: “Het vooruithelpen van twee miljoen mensen in de samenleving willen wij bereiken door initiatieven als Online Masters, een online lesprogramma voor scholen over de digitale wereld. De Minecraft Challenge sluit hierop naadloos aan en het is natuurlijk fantastisch om dankzij gamification jongeren digitaalvaardig te krijgen.”
Bouwen aan innovatieve concepten
De leerlingen kunnen alleen of in teams werken aan de challenge en krijgen hiervoor een digital skills-certificaat. Na de ontwerpfase, kunnen zij hun toekomstige visie op Pampus uploaden op de website van de Green Innovation Hub (GIH). Een groep experts kiest de winnaar. Danny Frietman, Projectdirecteur van de GIH: “De winnende uitkomsten van de Minecraft Challenge vormen de basis voor ons om start-ups en scale-ups uit te dagen om de concepten van de scholieren daadwerkelijk in de praktijk te brengen.”
“Hoe ziet het er dan uit”
Kijk HIER naar de video aankondiging van de eerder gehouden Minecraft-challenge in Londen. Daarin zie je duidelijk hoe de challenge werkt en welke mogelijkheden Minecraft hiervoor biedt.
Fotografie Daan Klunder, Almere City Marketing
7. Accessibility

This is the 7th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. The question is whether motorized traffic must be banned from central parts of the city to improve the quality of the urban environment.
Most cities face a choice when it comes to accessibility of their central parts: Whether they renovate the road infrastructure or they face a growing and lasting conflict between car traffic and visitors, whose numbers will decrease further as a result of prioritizing cars. This post deals with the first option.
Changing priorities in the use of road space
The starting point for this renovation is choosing the best experience for both residents and visitors. Therefore, the use of road space in all parts of cities must be under scrutiny. This also applies the connecting roads between centers and the other parts of the city. The distribution of space between pedestrians, cyclists, cars, and public transport has to be reconsidered. A good example is the Ferdinand Bolstraat in Amsterdam. Cars have been banned, the sidewalks are widened, cyclists have their own lanes and the tram uses a switch track (photo below left), just as in Leidsestraat (photo above left).
Accessibility
The rule of thumb is that the larger a city and the better public transport is functioning, the more the accessibility by car of the central parts and the residential areas as well can be reduced. Visitors who rely on the use of a car then store their vehicle in a parking on the edge of the center, preferably near supermarkets or other places where voluminous purchases can be made. From these parking spaces they enter the central area on foot. Incidentally, it is worth considering opening the entire center to cars until 11 a.m. to pick up orders.
Cyclists can be allowed deeper penetration in the central urban area, but not unlimited. They leave their bicycles in (guarded) parking facilities too.
Public transport never stops more than 300 meters from the middle of the center, where comfortable waiting areas are offered, and information is available.
Separation of traffic flows
A separation of traffic flows is required for the entire urban area. The most central streets will be exclusively intended for pedestrians, emergency services and occasionally the tram. Bicycles are allowed in streets in the center, depending on their wideness.
Public transport has always priority at traffic lights. It ensures not only transfer-free accessibility of the urban center, but also connects the most important residential and work areas with a minimum number of transfer. The possible arrival of autonomous minibuses will radically improve the flexibility of public transport (photo above right).
Intra-urban walking and cycling routes
Pedestrians’ and cyclists’ safety and amenity are improved if the connections between the central and outlying parts of the city are accessible by separate routes too. In a city whose green space penetrates deep into the central area, these routes can partly run through nature. A good example is the cycle route from the center of Utrecht to Leidsche Rijn (photo bottom right). Pedestrians need an attractive route through the built-up area for reasons of social safety.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
What can Amsterdam learn from YIMBY Arnhem!

At the 22nd of September 2023 we celebrate the tenth YIMBY Harvest Festival at the Hoeve Klein Mariëndaal in Arnhem. What is YIMBY? YIMBY is the acronym for Yes-In-My-Back-Yard. YIMBY Arnhem! started in 2013 with the distribution of small scale food platforms, called YIMBY's, to the citizen of Arnhem. At the same time green education was offered to urban food growers to convert green enthusiasm into green harvest. During ten years hundreds of citizen in Arnhem joined the YIMBY social network of growing healthy, organic food in the city. The succes of YIMBY Arnhem! are the people supported by local government and local branches of green companies.
YIMBY is a culture of YES, positively stimulating social innovation for a healthier, greener and more social neighbourhood. The YIMBY experience demonstrates that changes do not start in The Hague, Brussels or Strasbourg. The change to a greener and more social Europe starts at home, in the backyard of people. We invited Frans Timmermans to the YIMBY Harvest Festival in Arnhem to share and to learn from ten years of YIMBY experience in the city of Arnhem. YIMBY Arnhem! shows that in due time small grassroots initiatives steadily grow and empower people to social inclusion and green cooperation.
