Stay in the know on all smart updates of your favorite topics.
Breaking news for Amsterdam: The Global Startup Ecosystem Report 2021 is available
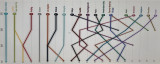
In the recent past, the value of startups in Amsterdam Delta (Amsterdam metropolitan region) has taken a giant leap. In 2015, Amsterdam startups were valued at $11.1 billion. Today, Europe's number 3 ecosystem is worth $83.3 billion. The extraordinary success stories of Adyen and Takeaway have been a major contributor to this success, but its base is much broader. On the annually published Global Startup Ecosystem ranking Amsterdam Delta rose from the 19th place in 2015 to 12th place in 2020. Everyone was curious about the 2021 ranking. Well, as the table shows, Amsterdam Delta has been overtaken by Paris and Tokyo, but only lost one place due to a significant drop in Stockholm.
The value of rankings is easily overestimated. However, the value of startups should not be underestimated. More than 30% of the 4000 startups in the Netherlands are located in the Amsterdam metropolitan region. Together, the Dutch startups have created more than 100,000 jobs and are responsible for 60% of the annual job growth.
Globally, 2020 and 2021 were amazing years for startups as the pandemic fueled technology. According to the Global Startup Ecosystem Report 2021, Internet capacity increased by 35% and global broadband traffic by 51%. Consumers bought 30% more food online. Global venture capital funding nearly doubled to $288 billion in the first half of 2021, compared to the first half of 2020. Startups have benefited from the explosive technology market, supported by significant government support. Following China and the US, the European Union has been generous to startups, and the same goes for its member states. The Dutch government offers tax credits to innovative companies and environmentally friendly investments. The city of Amsterdam promotes startups that support inclusive growth and diversity, for example by subsidizing female entrepreneurs.
The Amsterdam Delta startup ecosystem can be characterized as vibrant. Still other ecosystems in the world are growing faster, including those in some European cities. In the global top ten emerging ecosystems, we find Copenhagen in second place and Barcelona, Madrid, and Zurich in places 5, 8 and 9.
To detect possible vulnerabilities in the Amsterdam Delta startup ecosystem, analyzing of success factors of the 30 highest-ranked ecosystems in the report is informative. In terms of performance, Amsterdam's composite score is in a middle position (6 out of 10 points). In terms of funding, the position is good (8). In terms of market reach, the overall score is satisfactory (7): The Amsterdam Delta startups are primarily focused on global markets and score low on the local market. Like most European ecosystems, Amsterdam Delta scores excellent (9) in connectedness, which is related to its strength on the global market. In terms of talent, the overall score is satisfactory (7), but the components differ considerably. The quality of technology students and graduates is good, but their number is insufficient, resulting in high salary costs. The scalability of the Amsterdam startup ecosystem is also insufficient, due to a lack of experience, which keeps many startups small. The overall knowledge success is assessed as poor (1) because the number of life science patents is disappointing.
When assessing the success factors, it should be considered that the population of Amsterdam Delta is about 10% of the population of London, and in this perspective the need to improve the global 13th place is not urgent. On the contrary, understanding why the Amsterdam Delta is performing so well is more relevant than looking for opportunities to improve it.
The explanation of Amsterdam's success has its roots in the fundamental strength of the Netherlands as a whole, which has at least ten other vibrant startup ecosystems. Against this background, one might be curious about the Global Startup Ecosystem ranking of the Randstad, including Eindhoven as a whole. According to the report, the strength of the Netherlands is its well-educated population, international orientation and English proficiency, excellent infrastructure, an 'extremely high quality of life' and business-friendly laws. Amsterdam is also the headquarters of many international companies, a large pool of potential startup founders.
In a next post, I will focus on Amsterdam's policy towards startups and evaluate whether a higher ranking is within reach or whether more qualitative objectives are preferable, taken into account the considerations in a former post on the Amsterdam Smart City website.
I will regularly share ‘snapshots’ of the challenge of bringing socially and ecologically sustainable cities closer using technology if useful. These posts represent findings, updates, and additions to my e-book Humane cities. Always humane. Smart if helpful. The English version of this book can be downloaded for free below.
Barcelona and Madrid: Forerunners in e-governance

