Stay in the know on all smart updates of your favorite topics.
Sustainable energy is the future. The city of Amsterdam has the ambition to provide every citizen with a solar panel in the next years. How do you contribute? Share your innovative initiatives on energy here.
Amsterdam and Haarlem launch groundbreaking sustainable artificial turf pitch innovations

The pioneering innovations were presented of the Scale Up Future-proof artificial turf pitches project, a collaboration between Amsterdam and Haarlem focused on sustainable artificial turf pitches. Over the next few years, more than 250 sports pitches in both cities will be transformed into circular, energy-generating and climate-adaptive sports venues. These artificial turf pitches can not only generate and store energy, but also involve smart water management. An approach that is globally relevant for urban sports infrastructure.
Three consortia collaborate on the sport pitch of the future
The three selected consortia Antea Sport, EnergieVeld and GOO4iT together comprise more than 15 market players. They join forces within this innovation partnership, where there is room for long-term collaboration, co-creation and scalable innovation. The pioneering solutions will make it possible to cool down sport pitches on warm days, help dispose of and collect rainwater, make the pitches more pleasant for the users and possibly even generate energy for the surrounding area. Find out how these innovations are shaping the sport pitch of the future here.
Two municipalities: joint procurement
The Scale Up Future-proof artificial turf pitches project is a unique collaboration between two municipalities and market players. The municipalities jointly procure pooling their purchasing power and use an innovation partnership to challenge the market to test and scale up innovative and sustainable solutions. In doing so, the solutions are also scalable and transferable to other cities in the Netherlands and Europe.
From prototype to pilot fields
The first prototype fields will be constructed in Amsterdam and Haarlem in 2026, in different capacities and combining multiple innovations, where they will be extensively tested and monitored for a year. Successful concepts are then scaled up to full-scale pilot pitches and tested and monitored for another year. This will form the basis for the new standard of sustainable sports pitches, with potential for adoption in other cities around the world. At the same time, existing pitches are already being improved with the most sustainable solutions available, making an immediate impact from the start. The project thus shows how cooperation between municipalities and market players can lead to innovative, climate-proof sports infrastructure with international relevance.
Join us
This project provides cities worldwide a blueprint for sustainable, smart, and future-proof artificial turf pitches. Interested municipalities and industry partners can get in touch and subscribe to our news updates by sending an e-mail to: sportveldvandetoekomst@amsterdam.nl.
Demoday #28: How to keep our mechanics on the move?

On the 5th of July, during Demoday #28, we zoomed in on one of the pressing challenges facing the energy transition: grid congestion, and more specifically, how to keep the people who maintain the grid moving efficiently.
Grid congestion is a serious and growing concern for grid operator Alliander. It is therefore essential to speed up the grid reinforcement as much as possible. Alliander’s Operation 2.0 team is exploring innovative ways to work smarter, faster, and more flexibly to keep pace with these developments.
Their efforts focus on three tracks:
• Alleviating staff shortages by training office employees to occasionally support fieldwork.
• Exploring technologies like advanced ground radar to get better insights into underground assets.
• Improving the logistics of supplying mechanics to ensure they have the right tools, in the right place, at the right time.
This last track was the main focus of our work session.
Inefficient supply of mechanics
Logistics experiences show that mechanics collect materials inefficiently when supplying their vans and jobs, resulting in stock corrections, less control over stock, unnecessary work for logistics staff, and valuable mechanic hours being lost, which leads to less execution work. A few key problems stood out:
• Supplies are scanned inconsistently, so the system doesn’t reflect what is actually in stock.
• Every van is different, with a custom layout that suits the preferences of its mechanic.
• The work itself is unpredictable, which makes standardised restocking difficult.
• With a transition to smaller electric vans, space is becoming even more limited.
A simple optimisation of the process is not enough, especially without considering the human element. For many mechanics, a visit to the supply centre is more than just logistics. It is a moment of connection, a short break from the road, or simply a chance for a good coffee.
Ideas from the network
In groups of four, we brainstormed creative ideas to improve the supply of Alliander vans while keeping the needs and routines of mechanics in mind.
Some highlights:
• Peer-to-peer van inspiration: Let mechanics share the layout of their vans with colleagues. They can exchange best practices and take pride in an efficient setup. Adding a bit of gamification might boost motivation even more.
• A mobile supply service: A supply van could drive around to restock mechanic vans, reducing the need to visit the supply centre. However, this might remove the social element of taking a break with colleagues.
• Smarter routing: Track the location of mechanics only in relation to nearby grid faults. This way, the closest available mechanic can respond without feeling like their movements are constantly being monitored.
• Package-based resupply: Inspired by delivery service Picnic, mechanics could exchange complete “supply packages” instead of picking out materials individually. Collaborating with wholesale suppliers could reveal more useful insights.
• Automatic stock tracking: Tag all materials with RFID chips and use sensors installed in the door of the van to register what is removed from the van. This eliminates the need for manual scanning and reduces the chance of mistakes.
Do you have a bright idea to improve how mechanics work? Let us know in the comments or send a message to Noor at noor@amsterdaminchange.com.
A big thank you to Thomas Hoekstra and Iris van der Zanden from Alliander for bringing this challenge to the network, and to Chantal Inia from Royal HaskoningDHV for moderating the session.
Underground Challenges and Shared Solutions: Lessons from Amsterdam for District Heating in Haarlemmermeer