6. Appropriate density
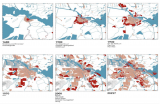
This article is part of the series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Read whether Increasing density of cities complies with the quality of the urban environment.
There is widespread agreement to use the available space more thoughtful than during the last decades. In the Nationale Omgevingsvisie (NOVI), the Dutch government has unambiguously expressed its preference for housing locations within existing built-up areas or in the vicinity of stations.
The need for density
Frequently, references are made to ‘urban sprawl' in the USA to illustrate the disadvantages of low density. However, but The Netherlands is also familiar with extensive growth of the urban area. The maps above show the growth of the Amsterdam area. Between 1900 and 2000, the population of Amsterdam grew from 317,000 to 727,000 inhabitants. Its surface from 560 to 11,500 hectares.
The spread of urban activities over an ever-increasing surface and the associated traffic movements have led to vast monotonous areas, car dependence, expansion of the road network, increasing congestion, impoverishment of social life, air pollution, emissions of greenhouse gases and decline of nature.
A summary of 300 OECD research projects shows that compactness results in more efficient use of facilities, but that there are also disadvantages in terms of health and well-being, usually as results of air pollution and traffic.
Advantages of density
Denser development is generally associated with the availability of amenities within walking distance, creating support for better public transport accessibility, and leading to more efficient use of utilities. Moreover - corrected for the composition of the population - CO2 emissions in urban areas are at least 30% lower than in the suburbs. An advantage that disappears in case of high-rises.
No necessity to expand building outside urban areas
According to many urban planners, there is no reason to divert to locations outside the existing built-up area. They claim that there is sufficient space in every city for new residential locations, for instance disused office buildings and factory locations. Many new homes can also come available through the division of oversized single-family homes and the renovation and raising of older (porch) homes.
These arguments only hold if at the same time the nuisance by densification is limited. For example, by reducing car useto prevent the roads from becoming even more crowded and the streets even more filled with parked cars. I don't see that happening yet.
Competing claims on urban land use
There is another important objection to further densification and that is the fact that other forms of land use also appeal to available land within the urban space. For example, the expansion of industry, trade, research etcetera. preferably in the vicinity of living areas to reduce the length of trips.
The most important claim on the available space is the need to expand the city’s greenery. Research into the development of 'green' in Amsterdam and Brussels since 2010 shows that the open space ratio (OSR) in both cities has decreased. In Amsterdam this was 3.68 km2 (4.7%) and in Brussels 9.17 km2 (11.9%). This is in line with a recent study by Arcadis, which shows that the four major cities in the Netherlands score very poorly on healthy outdoor space, greenery, air quality, noise nuisance, heat stress and safety.
Inner- and outer-urban development revisited
The report therefore concludes that extension of the use of urban space for housing must be weighed up against other claims for the use of space, such as urban greening, urban agriculture, and the maintenance and expansion of business activities. At the same time, the objections to ecologically responsive building activities outside the already urbanized areas must be reconsidered. Three-quarters of the agricultural land is used for intensive livestock farming, not exactly creating valuable nature. I will come back to it later.
In the 'Dossier leefbaar wonen' (in Dutch)' I wrote extensively about the subject of providing affordable housing. You can download this e-book using the link below:
5. Integration of high-rises

This article is part of the series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Read how the design of high-rises might comply with the quality of the urban environment.
High-rises are under scrutiny in two respects. First, its necessity or desirability. Secondly, their integration in the urban fabric. This post is about the latter.
Options for high-rises
Suppose you want to achieve a density of 200 housing equivalents in a newly to build area of one hectare. A first option is the way in which Paris and Barcelona have been built: Contiguous buildings from five to eight floors along the streets, with attractive plinths. In addition, or as an addition, others prefer high-rises because of their capacity of enhancing the metropolitan appearance of the area. Not to increase the density in the first place.
Integrative solution
Almost all urban planners who opt for the latter option take as starting point rectangular blocks, which height along the streets is limited to 4-6 storeys, including attractive plinths. The high-rise will then be realized backwards, to keep its massiveness out of sight. The image at top left gives an impression of the reduced visibility of high-rises at street level on Amsterdam's Sluisbuurt. According to many, this is a successful example of the integration of high-rises, just like the Schinkelkwartier under development, also in Amsterdam(picture top right).