Barcelona is one of the oldest examples of a city that deploys technology as part of its government. Sensor networks have been producing an array of data on transport, energy usage, noise levels, irrigation, and many other topics without having much impact on the life of citizens or solving the underlying problems.
In 2015, Francesca Bria, chief technology, together with mayor Ada Colau started to reverse the smart city paradigm: Instead of starting from technology and extracting all the data we started aligning the tech agenda with the agenda of the city, she said.
One of the first challenges was using technology to increase ordinary citizen’s impact on policy. A group of civic-minded coders and cryptographers created a brand-new participatory platform, Decidem (which means We Decide in Catalan). For more information watch the video below.
Spain offers more inspiring examples. The city of Madrid has also created a participatory citizen platform, not for chance called Decide Madrid, which is in many respects comparable with Decidem, as this short video demonstrates.
The most important features of both platforms are:
Active participation in policy making
Citizens are stimulated to suggest ideas, debating them, and vote. In Barcelona, more than 40.000 citizens have suggested proposals, which form 70% of the agenda of the city administration. The most frequently mentioned concerns are affordable housing, clean energy, air quality and the public space.
The Municipal Action Plan of Barcelona includes almost 7,000 proposals from citizens. Decidem enables citizens to monitor the state of implementation of each of them to increase citizen’s engagement.
Debating
Decide Madrid and Decidem emphasize the value of being informed as starting point for deliberation. Citizens can start discussions on their own and participate in threaded discussions started by others.
As soon as citizens feel informed and have exchanged opinions voting can start. Both Decide Madrid as Decidemhave a space where citizens can make proposals and seeks support. Proposals that reach enough support are prepared for voting. These votes generally are advising the city council.
Policy preparation
Decide Madrid enables citizens amendment legislative texts. The public is allowed to commend any part of it and to suggest alternatives. This also might result in discussions and the suggestions are used to improve the formulations.
Data governance
Decidem and Decide Madrid are also data portals that show data that have been collected in the city, partly on citizens themselves. Decidem has the intention, because of its participation in the European project Decode to enable citizens to control the use of data of their own for specific purposes.
Hybrid solutions
As not every citizen has a computer or is skilled to use the Internet platforms, both cities combine virtual discussions and discussion in a physical space.
It is not only the traditional rivalry between Barcelona and Madrid that has inspired the development of two comparable systems, independently from each other. It is also the fact that the Spanish people had to fight for democracy until rather recently. Democratic institutions that have long existed in many other countries had to be reinvented, but with a 20th-century twist.
The community of Madrid has developed Decide Madrid together with CONSUL, a Madrid-based company. CONSUL enables cities to develop citizen participation on the Internet quickly and save. The package is very comprehensive. The software and its use are free. CONSUL can be adjusted by each organization to meet its own needs. As a result, Consul is in use in 130 cities and organizations in 33 countries (see the map above) and reaches out around 90 million citizens worldwide.
In contrast with e-Estonia, the topic of a former post, the footing of Decidem and Decide Madrid is enabling citizens to make their voice heard and to participate in decision-making. Both cities offer excellent examples of e-governance. e-Governance reflects the mutual communication between municipal authorities and citizens using digital tools to align decision making with the needs and wants of citizens. Instead, the intention of e-Estonia is to improve the efficiency of the operation of the state. Both aims are complementary.
I will regularly share ‘snapshots’ of the challenge of bringing socially and ecologically sustainable cities closer using technology if useful. These posts represent findings, updates, and additions to my e-book Humane cities. Always humane. Smart if helpful. The English version of this book can be downloaded for free below.
Who should win the Dutch Applied AI Award?