How do you install district heating in villages with narrow streets and limited underground space? This was the central question during a recent deepdive session hosted in the municipality of Haarlemmermeer. The session brought together experts from the City of Amsterdam, local officials and experts from Haarlemmermeer, and Arcadis to explore practical solutions to the physical challenges of implementing district heating in dense and complex infrastructure environments.
From complexity to coordination
Amsterdam has years of experience addressing similar challenges in dense urban areas where underground infrastructure is already under pressure. Experts from the City of Amsterdam were invited to share their approach, which combines long-term planning, integrated design processes, and flexibility in applying standards.
Some key principles they shared:
- Planning 15 years ahead: Amsterdam actively involves all utility providers to map out future plans and co-create underground infrastructure layouts.
- Using standard ways of working in the underground (WIOR) and a standardised scheme for subsurface infrastructure planning: These frameworks help assess available underground space and guide decisions when concessions are necessary.
- Embracing alternative methods: Stacking pipelines instead of placing them side-by-side, drilling under roads, or clustering transport cables in walls or consolidated zones are all viable options.
Sometimes, this requires deviating from standard spacing requirements. Such exceptions are only made with strong justification and agreement at the decision-making level.
A fresh look at Haarlemmermeer’s challenges
Participants from Haarlemmermeer acknowledged that they face several pressing issues. With limited space in the underground and a lack of an integrated planning framework, it is difficult to make informed, long-term decisions. Three villages in the municipality are particularly challenging due to their narrow streets and aging infrastructure.
Key challenges included:
- Underestimating the space needed for district heating infrastructure (including expansion loops, communication lines, and insulation).
- Rigid adherence to guidelines, which may not always be feasible locally.
- A missing coordinating role to oversee all the different parties operating in the underground to facilitate collaboration.
Shared lessons, shared responsibility
The session made clear that while every context is different, the challenges of underground infrastructure for district heating are shared across municipalities. The city of Amsterdam is a bit further ahead than Haarlemmermeer, and their expertise was already tremendously helpful. The Amsterdam case shows that smart, flexible planning—backed by clear coordination of all parties active in the underground —can lead to effective, long-term solutions.
Now the task for Haarlemmermeer is to translate these insights into concrete next steps. As one participant concluded, “We need to move from awareness to action.”
Would you like to learn more about this topic? Please contact Noor at noor@amsterdaminchange.com.
Demoday 27# District heating and resident participation in the municipality of Haarlemmermeer

The municipality of Haarlemmermeer is actively working on the realisation of the energy transition in the municipality by, among other things, focusing on sustainable heat supplies. As part of this, a heat initiative has been started in the village of Rijsenhout (east of Haarlemmermeer). This initiative has not been taken up by the market in the past. This has led the municipality to want to take a more active role in the development of District heating in which resident participation is a crucial factor.
During the Knowledge- and Demodag on 13th of March (2025), Kelly Winters and Sophie Keijzer (Hieroo) led a session with the participants that looked at similar successful processes in the past of realising a heat network. The central questions were: What was the success and why was it a success?
Session structure and focus
During the session, the participants split into two groups. Similar processes were then discussed in the two groups in which the success factors of the realisation of energy transition projects were examined. An important example that was discussed in the session was the Schoonschip project in Amsterdam North. This project is a sustainable initiative in which residents have researched how they can live on the water in a circular and sustainable way. This resulted in a community of 46 houseboats that share energy with each other via a Smart Grid that’s cheaper and more efficient.
Outcomes and insights
During the session, various strategies were discussed to strengthen resident participation and make heat network initiatives successful. The most important points from the discussions are:
1. Composition of the initiator group: A diverse and enthusiastic group is crucial. In the Schoonschip project, the core of the success was a group of pioneers who complemented each other in creativity and expertise. Such a group can also be formed in Rijsenhout if they are properly guided and supported.
2. The role of the municipality: The municipality must be aware of the distrust that residents often have towards government institutions. Using an external intermediary or an independent entity can help to reduce this mistrust.
3. Reward and inspire: One way to involve residents in a low-interest topic such as energy is to reward them. Examples are setting up competitions, the use of ambassadors or energy coaches and the organisation of events. Linking opportunities, for example by combining energy transition with social goals such as combating energy poverty, can also play an important role.
4. Using the right moment: An important lesson from the Schoonschip project is to use external circumstances to arouse interest. A crisis, such as rising energy costs or limited energy production, can turn a low interest topic into a high interest topic for people.
5. Governance and structure: A solid Governance structure is essential. The municipality can play a role as a project manager by setting clear deadlines and formulating requirements. This helps both initiators and residents to keep focus and take steps towards concrete results.
Follow up
Do you have a tip to help the municipality of Haarlemmermeer with their district heating plans? Or do you have a question about this project? Contact Ouassim at Ouassim@amsterdaminchange.com or Noor at Noor@amsterdaminchange.com. Later this week on 27th of march, we'll dive into the technical problems that district heating poses, when there just isn't enough space in the underground to build it. If you would like to know more about this, let us know.
Artikel 'Eigen opwek voor de buurt - Slim omgaan met het bestaande net'

Hugo Niesing, directeur van Resourcefully, werd geïnterviewd in het decembernummer 2024 van het gemeentelijk magazine van Amsterdam over innovatieve oplossingen voor de integratie van mobiliteit, energie en netcongestie. Het artikel laat zien hoe projecten zoals de pilot in Sporenburg in het Oostelijk Havengebied bijdragen aan een duurzaam en toekomstbestendig lokaal energiesysteem. Hier werken we met 500 huishoudens om piekuren te verminderen en lokaal opgewekte energie optimaal te benutten.
Lees hier meer over dit inspirerende initiatief via de link.
Smart City Expo World Congress | Barcelona 2024 | Personal highlights