Separate towers
The last option is also recognisable in all urban plans with a metropolitan character in Utrecht and Rotterdamand more or less in The Hague too. This represents a turnaround from the past. Research by Marlies de Nijsshowed that only 20% of all high-rises built before 2015 met this condition. These buildings consist of separate towers without an attractive plinth. What you see at ground floor-level are blank walls hiding technical, storage or parking areas. The Zalmtoren in Rotterdam, the tallest building in the Netherlands, exemplifies this (picture below right). This kind of edifices is mostly surrounded by a relatively large space of limited use. Other disadvantages of detached high-rises are the contrast with adjacent buildings, their windy environment, the intense shadows, its ecological footprint, and the costs.
Paris
Two extreme examples of disproportionate high-rises can be found in Paris. Paris has always applied a limitation of the building height to 37 meters within the zone of the Périférique. The exception is the Eiffel Tower, but it was only meant to be temporary. In the two short periods that this provision was cancelled, two buildings have risen: The first is the 210-meter-high Tour Montparnasse, which most Parisians would like to demolish immediately. Instead, the building will be renovated at a cost of €300 million in preparation for the Olympic Games. After 10 years of struggle, construction of the second has started in 2021. It is the 180-meter-high Tour Triangle, designed by Herzog & de Meuron, so-called star architects. The photos at the bottom left and centre show the consequences for the cityscape.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fi/x39qvzkw687rxsjvhsrzn/overzicht-blogposts-Eng.docx?rlkey=vpf7pwlfxkildpr9r062t5gf2&dl=0
4. Informative plinths

This article is part of the series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Read how design, starting from street-level view contributes to the quality of the urban environment.
Plinths express the nature of activities inside
The visual quality, design and decoration of the plinth, the 'ground floor' of a building, contributes significantly to the quality of the streetscape and to the (commercial) success of the activities that take place at plinth level. This also applies, for example, if the activities of a workshop can be observed through the windows. Blank walls speed up visitors' pace, unless this wall has attractive art. Vacancy is disastrous.
A plinth displays the destination of a building or a part of it (photo bottom left). Fashion stores and suppliers of delicacies depend on its ability to attract buyers. There is nothing against allowing the plinth to expand slightly onto the street - think of beautiful displays of fresh vegetables - if a sufficiently wide barrier-free pedestrian route is maintained.
The total length of streets that must generate customers and visitors must not be too long in order to keeps vacancy to a minimum. This may mean that still profitable shops in streets where the number of vacancies is increasing must consider moving if revitalization of the street is infeasible. The space left behind can best be revamped into space for housing or offices to prevent further dilapidation.
Plinths of non-commercial destinations
The need for an attractive plinth also applies to non-commercial spaces. This may concern information centers, libraries, day care centers for children or the elderly, places where music groups rehearse, etcetera. Co-housing and co-working centers might also concentrate several activities in a semi-public print. In an apartment building, you might like to see an attractive portal through the glass, with stairs and elevators and a sitting area.
Residential plinths
Houses in the more central parts of the city can also have an attractive plinth. In practice, this happens often by placing plants and creating a seat on the sidewalk. The so-called Delft plinths are narrow, sometimes slightly raised additional sidewalks for plants, a bench, or stalling bicycles (photo bottom middle). The worst is if the plinth of a private house is mainly the garage door.
The aesthetics of the plinth
In many pre-war high streets, the plinth was designed as an integral part of the building. In the ‘60s and ‘70s, many retailers modernized their businesses and demolished entire ground floors. The walls of the upper floor, sometimes of several buildings at the same time, rested on a heavy steel beam and the new plinth was mainly made of glass (photo top left). Often a door to reach the upper floors is missing, complicating the premises’ residential function. Initially, these new fronts increased the attractivity of the ground floor. However, the effect on the streetscape has turned out to be negative. In Heerlen, artist and 'would be' urban planner Michel Huisman (the man behind the Maankwartier) is busy restoring old shopfronts together with volunteers and with the support of the municipality (photos top right). In Amsterdam, shopfronts are also being restored to their original appearance (photo bottom right).
Plinths policy
The sky is the limit for improving plinths, as can be seen in the book Street-Level Architecture, The Past, Present and Future of Interactive Frontages by Conrad Kicker and the *Superplinten Handbook</em> , commissioned by the municipality of Amsterdam.
In 2020, a plinth policy was introduced in the Strijp-S district in Eindhoven from a social-economic background. 20% of the available plinths is destined for starters, pioneers and 'placemakers'. Continuous coordination with the target group is important here. In The Hague, 100 former inner-city shops have now been transformed into workplaces for young and creative companies. Differentiating rents is part of the plinth policy too.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Stay up to date
Get notified about new updates, opportunities or events that match your interests.