Last year, during the Month of the AAI in November, the Centre of Expertise Applied Artificial Intelligence (AUAS - Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences) presented the Dutch Applied AI Award for the first time. This year we are back for a second edition. The award is part of the Computable Awards and is for suppliers of AI solutions, start-ups in the AI field and good examples of the implementation of AI.
This award is jointly organized with AUAS, Computable and podcast De Dataloog . You can nominate an individual or organisation, based on a project you think has stood out in the past 12 months. The projects may have been particularly successful, innovative or extensive.
You can nominate until 16 August 2021
The winner will be announced on 2 November 2021 during a spectacular show in the Jaarbeurs Utrecht. Last year, healthcare platform DEARhealth won the Dutch Applied AI award. Who will walk away with the prize this year? 🙌🏻
About the Computable Awards
This will be the 16th year in a row that Computable will present the Computable Awards in November 2021. These prizes are awarded to companies, projects and individuals who, according to Computable readers, have clearly distinguished themselves in the past year.
An independent jury of experts will select five nominees for each award from the nominated parties. The ranking by the jury and the number of votes from Computable readers each determine half of which nominee will receive the award in November. The number of times a party is nominated for a nomination does not play a role, but the quality of the substantiation and information about the project mentioned does.
Beyond the smart city: Digital innovation for the Good of citizens

About ten years ago, technology companies started to provide cities with technology, luring them with the predicate ‘smart(er)’, a registered trademark of IBM. At that time Cisco's vice-president of strategy Inder Sidhudescribed the company’s ‘smart city play’ as its biggest opportunity, a 39,5 billion dollar-market. During the years, that followed, the prospects rocketed: The consultancy firm Frost and Sullivan estimated the global smart city technology market to be worth $1.56 trillion by 2020.
The persistent policy of technology companies to suggest a tight link between technology and the wellbeing of the citizens, angers me. Every euro these companies are chasing at, is citizens’ tax money. What has been accomplished until now is disappointing, as I documented in the IET Journal. According to The Economist it is not surprising that a ‘techlash’ is underway: Many have had it with the monopolistic dominance of behemoths like Google, Amazon, Facebook and the like, because of their treatment of sensitive data, the lack of transparency and accountability of algorithm-based decision making and the huge profits they make from it.
Regaining public control
However, let's not throw out the baby with the bathwater and see how digital innovation can be harnessed for the Good of all citizens. Regaining public control demands four institutional actions at city level.
1. Practicing governance
Before even thinking about digitalization, a city must convert into best practices of governance. Governance goes beyond elections and enforcing the law. An essential characteristic is that all citizens can trust that government represents their will and protects their interests. Therefore, it is necessary to go beyond formal democratic procedures and contact stakeholders directly, enable forms of participatory budgeting and deploy deliberative polling.
Aligning views of political parties and needs and wants of citizens takes time and a lot of effort. The outcome might be a common vision on the solution of a city’s problems and the realisation of its ambitions, and a consecutive political agenda including the use of tools, digital ones included.
2. Strengthening executive governmental power
Lack of cooperation within the departmental urban organizations prevents not only an adequate diagnosis of urban problems but also the establishment of a comprehensive package of policy instruments, including legislation, infrastructure, communication, finance and technology. Instead, decisions are made from within individual silos, resulting in fragmented and ineffective policies. Required is a problem-oriented organization instead of a departmental one and a mayor that oversees the internal coherence of the policy.
3. Level playing field with technology companies
Cities must increase their knowledge in the field of digitization, artificial intelligence in particular. Besides, but they should only work with companies that comply with ethical codes as formulated in the comprehensivemanual, Ethically Aligned Design: A Vision for Prioritizing Human Well-being with Autonomous and Intelligent Systems, drafted by the influential Institute of Electric and Electronic Engineers (IEEE)
Expertise at city level must come from a Chief Technology Officer who aligns technological knowledge with insight in urban problems and will discuss with company representatives on equal foot. Digitalisation must be part of all policy areas, therefore delegating responsibility to one alderman is a bad idea. Moreover, an alderman is not an adequate discussion partner for tech companies.
4. Approving and supporting local initiatives
Decentralization of decision-making and delegating responsibility for the execution of parts of the policy to citizen’s groups or other stakeholders helps to become a thriving city. Groups of citizens, start-ups or other local companies can invoke the right of challenge and might compete with established companies or organizations.
In summary: steps towards seamless integration of digitalization in citizen-orientated policy
1. Define together with citizens a vision on the development of the city, based on a few central goals such as sustainable prosperity, inclusive growth, humanity or - simply - happiness.
2. Make an inventory of what citizens and other stakeholders feel as the most urgent issues (problems and ambitions).
3. Find out how these issues are related and rephrase them if desirable.
4. Deepen insight in these issues, based on available data and data to be collected by experts or citizens themselves.
5. Assess ways to address these issues, their pros and cons and how they align with the already formulated vision.
6. Make sure that digital technology has been explored as part of the collected solutions.
7. Investigate which legal, organizational, personnel and financial barriers may arise in the application of potential solutions and how to address them.
8. Investigate undesired effects of digital techniques, in particular long-term dependence ('lock-in') on commercial parties.
9. Formulate clear actions within the defined directions for dealing with the issues to be addressed. Involve as many expert fellow citizens as possible in this.
10. Make a timetable, calculate costs, and indicate when realization of the stated goals should be observable.
11. Involve citizens, non-governmental and other organizations in the implementation of the actions and make agreements about this.
12. At all stages of the process, seek support from those who are directly involved and the elected democratic bodies.
13. Act with full openness to all citizens.
I can't agree more than with the words of Léan Doody (smart city expert Arup Group): I don't necessarily think 'smart' is something to strive for in itself. Unlike sustainability or resilience, 'smart' is not a normative concept…. The technology must be a tool to deliver a sustainable city. As a result, you can only talk about technological solutions if you understand which problems must be solved, whether these problems are rooted in the perceptions of stakeholders and how they relate to other policy instruments.
Metropolitan Mobility Podcast with Karen Vancluysen (Polis Network)