In early November, I travelled to Barcelona for the third time to attend the Smart City Expo World Congress. Together with the Amsterdam InChange Team, some of our network partners, and the Dutch delegation, we put together a strong content-focused programme, gained inspiration, and strengthened both international and national connections. In this article, I’ll briefly share some of my personal highlights from this trip.
International Delegations: Building International Connections and Knowledge Exchange at the Expo
During the congress, I organised several guided visits from the Dutch Pavilion in collaboration with the DMI-Ecosystem. The aim of these visits was to connect the Dutch delegation with international colleagues and facilitate knowledge exchange. At the busy expo, full of companies, cities, regions, and conference stages, it’s really appreciated to join planned meetings on specific themes. It’s also a great chance to meet many international representatives in just a few days, since everyone is in the same place at the same time.
We visited and connected with the pavilions of EIT Urban Mobility, Forum Virium (Helsinki), the European Commission, and Catalonian innovations. Topics such as The Future of Mobility, Digital Twins, and Net Zero Cities were central to the discussions. It was a good opportunity to strengthen existing networks and establish new connections. For myself, for Amsterdam InChange, and for the participants joining the meetings.
A few aspects of the visits particularly stood out to me. At Forum Virium Helsinki we met with Timo Sillander and Jaana Halonen. I was impressed by their work with Digital Twins. They focus not only on the technology itself and the efficiency of urban systems, but also on the social dimensions a digital simulation can play into. Think of; unequal distributions of risks related to climate change and extreme weather conditions.
I also appreciated the efforts of the European Commission. They are working to make it easier to navigate research topics, funding opportunities, and findings related to themes like energy-neutral cities. With their new marketplace, there is more focus on small and medium-sized cities across Europe, helping them to benefit from innovations that are often developed in larger urban areas.
Collaborating Internationally on a Regional Challenge: Zero-Emission Zones and City Logistics
On Tuesday, my colleague Chris and I organised a session on zero-emission city logistics. We brought together representatives from Oslo, Helsinki, Stockholm, Munich, and EIT Urban Mobility, as well as the Dutch municipalities of Haarlemmermeer and Amsterdam.
The session built on connections we made during other events on Sunday and Monday, bringing together an international group of stakeholders interested in this topic. During the discussion, we compared how different cities are approaching zero-emission zones and identified shared challenges, particularly in policymaking and working with logistics companies and local entrepreneurs.
It was interesting to see how this topic lends itself so well to international comparison and exchange. For instance, while Amsterdam will be one of the first to implement a strict ZE zone in the city centre, other cities are already ahead in areas like charging infrastructure and the transition to cargo bikes. The group was eager to keep the discussion going, and we’re already planning a follow-up online meeting to continue learning from one another.
Future-Proof Sports Fields, International Dinners, and Bicycles
Finally, a few other topics worth mentioning: I joined an international session hosted by the City of Amsterdam about future-proof sports fields. It was inspiring to reflect on the value and potential of sports fields for neighbourhoods, as well as their use as testing grounds for sustainable innovations. For me, the session reinforced how important these spaces are for local communities in cities, and sparked a new personal interest in this subject.
I also really enjoyed both our own international changemakers’ dinner and another international dinner hosted by Drees & Sommer (thanks for the invitation!). Bringing together an international network — whether as individuals or in small groups — and mixing them at the table sparked meaningful conversations that felt different from those during the formal congress sessions or workshops.
Lastly, it’s great to see more Superblocks and bicycles in the city every year! Go Barcelona!
𝗛𝗼𝘄 𝗰𝗮𝗻 𝗖𝗦𝗥𝗗 𝗯𝗲 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗹𝗮𝘂𝗻𝗰𝗵𝗽𝗮𝗱 for 𝘆𝗼𝘂𝗿 𝘀𝘂𝘀𝘁𝗮𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗯𝗶𝗹𝗶𝘁𝘆 𝗷𝗼𝘂𝗿𝗻𝗲𝘆?

A systems approach is key.
Climate transition plans that lack a systemic perspective can unintentionally shift risks, disrupt supply chains, harm human rights, or even contribute to biodiversity loss. For example, switching to a low-carbon product that requires three times more land may address your carbon goals, but jeopardize your biodiversity targets.
Without considering these interdependencies, your climate strategy may become inefficient and require reworking as new issues arise.
𝗧𝗵𝗲 𝘀𝘆𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗺𝗶𝗰 𝘀𝗰𝗲𝗻𝗮𝗿𝗶𝗼👇
By addressing root causes and considering the ripple effects of climate decision-making in other areas, a systems lens ensures your plan goes beyond regulatory box-ticking.
Together, we can co-create effective action plans with your stakeholders and develop customized decision-making frameworks, accounting for material impacts on climate, nature, and people across your operations and value chain.
How? Learn how our Systemic Transition Suite can unlock your business’s full potential ⬇️
#BeyondCompliance #climatetransition #sustainabilityreporting #CSRD #ESG #circulareconomy
In Residence Open Events program 2025

Entrepreneurs test innovations during SAIL and Marathon
Public events like SAIL and the Marathon draw millions of visitors to Amsterdam. These events often take place in central locations where large crowds gather. As a result, various logistical arrangements need to be made, such as providing food and drinks, public toilets, and temporary modifications to streets. These situations pose sustainability and accessibility challenges for the city. However, they also make these events ideal testing grounds for innovations.
Testing with the city and event organizers
The In Residence program offers entrepreneurs the opportunity to test their innovations during public events. They work closely with event organizers, the City of Amsterdam, and an experienced mentor. Additionally, funding is available to support the pilot. If the innovation proves to benefit the city, the municipality may purchase it after the program.
Applications are open from October 1 to November 17. Selected entrepreneurs will prepare their pilot in early 2025, and most pilots will take place during the summer events, especially during SAIL 2025.
Apply via the website: https://innovatiepartners.nl/project/in-residence-open-evenementen-2025
Amsterdam 750th anniversary year
This is the second round of the In Residence Events program. During the 2024 event season, nine entrepreneurs tested their innovations, including at Pride Week, the Marathon, and the Dam tot Dam Run. If successful, innovations from both rounds of the program may be implemented during the events of Amsterdam’s 750th anniversary celebrations.
Interested or any questions? You can get in touch with Mark Stoevelaar (mark.stoevelaar@amsterdam.nl)
Photo: Edwin van Eis
Kennisland-podcast #1: geen vernieuwing zonder ongemak

Geen vernieuwing zonder ongemak. Maar durven vernieuwers het ongemak zelf in de bek te kijken? En wat kunnen we daarvan leren? In deze podcastserie ter ere van 25 jaar Kennisland gaan we in gesprek met sociale vernieuwers over scheve machtsverhoudingen, schijnparticipatie, gebrek aan diversiteit, preken voor eigen parochie, haperende verdienmodellen, de paradox van vernieuwing en andere olifanten in de kamer waar wíj het juist wel graag over willen hebben. In deze eerste aflevering gaat Marieke van Doorninck in gesprek met Tofik Dibi.
Eerste gast: Tofik Dibi
Tofik is een Marokkaans-Nederlandse oud-politicus, schrijver, activist en sinds 2018 bestuursadviseur van het stadsdeel Nieuw-West in Amsterdam. Hij richt zich onder andere op het vergroten van kansen van jongeren in grote steden. Tofik staat bekend om zijn gedrevenheid en is niet bang om de knuppel in het hoenderhok te gooien. Regelmatig zorgt hij met scherpe tweets voor reuring op X. Hij is bovendien lid van onze Raad van Advies. Marieke van Doorninck, directeur van Kennisland, gaat met hem in gesprek over ongemak en vernieuwing.
> “De realiteit vraagt soms om een bittere toon.”
Ongemak inzetten en toch verbinden
Ze praten over hoe je ongemak kunt inzetten om de status quo te bevragen en de gevestigde orde uit te dagen. Belangrijk daarbij is om tegelijkertijd comfort te bieden. Ongemak werkt het beste in een veilige setting. Hoe kun je de confrontatie aangaan zonder de ander te verliezen?
Luister de podcast (28 minuten) via onderstaande link.
Ondernemers met duurzame oplossingen gezocht voor aanbesteding