How can local governments deal with (technological) innovations? Listen to the #podcast with Karen Vancluysen of POLIS Network: https://bit.ly/mobilitypod
A comprehensive introduction into a human-centric approach of the smart city
Recently, the peer-reviewed Journal of the Engineering and ˜Technology published an overview of the emergence of a human-centric approach into smart cities in contrast to the techno-centric approach. In this article I give many examples how technology can be applied as an enabler tp improve social and ecological sustainable city actions, starting from the principles of the donut-economy
YIMBY Arnhem! groeit.

Dit voorjaar bouwen de makers van de zorgboerderij Hoeve Klein Mariëndaal in Arnhem-West YIMBY moestuinbakken voor de nieuwe stadsboeren in de wijken Klarendal, Geitenkamp, Presikhaaf, 't Broek en Malburgen van de stad Arnhem.
Angela Jong heeft haar buurtgenoten in de wijk Klarendal warm gemaakt voor het biologische tuinieren in de stad met YIMBY's. "Het komt mooi uit dat de Gemeente Arnhem 50% van de aanschafprijs bijdraagt door de groene subsidieregeling De Eetbare Stad". Bart van Dalsem van de Hoeve Klein Mariëndaal geeft aan: "Door de lokale sponsoring door de bedrijven Welkoop Elst en De Bolster kunnen we de YIMBY;s leveren met biologische moestuinaaarde en biologische zaden"
Zéger Nieuweboer heeft met zijn groene onderwijsbedrijf learningisgrowing.nl al acht jaar ervaring met de begeleiding van YIMBY Arnhem! "In de periode 2013-2020 zie je dat nieuwe stadsboeren starten met een YIMBY moestuinbak en doorgroeien naar een biologische voedseltuin". https://lnkd.in/eYbrQiH
#YIMBY #voordeoogstvanmorgen
Recycling, downcycling and the need for a circular economy

What happens to the plastic and paper that you’ve carefully sorted into separate bins?
Many of the products we recycle today are essentially downcycled. While this generally helps to preserve the life of raw materials and some of the value that went into creating them, there might be better ways to do it.
Find out more about the nuances between recycling, downcycling, and a truly circular economy, in this article.
Metropolitan Mobility Podcast met Maurits van Hövell: van walkietalkies naar het Operationeel Mobiliteitscentrum

“Voorheen werd er gewoon rondgebeld: ‘Wij zitten in de instroom van de ArenA. We hebben nu 20.000 man binnen. Hoe gaat het bij jullie op straat?’” In de achtste aflevering van de serie A Radical Redesign for Amsterdam, spreken Carin ten Hage en Geert Kloppenburg met Maurits van Hövell (Johan Cruijff ArenA). Hoe houdt je een wijk met de drie grootste evenementenlocaties van het land, bereikbaar en veilig? Ze spreken elkaar in het Operationeel Mobiliteitscentrum over de rol van de stad Amsterdam, data delen en het houden van regie. A Radical Redesign for Amsterdam wordt gemaakt in opdracht van de Gemeente Amsterdam.
Luister de podcast hier: http://bit.ly/mvhovell
Amsterdam: circulaire stad in 2050

Amsterdam: circulaire stad in 2050
Ondanks de coronacrisis zijn tal van bedrijven in regio Amsterdam bezig met circulaire projecten, business cases en onderzoeken. Net als de gemeente Amsterdam streven zij naar een circulaire stad in 2050.
Benieuwd? Bekijk de video Amsterdam: circulaire stad in 2050. Voor meer informatie kun je ook kijken op de CACR pagina of op amsterdam.nl/circulair.
Inkopen met Impact - hoe start je daarmee?

Met elke euro die je als organisatie uitgeeft aan producten en diensten, heb je de keuze voor het duurzamer, eerlijker of innovatiever alternatief. Denk aan circulaire en energiebesparende producten en diensten, maar ook aan verantwoorde inzet van technologie. Daarmee is inkopen een belangrijke driver voor een slimme, groene en gezonde toekomst. Budgetten worden anders ingezet en systemen en gewoontes worden zo doorbroken.
De Amsterdam Economic Board heeft inmiddels een heel Insights dossier gericht op Inkopen met Impact. Daarin vind je achtergrondartikelen, maar ook quickstarts die je op weg helpen bij het verantwoorder inkopen van bijvoorbeeld bedrijfscatering, werkkleding of bouw en onderhoud van je organisatie. Je vindt al deze quickstarts in het dossier Inkopen met Impact. Je vindt er ook links naar hoe je je kunt aansluiten bij activiteiten van de Board die je helpen met beter inkopen.
Two Communications vacancies at Metabolic

Before we can transition to a circular economy, people need to be inspired and engaged. We're looking for two communications professionals want to dedicate their career to a sustainable cause!
We're looking for a digital communications manager, who can help us get the right messages to the right people to galvanize real change. From social media to big speaking events, digital advertising and email newsletters, spreading key ideals, ideas and messages as effectively as we can: https://bit.ly/38g9uBI
We're also looking for an experienced science journalist or environmental PR professional who can be the core pillar of our content engine: https://lnkd.in/dhc4V9c
Want a printed version of my free e-book Cities of the Future?

Recently, I published my new e-book: Cities of the Future. Always Humane. Smart if Helpful.
You can download this book for free here:
Dutch version
https://www.dropbox.com/s/ytdadwgdsdw6zke/Looking%20for%20the%20city%20of%20the%20future%20NL.pdf?dl=1
English version
https://www.dropbox.com/s/kfywoszhrn4xi5j/Looking%20for%20the%20city%20of%20the%20future.pdf?dl=1
In case you prefer a compact printed version in Dutch (180 pages), transfer €20,00 to IBAN NL35 INGB 000 167 55 50 on behalf of H. van den Bosch, mention your address and you will receive your copy in a few days
Looking for partners on Inclusive and AI

With Inclusive Algorithm, we would like to bring more inclusion and diversity in Artificial Intelligence revolution and business.
Our main objective is to generate more network and knowledge in the Artificial Intelligence field to better understand how artificial intelligence, algorithms and big data can be ethically developed for societal benefit by involving the marginalized groups (groups with migrant backgrounds & bi-culturals).
We just started this initiative and we are building alliances with people believing in our cause. Please feel welcome to reach out if you think we can add value to the work you do or vice versa.
Start inhaarlemmermeer.nl