De aanbesteding Scale Up Toekomstbestendige kunstgrasvelden is gepubliceerd. Met het project dagen de gemeenten Amsterdam en Haarlem ondernemers uit om duurzame oplossingen op kunstgras sportvelden toe te passen. De inschrijving hiervoor sluit op 17 juni 2024 om 14.00 uur.
De genoemde gemeenten zijn op zoek naar partijen met innovaties op het gebied van: duurzame energie, klimaatadaptie, circulariteit of slim en schoon bouwen. De duurzame oplossingen willen ze vervolgens toepassen bij de vervanging en nieuwe aanleg van kunstgras sportvelden. Naar verwachting staan er de komende tien jaar meer dan 200 velden op het programma. Hiermee wordt verwacht een grote bijdrage te leveren aan de doelstelling van de gemeenten Amsterdam en Haarlem om in 2050 een klimaatneutrale stad te zijn.
Doe mee!
Doe mee met dit project en schrijf je in voor de aanbesteding op Mercell.
Kijk voor meer informatie op de website van het project of stel je vraag door een e-mail te sturen naar sportveldvandetoekomst@amsterdam.nl.
Disclaimer: Het project wordt medegefinancierd door het LIFE Programme van de Europese Unie. Noch de Europese Unie, noch de subsidieverlenende autoriteit kan voor de inhoud van het project verantwoordelijk worden gehouden. Aan dit artikel kunnen geen rechten worden ontleend, de aanbestedingsdocumenten zijn leidend.
Reducing Carbon Footprints: Erasmus MC Leads the Way to Climate-Neutral Hospitals
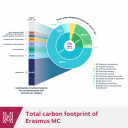
The healthcare sector is responsible for approximately 7% of all greenhouse gas emissions in the Netherlands. How can a hospital become climate-neutral?
The first step on the sustainability journey is to measure the organization’s carbon footprint. A precise carbon footprint is crucial for setting impactful and realistic targets, and for aligning with regulations and Green Deal Healthcare 3.0.
In support of Erasmus Medical Center's sustainability goals to reduce its CO2e emissions by 55% by 2030 and to achieve climate neutrality by 2050, Metabolic mapped its carbon footprint, focusing on scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions.
💡A sneak peek: 60% of Erasmus’ CO2e footprint results from indirect emissions from purchased goods and services, such as medicines.
Erasmus MC is one of the first hospitals to use this method to map emissions across all its operations. This research provides the hospital—and the entire sector—with insights into emission hotspots and highlights potential areas for impactful sustainability interventions.
Explore Metabolic's work with Erasmus in the link below
Interested in learning more about carbon footprint assessment? This is for you: https://bit.ly/3UUdMHf
#sustainability #carbonfootprintassessment #environmentalimpact #sustainablehealthcare
Samenwerken aan transitievraagstukken; wat is er nodig? - Opbrengsten van het Amsterdam Smart City partnerdiner 2024

Als Amsterdam Smart City netwerk bijten we ons vast in complexe stedelijke transitievraagstukken. Ze zijn complex omdat doorbraken nodig zijn; van kleine doorbraakjes, tot grotere systeem doorbraken. Denk aan bewegingen rond; organisatie-overstijgend werken, domein-overstijgend werken, en van competitief naar coöperatief. Als netwerk zetten we samenwerkingsprojecten op waarin we gaandeweg ondervinden met wat voor barrières we te maken hebben en wat voor doorbraken er nodig zijn.
Tijdens ons jaarlijkse Partnerdiner op 2 april, hadden we het samen met eindverantwoordelijken van onze partnerorganisaties over de strategische dilemma’s die spelen bij transitievraagstukken. Als gespreksstarters gebruikten we onze lopende onderwerpen van 2024: De coöperatieve metropool, de ondergrond, de circulaire metropool en drijvende wijken. De gesprekken aan tafel gingen echter over wat er aan de basis staat van het werken aan transitievraagstukken. Zo ging het bijvoorbeeld over; het samenwerken aan visies en scenario’s, leiderschap, burgerlijke ongehoorzaamheid en de kracht van coöperaties. In dit artikel bespreek ik beknopt een aantal onderwerpen die onder de aandacht werden gebracht door onze gasten.
Belangen en visie organiseren
Bij een vraagstuk of onderwerp als de ondergrond, gaan we het al snel hebben over de data en de oplossingen. Dat is ‘te makkelijk’. Technisch gaat het allemaal wel kunnen, maar als we daar te snel beginnen met de oplossing lopen we over een aantal jaar weer vast. Het is belangrijk om eerst een stapje terug te doen en een gedeeld belang en gedeelde visie te organiseren.
Hoe je belanghebbenden verzamelt, en de methode om tot een gedeelde visie te komen, dat is wat meer aandacht verdient. Neem het ondergrond vraagstuk als voorbeeld. Op welke schaal organiseer je daarvoor de belanghebbenden? Aan de oppervlakte hebben we Gemeentelijke en Provinciale grenzen, maar in de ondergrond liggen netwerken van kabels en leidingen die op andere schaal zijn geïnstalleerd en hebben we te maken met bodemtypologieën met verschillende behoeften.
Samen voorstellen en voorspellen
Dat waar je naartoe wilt werken, dat moet van iedereen voelen. Het is belangrijk om een setting te creëren van gedeeld eigenaarschap, waarin iedereen zich ook gehoord voelt, en dat je voelt dat de mensen met wie je gaat samenwerken ook voor jouw belangen op zullen komen. Om samen tot een visie te komen, is het belangrijk om te werken aan scenario’s en die samen te doorleven. Je moet het dan niet alleen hebben over waar je heen wilt, maar ook uitwerken wat er gebeurt als je niets doet of als het helemaal verkeerd uitpakt.
De scenario’s zouden op waarden moeten rusten. Het beeld wat bij de scenario’s hoort is veranderlijk, maar de waarden niet. Samen ben je continu in samenspraak over wat de waarden betekenen voor het verhaal dat je creëert.
Leiderschap en een interdisciplinaire werkwijze
Transitievraagstukken en bovenstaande aanpakken verdienen een bepaald soort leiderschap. Zo zou een leidinggevende bijvoorbeeld een veranderlijke en faciliterende houding moeten tonen, en moet hij/zij vanuit waarden werken die inspireren en verbinden. Het zou meer moeten gaan over het faciliteren van doeners, het stimuleren van doelgericht samenwerken in plaats van taakgericht en ruimte bieden voor menszijn en persoonlijke expertises. Met dit laatste wordt verwezen naar een stukje burgerlijke ongehoorzaamheid. Om dingen die we belangrijk vinden in gang te zetten moeten we soms even los kunnen denken van onze organisatiestructuren en functies. We zouden wel wat vaker mogen appelleren aan ons menszijn.
Meer faciliteren en minder hiërarchie helpt ons om beleid en praktijk dichter bij elkaar te brengen, en om van competitief naar meer coöperatief te bewegen. Als je naar de uitvoering gaat mag de kracht verplaatsen naar de uitvoerders. De machtsverschuivingen tussen leidinggevenden en de doeners, met specifieke rollen en expertises, mag in een constante wisselwerking rond gaan.
Ook interdisciplinair samenwerken aan transitievraagstukken zal nog meer moeten worden gestimuleerd, en misschien wel de norm moeten worden. Bij overheden en bestuurders bijvoorbeeld, zijn transitie thema’s verdeeld over domeinen als energie, mobiliteit, etc. maar de vraagstukken zelf zijn domein overstijgend. Als voorwaarde zou je kunnen stellen dat je altijd twee transities aan elkaar moet koppelen. We zouden meer inspirerende voorbeelden moeten laten zien waarbij verschillende domeinen en transities aan elkaar worden gekoppeld, door bijvoorbeeld overheden.
Publiek-privaat-civiel
Publieke, private en civiele partijen zouden nog meer naast elkaar aan tafel mogen, in plaats van tegenover elkaar. Bedrijven kunnen verzuild zijn, of zich zo voelen, en zouden nog meer om zich heen kunnen kijken en samenwerken. Niet alleen met overheden, maar ook met civiele organisaties. Er zijn vaak meer gezamenlijke belangen dan we denken.
In een beweging naar niet-competitief samenwerken kunnen coöperaties een belangrijke factor zijn. Wanneer je meer autoriteit bij coöperaties neerlegt, weet je zeker dat er in de basis voor een wijk, een stad, haar inwoners, een publiek belang wordt gewerkt. Er liggen dan ook veel kansen bij een faciliterende houding vanuit de overheid naar coöperaties toe, en in de samenwerking tussen bedrijven en coöperaties.
Er zijn tijdens dit diner veel onderwerpen aan bod gekomen waar we met het netwerk mee aan de slag kunnen in onze programmering. De input wordt gebruikt voor onze lopende vraagstukken en we gaan de komende tijd in gesprek met partners om te kijken of we van start kunnen met verdiepende sessies of het ontwikkelen van methoden op (enkele van) deze onderwerpen.
<em>Wil je doorpraten over deze onderwerpen, met ons - of een van onze partners? Mailen kan naar pelle@amsterdamsmartcity.com*</em>
Demoday #23: Co-creating with residents in the heat transition