Lokaal Community Platform voor bewoners, bedrijven en bezoekers van Haarlemmermeer. (Amsterdam Metropolitan Area)
Sinds 1995 zijn wij inwoners in de gemeente Haarlemmermeer. In de afgelopen 25 jaar is er veel veranderd binnen de gemeente. Soms als antwoord op, maar vaker vooruitlopend op de ontwikkelingen. De gemeente groeit. Mensen willen er wonen, werken en studeren, maar ook meer bedrijven vestigen zich hier in het hart van de economie.
Daarnaast vertegenwoordigen toeristen en evenementen in de regio elk jaar een aanzienlijk aantal bezoekers.
We denken na over het juiste evenwicht tussen leefbaarheid en welvaart.
- Over duurzaamheid en sociale verantwoordelijkheid.
- Over lusten verhogen en lasten verminderen.
- Over een integrale aanpak die zowel bewoners centraal zet, als bezoekers gastvrij ontvangt.
- Onze focus ligt op beter en niet op meer.
- Op kwaliteit en niet op kwantiteit.
We dragen actief bij aan een leefbare, aantrekkelijke en welvarende gemeente waar de economische ontwikkeling niet ten koste gaat van de leefbaarheid.
We werken intensief aan het verbeteren van de reputatie van Haarlemmermeer.
Wij willen met dit Community Platform bewoners verbinden zowel jong als oud. Ideeën transparant maken en een ieder hierbij betrekken. Elke leeftijdsgroep moet hiervoor in aanmerking kunnen komen. Door het initiëren van dit platform hopen wij bewoners een kans te geven door zijn/haar ideeën te ventileren en eventueel te implementeren, zodat wij allen als bewoners van Haarlemmermeer hiervan gebruik kunnen maken. Door het zichtbaar maken van de mogelijkheden en behoeften kunnen we de band als bewoners versterken en hierdoor een veilige, sfeervolle leefomgeving creëren.
Wij zijn dit community platform gestart vanuit onze eigen ideologie. Het geloof om een community te starten waar mensen elkaar kunnen helpen en bereiken. Waar wensen werkelijkheid kunnen worden als we gezamenlijk onze krachten bundelen. Laten we starten met de bewoner die bepaalt wat er noodzakelijk is en de gemeente kan informeren over de benodigdheden.
#Citizens&Living #DigitalCity
Research accelerates the sustainability of heating
AUAS contributes to accelerated roll-out of sustainable low-temperature heating networks in HeatNet project
The international research project HeatNet is all about making heat more sustainable. Less use of natural gas and more use of sustainable heat sources such as the residual heat from data centres. The project aimed to accelerate the roll-out of heating networks in urban areas. And that has been a success! Not only have new heating networks been developed in six European cities, the participating partners have gained knowledge about operating smartly in complex urban transitions. The professors and researcher involved from the Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences (AUAS) talk about the approach and the insights gained.
The role of the AUAS in the research project involves leading evaluations. During six evaluation meetings over three years, the partners reflected on their process of learning from each other and helping each other move forward. Professor of Energy and Innovation, Renée Heller: “As an evaluator, we not only wanted to determine how it went afterwards. But in accordance with the aim of this Interreg project – transnational learning – we embarked on a continuous learning process with each other.”
ON THE SHOULDERS OF GIANTS
This helps the pilot partners gain insights and build on each other’s discoveries. Frank Suurenbroek, professor of Spatial Urban Transformation: “In such complex transition projects, there is so much to consider. This process-based evaluation approach helps you gain insight into the issues you are facing. Such transitions are not a linear process and the insights cannot always be translated directly to other projects. But this approach does make complex processes navigable. It offers pathways for innovation that you can consider.”
The researchers translated this knowledge into various publications and guides, which have been made available to parties dealing with the roll-out of a heating network. Suurenbroek: “The Stakeholder Guide is also interesting for all parties that work on complex urban transitions.” Lecturer-researcher Egbert-Jan van Dijck was responsible for the development of the Stakeholder Guide.
“The heat transition requires an innovation at system level. Therefore, we carried out an extensive stakeholder analysis at meso-level,” explains Van Dijck. “It not only provides an impression of the individuals and organisations involved at the energy sector level, but also of their role in the chain, their interests and concerns. This step towards a situational analysis has enabled us to outline a holistic picture and carry out an in-depth analysis of barriers to the development of the new generation of heating and cooling networks in terms of finance, legislation and regulations and organisation.”
INVOLVING STUDENTS
“We are further expanding this analysis for education.” Van Dijck: Besides the human elements, we also analyse non-human elements, such as buildings, technologies, infrastructure, energy sources and subsurface. These are just as important in determining the situation as the human elements. For example, the pipes for a heating network cannot be laid through a river or a railway track. You need to be aware of these barriers.” Instead of just the people or the stakeholders, students see a much more complete situation at a glance. This goes for fourth-year students as well as second-year students.
Heller: “Several students have used this project for their graduation thesis. Students have even travelled to Ireland on their own initiative to learn more about the energy and heating situation there and to interview partners.”
ROLL-OUT OF HEATING NETWORKS
“There is a lot involved in creating a heating network,” says Heller. “Considering the complexity, it is unusual and significant that all six partners have succeeded in doing so in such a short space of time. It would be a shame not to use the valuable sources of heat available in a country. Data centres, for example, have a huge amount of heat left over. The roll-out of one heating network to multiple heating networks helps us to use available heat sources to increase sustainability and reduce our CO2 emissions.”
INTERDISCIPLINARY AND CROSS-THEMATIC
The HeatNet project is a good example of interdisciplinary collaboration between two research groups with different specialist knowledge. Frank Suurenbroek: “While the implementation of a heating network may appear to be a technical project, it is also an urban transformation process.” Heller adds: “Urban transition involves projects in which taking the energy leap seems the obvious choice, but where there is still little attention for the heat transition, while a great opportunity exists in that respect. Through our collaboration, we have seized that opportunity.”
Personal User Interface for Office Climate

Hello all,
I am proudly sharing and same time invite you for visiting my exhibition at the Dutch Design Week #ddw20. My Final Master Project is selected as a part of Drivers of Change under the categories of sustainable future hosted by the Technical University of Eindhoven.
My project is a cross-faculty project at the Department of Industrial Design and Building Services Research Group at TU/e. I designed and programmed a smart user interface for a personal cooling system, which not only collects data in real-time for the development of machine learning models, but also creates an easy and intuitive way for users to achieve a comfortable thermal climate. This graduation project scored an 8 as a result.
Thanks to the industry and academia for their recognition and support of my graduation project, with special thanks and respect to my graduation mentor Professor Mr Loe Feijs.
The #ddw2020 shall be online and free of charge!
SEE YOU ALL THERE.
https://ddwtue.nl/projects/the-cooling-stat/
Urban and Smart City Professionals Invited to Join Online Smart City Course: Transferring the Amsterdam Approach to the Brazilian Context
Amsterdam Smart City (ASC) and Amsterdam University of Applied Science (AUSA) have teamed up with Insper to develop a course focused on transferring the Amsterdam smart city approach to the Brazilian context. The course is designed to introduce Brazilian urban and smart city professionals to collaborative innovation and governance topics. The course will enable participants to understand the possibilities of technical innovations for the benefit of a liveable city as well as the socio-economic preconditions that make these projects possible. Participants will better understand technological trends, discover opportunities for metropolitan improvements and learn how to organize and scale up smart city projects.
Course Overview:
· Dates & time: Nov 17, Nov 19, Nov 24, Nov 26, Dec 1, Dec 3 from 9:00-11:00 BRT / 13:00-15:00 CET
· Assignment: participants will work on an assignment that will apply the concepts from the course to a Brazilian case study
· Discount: organizations which enrol two employee will benefit from a 50% discount for the second registration
For more information and to apply visit: https://www.insper.edu.br/cursos-online/smart-city-transferring-the-amsterdam-approach-to-the-brazillian-context/
Helsinki publishes guide to agile urban pilots
How to get the most out of urban experimentation? The guidebook for urban developers sums up learnings and experiences from agile piloting in Helsinki.
The Pocket Book for Agile Piloting shares the experiences from Smart Kalasatama and Jätkäsaari Mobility Lab in Helsinki and condenses the key learnings in a pragmatic and easily digestible way. Free download via Forum Virium
WeMakeThe.City RESET: Digital Rights