The heat transition is in full swing. Municipalities want their residents off the gas and want them to switch to renewable sources of heat. Unfortunately, heat grids have often led to frustrated residents. Which in turn has led to delayed or cancelled plans for the municipality.
Dave van Loon and Marieke van Doorninck (Kennisland) have looked into the problems surrounding heat grids and came up with a plan. In this Demoday work-session we dived into the problems surrounding heat grids and their plan to solve them. The session was moderated by our own Leonie van Beuken.
Why residents get frustrated with heat grid plans
Involving residents in the planning of a heat grid is difficult. It takes a lot of time and effort and the municipality is often in a hurry. This is why they choose for a compromise in which they already make the plan, but try to involve citizens at the end part. However, this leads to residents not having anything to say in the plans. They can block the plans, but they can’t really make changes. This leads to a lot of dissatisfaction.
This top-down approach doesn't seem to be ideal for involving residents in the heat transition. That's why Kennisland is working on developing a plan for early collaboration with residents in the heat transition of neighbourhoods, with a focus on connecting with the community's concerns.
They have seen that this kind of approach can be successful by looking at the K-buurt in Amsterdam-Zuid-Oost. In the initial stages, the first plan for the K-buurt didn't gain much traction. However, when they shifted towards a more collaborative approach, people felt empowered to engage, leading to a more meaningful participation process. Instead of traditional town hall meetings, discussions took place in community spaces like the local barber shop. This shift towards genuine participation and co-creation has resulted in a much-improved end product, one that residents truly support and believe in.
The plan for co-creation in the heat transition
The plan that Kennisland came up with consists of a few key points that are necessary for success:
• Engage with residents early on in the process.
• Also consider other issues in the neighbourhood. There might be more pressing concerns for the residents themselves.
• Ensure accessibility for everyone to participate.
• Truly collaborate on developing a list of requirements.
• Harness creativity.
• Work in a less compartmentalized manner.
They aim to form a neighbourhood alliance and organize a community council. Together a plan can be made for the neighbourhood that all residents can get behind.
This plan might take a bit longer at the start, but that investment in time will pay itself back in the end.
SWOT analysis of co-creation plan
After Dave and Marieke explained their plan we did a SWOT analysis with the group. We looked at the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of the plan.
The main strength that was pointed out was the ability to make a plan together with the residents. The residents experience the neighbourhood differently than a government official, which makes the final plan more beneficial to everyone.
The weaknesses the group saw in the plan were mainly that this could potentially slow down the process. Should we maybe do less participation instead of more and use force to get this heat transition going?
There were a lot of opportunities identified for this plan. The quality of the plan (and the neighbourhood) can greatly increase. By slowing down at the start we can actually accelerate and improve the neighbourhood on many levels. This plan also offers a great learning experience.
Finally, we went into the threats. One of the big threats that was pointed out was the lack of trust. If residents don’t trust the municipality and the process then it will never be possible to let this plan succeed. The explanation to residents also needs to be understandable. The explanation around a heat grid can get technical very quickly, and residents often don’t have the background to understand everything. The last threat that was pointed out was that if you get a lot of input from the residents for the plan, you also have to do something with that, and still be realistic. You have to work hard to manage expectations.
We completed the session by asking the participants if they knew any partners and places to collaborate with for this plan, or if they had any other ideas to make this plan successful.
We would now like to ask the same questions to you! Do you know someone who would like to partner up with Kennisland, do you know a place where this plan can be tested, or do you have any other ideas? Let us know by contacting me at noor@amsterdamsmartcity.com.
Ondanks congestie toch bedrijvigheid op Schiphol Trade Park