After two successful editions, the WeMakeThe.City festival is heading for 2025 as a biennale: the 750th anniversary of Amsterdam. This year the uncertain future of our city and metropolitan region was discussed in a 12-hour livecast marathon on the 21st of September. The WeMakeThe.City theme ‘Reset’ brings together genius thinking, imagination and creativity to formulate alternative perspectives for action. How are we going to do things differently in the coming years? How do we work together to make our metropolis fairer, more inclusive, more sustainable, more climate-resilient, safer, more successful and happier? After all, together we make the city of, for and by everyone!
During last spring's lockdown, it became even clearer how much we depend on the digital world. We meet, chat and date in front of the screen. A solution to combat the spread of Covid-19 is also being sought in the digital domain. These developments have raised the privacy issue again: how can people's data rights be protected? Such as anonymity, transparency and control over data. Time for a good conversation about values and the importance of digital civil rights.
The session kicks off with Marleen Stikker, director of Waag and Ger Baron, Chief Technology Officer of the City of Amsterdam. Marleen explains what our digital human rights are. ‘These are the same rights just as in the analogue world. Where there is relatively much attention for analogue human rights, our civil rights in the digital domain have run wild, too little attention has been paid to this. Let's reclaim those rights! It is for example about the right to be forgotten, the right to be anonymous, but most important to me is digital sovereignty. Everyone should have the possibility to have insights in their own actions online.’
Ger agrees with Marleen. According to him, governments, and cities as well, collects too many data about residents and the public space without even knowing what they want to do with these data.’ The reason to collect them should be to learn something specific that you can improve or help people. Helping people with the collection of data also brings in new dilemmas. The city used to have a collaboration with energy providers for example. Once someone didn’t pay for the energy service, they sent out a message to the city administration. The City could then prevent someone get evicted from his/her home.
This example is not enough reason for Marleen to collect the data: ‘To me, this sounds as if we didn’t invest in our society. We could have helped these people as well if they had adequate supervision or guidance. In last years, we invested heavily in the digital domain and we made budget cuts on home care, debt counselling and community police officers. Digital solutions are not always the best solutions! Especially not when all kinds of companies have data without people knowing about this.’ Ger: ‘To a certain point I agree with this point. Digital rights also include rights to know about the data that is collected, why this is and what you can do about this. This is currenty not transparant at all, even though the City of Amsterdam is becoming more and more about about his.
Marleen: ‘I see the City of Amsterdam going in the right direction, by starting for example the Coalition for Digital Rights. However, the steps in this direction go really slow, especially in politics. This way, it remains unclear what rules companies dealing with personal data should obey. That’s why Marleen also calls on politicians in The Hague: guarantee digital human rights by imposing conditions on the market.’
Next up is Miram Rasch, researcher and teacher at the Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences and writer of the book ‘Friction. Ethics in times of dataism. Her book opens with a story about escaping the eyes of data collectors and algorithms. She states this is only possible at home. And even there, it becomes harder. ‘We have smart meters, smartphones, smart tvs. It is not clear why these devices need to collect data, with whom they share them. We don’t know now, but especially we don’t know in the future. Everybody has something to hide, because we don’t know yet what we should hide. Of course you have to inform yourself about the conditions you’re accepting. However, this is not easy at all. Try to read the Terms and Conditions of the services you use, the texts are too long and complicated. Unfortunately it can take a long before something changes. The few individuals who are conscious about the digital world, won’t change it. We need rules and regulations! But we know from the past, that maybe something heavy has to happen before people open their eyes.’
Jim Boevink, advisor Taskforce Digital Safety at the City of Amsterdam, starts an intermezzo about the right to be anonymous. Marleen Stikker: ‘People who want to abuse others, are free to hide themselves. This is because platforms are not responsible for the content their users post. They earn money with these users, they are their business models. But they they are not responsible for things happening on their platform. This is the first thing that has to change. The legal system is not in order. Make them responsible for the content on their platforms.’ M****arleen: ‘And good to emphasize: someone who is critical about the digital domain and the internet, is not necessarily against the digital world. We only have to make the internet safe and reliable!’
Want to watch the livecast (in Dutch) yourself? Check <https://dezwijger.nl/programma/reset-digital-rights>.
Stay up to date
Get notified about new updates, opportunities or events that match your interests.