Wat in oktober 2020 begon als een urgent probleem – in het gebied waar Schiphol Trade Park in ontwikkeling was was geen extra transportcapaciteit meer mogelijk en de geplande bouw en uitbreiding moest noodgedwongen stoppen – is inmiddels opgelost. Onze baanbrekende virtuele netoplossing is daar nu namelijk ruim twee jaar in werking, en met succes: de bedrijven op Schiphol Trade Park zijn operationeel, breiden uit, en elektrificeren ondanks de netcongestie in het gebied.
Congestie op Schiphol Trade Park
Een blik op de congestiekaart maakt duidelijk dat Schiphol Trade Park in een door congestie grotendeels op slot gezet gebied ligt. Op het middenspanningsnet is geen extra capaciteit beschikbaar voor het transporteren van elektriciteit. Dat betekent dat er niet meer ontwikkeld wordt: een bedrijf krijgt namelijk wel een aansluiting, maar geen transportcapaciteit. Dit is niet alleen een probleem voor de bedrijven die zich hier willen vestigen, maar ook voor gebiedsontwikkelaar SADC (Schiphol Area Development Company), dat in 2020 nog de ambitie had om het meest duurzame business park van Europa te worden (en in 2023 door de BREEAM-NL Outstanding certificering zelfs het meest duurzame logistieke business park van de wereld is!). De ontwikkelaar wilde voorkomen dat bedrijven afzonderlijk een eigen oplossing zochten en er een wildgroei aan gasgeneratoren met de daarbij behorende uitstoot zou ontstaan. SADC zag dat dit slimmer, goedkoper en duurzamer kon, door op een innovatieve manier partijen te verbinden en te laten samenwerken. Bedrijven kunnen daardoor bouwen, uitbreiden en elektrificeren. Over de aanloop naar het project lees je meer op onze projectpagina.
Een doorbraak: de virtuele netoplossing
Alle bij de coöperatie aangesloten bedrijven delen hun eigen transportcapaciteit met elkaar. Zo maken ze slim gebruik van de gereserveerde ruimte. STELLAR Grid Management leest continu de slimme meters uit en stuurt de energiesystemen (zoals zonnepanelen, energie-opslag, en generatoren) achter de meter aan. Bovendien zorgen we voor de financiële afhandeling van deze aansturing, zodat de deelnemende bedrijven elkaar compenseren voor gebruikte elektriciteit en voor het beschikbaar stellen van hun stuurbare energiesystemen.
De resultaten van een jaar virtueel net
Het virtuele net is twee jaar actief. In het eerste jaar sloten zich nog gefaseerd bedrijven aan bij het collectief. De resultaten van dat jaar zijn voorspoedig, maar niet helemaal volledig.
Nu we een tijdje bezig zijn, delen we met vertrouwen onze resultaten. Voor deze resultaten keken we naar 2023. Zo nemen we dus alle seizoenen en bijbehorende energievraag mee in deze analyse.
Het collectief wordt goed benut: in 2023 is 2.104 MWh aan elektriciteitslevering extra mogelijk gemaakt door het delen van de capaciteit binnen het virtuele net. Zonder deze slimme oplossing hadden heel veel stuurbare energiesystemen, zoals batterijen en generatoren, deze elektriciteit moeten leveren. In het collectief nemen in totaal zeven bedrijven deel die weinig of geen netcapaciteit hebben. Dankzij deze slimme oplossing kunnen de bedrijven gebruikmaken van de beschikbare ruimte en opwek van de buren.
Om zeker te zijn van voldoende elektriciteit binnen de gestelde limieten hebben meerdere bedrijven geïnvesteerd in batterijen en gas- en dieselgeneratoren. Het collectief gebruikt die middelen als er een tekort aan capaciteit is. De generatoren dienen vooral als achtervang. Voordat STELLAR deze aanstuurt, bepaalt het systeem of de aangesloten batterijen kunnen voorzien in het verwachte moment van schaarste. Als de batterij niet voldoende is, schakelt STELLAR automatisch een generator in. In heel 2023 is ertwee keer een generator ingezet om binnen de netlimiet te blijven, voor in totaal 2 uur. Toen de generatoren aangingen waren de batterijen nog niet operationeel, anders waren die generatoren waarschijnlijk niet nodig geweest.
Zonder virtueel net hadden deze partijen moeten investeren in elk een eigen generator (en eventuele back-up generator). Die generatoren hadden gezamenlijk tot 31.000 draaiuren gemaakt. Dat is gelukkig voorkomen. Er is hiermee voor 468.000 m3 minder gas verbruikt, en daardoor is er lokaal 842 ton CO2 minder uitgestoten door generatoren.
Het virtuele net is dus een solide oplossing voor congestiegebieden. Dankzij de slimme aansturing zijn zeven bedrijven operationeel die zonder de virtuele netoplossing hadden moeten uitwijken naar een andere locatie in Nederland of daarbuiten,terwijl een aantal van hen al aan het bouwen was. En er is een enorme hoeveel CO2-uitstoot voorkomen.
De toekomst van Grid Management
We zijn trots op ons virtuele net bij Schiphol Trade Park. We horen ook een enorme urgentie in de markt: veel partijen worstelen met netcongestie en zoeken naar een vergelijkbare oplossing. Maar de toekomst van Grid Management is niet hapklaar. Het project bij Schiphol Trade Park is een pilot, en de voorwaarden van een standaard contractvorm voor een dergelijke collectieve oplossing (groeps-transportovereenkomst) zijn nog niet definitief vastgesteld.
Niet alleen bij Schiphol
Schiphol Trade Park is zeker niet de enige plek in Nederland waar sprake is van congestie. Eerder dit jaar lanceerden we onze oplossing bijvoorbeeld ook in het Zwolse Hessenpoort. Heb jij ook last van congestie? We denken graag met je mee. Neem contact met ons op.
ESG in de publieke sector: benut de EU duurzaamheidsagenda

Gebruik deze als kapstok voor uw strategie
De kracht van een integrale strategie die financiën, mens en milieu met elkaar in balans brengt. Duurzaamheid is de nieuwe norm. Veel organisaties hebben duurzaamheid reeds een plek gegeven in hun strategie. Maar hoe zorgt u dat u tot een integrale strategie en juiste verantwoording komt? De standaarden die de EU zet op het gebied van duurzaamheid, vanuit haar ambitie om de EU een duurzame regio te laten zijn in 2050, geven de mogelijkheid om als publieke instelling relevante duurzaamheidsthema’s te selecteren en prioriteren tot een integrale strategie en een heldere verantwoording. In aansluiting op de wensen en verwachtingen van alle stakeholders.
De meerwaarde van ESG voor uw organisatie
Onze maatschappij verlangt steeds sterker van organisaties dat zij hun financiële resultaten in balans brengen met hun sociale belangen en het milieu. In antwoord hierop heeft de EU de Green Deal vastgesteld, die de regio duurzaam moet maken op basis van vijf milieuthema’s (klimaat, vervuiling, water, biodiversiteit en circulariteit). Om daarop te kunnen sturen heeft de EU ook richtlijnen voor verslaggeving vastgesteld, de zogenoemde Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (hierna CSRD) vastgesteld. Uit deze richtlijn zijn de European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) voortgekomen. Deze standaarden bieden handvatten voor hoe een organisatie zich op het gebied van milieu (Environment), mens (Social) en bestuur (Governance) kan verantwoorden.
De EU-standaarden bieden publieke organisaties de kapstok om duurzaamheid een integraal onderdeel te maken van de organisatiestrategie en voorop te (blijven) lopen in de beweging. De ESRS zijn weliswaar primair gericht op verslaggeving, maar bieden ook een mooi afwegingskader voor bestuurders en management bij het maken van strategische keuzes. Daarmee bereidt u zich voor op een toekomst waarin organisaties nadrukkelijker worden gevraagd om een positieve impact op mens, milieu en maatschappij te maken en waarin bepaalde duurzaamheidsontwikkelingen (zoals klimaatverandering) risico’s kunnen gaan vormen voor uw organisatie.
Welke verplichtingen gelden voor publieke instellingen?
Iedere publieke instelling krijgt naar verwachting te maken met eisen op het gebied van duurzaamheid en transparantie daarover. Hetzij omdat dit verplicht wordt in Nederlandse wetgeving, dan wel doordat uw stakeholders u om verantwoording gaan vragen. Zo zal bijvoorbeeld uw bank bij het verstrekken van financiering naar verwachting u bevragen over het effect van de verstrekte lening op mens, milieu en maatschappij. Een bank heeft namelijk de verplichting te rapporteren over de duurzaamheid van haar portefeuille.
"Het is zo goed als zeker dat publieke organisaties gevraagd gaan worden zich te verantwoorden over duurzaamheid"
De weg naar een integrale strategie en heldere ESG-rapportage
Onderstaande roadmap vertelt hoe u in 7 stappen tot een integrale strategie en verantwoording kan komen. Het vormgeven van een integrale strategie - waarin duurzaamheid een prominente plek inneemt - en u als organisatie hierover kunnen verantwoorden, is een proces dat niet alleen afstemming behoeft met de stakeholders, het vraagt ook om inbedding in alle processen van het bedrijf – en dat komt met de nodige inspanning en doorlooptijd. Wij adviseren u dan ook om hiermee tijdig aan de slag te gaan.
Essentieel is allereerst te bepalen wie hiervoor verantwoordelijk is binnen uw organisatie (stap 1). Om vervolgens te beoordelen op welke duurzaamheidselementen uw organisatie een significante impact heeft (stap 2). Wanneer sprake is van een significante impact noemen we dat ook wel ‘materiële impact’.
Hoe bepaalt u op welke onderdelen uw impact materieel is?
Welke duurzaamheidsthema’s relevant zijn, wordt bepaald door de aard van uw activiteiten, de behoeften van de belanghebbenden van uw organisatie op dit vlak én uw eigen ambitie en beleid.
Uw stakeholders, zowel intern als extern, kunnen belangrijke informatie geven in de materialiteitsanalyse over de duurzaamheidsthema’s waar uw organisatie het verschil maakt. Zij zijn echter niet allesbepalend. U kent zelf uw organisatie het beste en de aanwezige expertise binnen uw organisatie is ook zeker van belang om te bepalen waar de belangrijkste thema’s liggen. Uiteindelijk bepaalt u als management welke thema’s u zich op richt, op basis van de verkregen input en aangevuld met uw eigen strategische keuzes.
Een materialiteitsanalyse is tweeledig: u kijkt niet alleen naar de impact van de organisatie op de omgeving, maar ook naar de financiële impact van duurzaamheidsthema’s op de organisatie. Als u bijvoorbeeld denkt aan vervoersbewegingen - en daarmee samenhangende uitstoot - die uw dienstverlening teweegbrengt, dan is niet alleen de vraag hoe groot de invloed van die uitstoot is op de omgeving, maar ook wat er gaat veranderen door bijvoorbeeld regelgeving. Komt er bijvoorbeeld regelgeving die uitstootreductie verplicht en betekent dat dat elektrisch vervoer de standaard wordt? Dan kan dat belangrijke financiële impact hebben op de waarde en levensduur van uw huidige vervoersmiddelen.
"Met input van uw stakeholders en experts bepaalt u in een materialiteitsanalyse de duurzaamheidsthema’s waar uw organisatie het verschil maakt."
In een volgende publicatie zullen we dieper ingaan op stappen 3 t/m 7.
Geen CSRD verplichting?

Waarom de dubbele materialiteitsanalyse tóch van belang is.
Voor publieke organisaties is de Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) niet verplicht. Toch is de dubbele materialiteitsanalyse een goede manier voor organisaties om inzicht te krijgen in hun impact, kansen én risico's op het gebied van duurzaamheid, vertellen Oscar Ferrero Scholte en Leon Stokman, beide senior manager bij Deloitte Audit & Assurance.
Als het gaat om duurzame bedrijfsvoering is er momenteel veel te doen rond het idee van 'dubbele materialiteit', en dat is niet zonder reden. Het uitvoeren van een dubbele materialiteitsanalyse is feitelijk de eerste cruciale stap om te voldoen aan de nieuwe Europese Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) die vanaf 2024 ingaan.
Met andere woorden: begrijpen wat de impact, kansen en risico's hiervan zijn én hoe je het kunt toepassen in je organisatie is nog nooit zo belangrijk geweest. Ook voor publieke organisaties, want al geldt deze verplichting voor hun (nog) niet, het is te verwachten dat ook zij zich in de nabije toekomst over hun duurzaamheidsprestaties zullen moeten verantwoorden.
Twee perspectieven
De dubbele materialiteitsanalyse vraagt van organisaties om enerzijds na te gaan hoe hun acties invloed hebben op de mens en de planeet (het inside-out perspectief), en anderzijds om in kaart te brengen hoe duurzaamheidskwesties hun financiële welzijn kunnen beïnvloeden (het outside-perspectief). Het gaat er dus om dat je vanuit twee verschillende perspectief naar het grote geheel kijkt.
Inside-out De impact van de acties van een organisatie op mens en planeet kunnen zowel positief als negatief zijn. Wanneer er schade aan de natuur ontstaat is dat een negatieve impact, terwijl je als organisatie juist ook kunt bijdragen, bijvoorbeeld aan de energietransitie. Schendingen van mensenrechten is een voorbeeld van een negatieve impact op mens en maatschappij. Maar een organisatie kan bijvoorbeeld ook de kansengelijkheid vergroten en daardoor armoede verminderen. Met als secundair gevolg een lagere druk op sociale zekerheid en hogere belastinginkomsten voor de (lokale) overheid.
Outside-in Hier gaat het om de impact van duurzaamheid en klimaat op jouw organisatie. Dit gaat om zaken zoals groei, prestaties en kapitaalkosten van je organisatie op de korte, middellange en lange termijn. Denk bijvoorbeeld aan de wettelijke CO2-heffingen en de ontwikkelingen van circulaire producten. Van oudsher vonden vooral investeerders dit perspectief van belang, maar inmiddels is er samenleving breed interesse in de manier waarop organisaties met duurzaamheidsrisico's en -kansen omgaan.
In de dubbele materialiteitsanalyse worden deze twee perspectieven gecombineerd, zodat je als organisatie kunt achterhalen welke duurzaamheidsrisico's en -kansen specifiek voor jouw organisatie materieel zijn en dus moeten worden meegenomen in je rapportage. Het is een forse opgave, maar biedt je organisatie ook voordelen. De belangrijkste meerwaarde is dat het handvatten geeft om de middelen van je organisatie te gebruiken voor zaken die er echt toe doen, én hierop ook actief te sturen. De strategie komt daarmee volledig in lijn met de duurzaamheidsambities. Bovendien draagt het actief betrekken van stakeholders bij aan het maatschappelijke draagvlak van je organisatie en de strategische keuzes die je maakt.
Eerste stappen
De logische, eerste stappen zijn:
- Het inventariseren van je waardeketen
- Beoordelen waar je organisatie een materiële impact heeft in de keten
- Het inventariseren en benaderen van de betrokkenen: wie zijn de relevante stakeholders?
Hou hierbij ook de twee perspectieven in gedachten en ga na op wie je activiteiten een directe invloed hebben, en wie er belang hebben bij jouw rapportage. Ga vervolgens met deze stakeholders (van afnemers van diensten tot financiers en sociale partners) in gesprek, en maak samen een lijst van de mogelijke relevantie duurzaamheidsonderwerpen. Het vastleggen van de wijze waarop je materialiteitsanalyse tot stand is gekomen is daarbij nuttig, want dat maakt het proces toetsbaar.
Deskundigen betrekken en samenwerken
Duurzaamheid is een breed begrip, waardoor de meningen van stakeholders sterk uiteen kunnen lopen. Op zo'n moment helpt het om zowel interne als externe deskundigen te betrekken om de gesprekken met stakeholders te structureren.
Bij het bepalen en beoordelen van effecten, risico's en kansen is bijvoorbeeld expertise nodig op de gebieden van strategie, financiën en risicobeheersing. Denk er in deze fase bijvoorbeeld aan om een externe accountant te betrekken, die moet immers in een later stadium ook de controle daarop uitvoeren. Het vroegtijdig betrekken van de accountant voorkomt ook dat er onderwerpen worden gemist, die vanuit het perspectief van de accountant materieel zijn. Op die manier wordt de lijst van duurzaamheidsonderwerpen teruggebracht tot de zaken die van materieel belang zijn en waarover dus moet worden gerapporteerd. Onderdeel hiervan is ook het inzichtelijk maken in hoeverre deze zaken zijn opgenomen in het risicomanagementsysteem van je organisatie.
Bij het inventariseren van de relevante duurzaamheidsonderwerpen is samenwerken het credo. In de publieke sector is al te zien dat organisaties elkaar om deze reden opzoeken, inspireren en onderling peer reviews uitvoeren. Ook diverse brancheorganisaties, zoals Aedes, ActiZen de VNG, pakken hier de handschoen op.
Als de lijst met relevant beoordeelde onderwerpen er eenmaal is, is het tijd voor de volgende stap: er moet per onderwerp worden beschreven wat de impact is, en welke risico's en kansen het oplevert. Dat is niet eenvoudig. Sommige onderwerpen beïnvloeden elkaar en de termijn van de impact kan verschillen van de termijn waarop een kans of risico zich voordoet. Daarbij is er ook aandacht nodig voor zaken waarvan geldt dat het risico dat ze zich voordoen klein is, terwijl de impact enorm zou zijn.
Denk aan de recente wereldwijde covid-epidemie. Per onderwerp moet dan ook de omvang en de reikwijdte worden beoordeeld. Daarbij moet worden aangegeven welke negatieve of positieve impact een activiteit heeft en wat de kosten zijn om de negatieve effecten ongedaan te maken. In feite moeten daarbij dus de financiële effecten worden beoordeeld die niet in de jaarrekening zijn verwerkt. Daarvoor is inzicht in de waardeketen noodzakelijk.
Start tijdig
De CSRD zal niet verplicht worden voor publieke organisatie (m.u.v. NV’s en BV’s), maar ons advies is om niet achter te blijven. Start tijdig, dat is noodzakelijk om de nodige ervaring op te doen. Het komen tot een afgewogen materialiteitsbeoordeling is namelijk een iteratief en tijdrovend proces. Een gedegen beoordeling ontstaat pas na het in verschillende stappen bouwen, verbeteren en verfijnen. Er is nog een reden waarom vandaag beginnen nut heeft: de dubbele materialiteitsanalyse heeft een effect op de strategie van je organisatie. Publieke organisaties hebben een voorbeeldfunctie wat betreft het verantwoord omgaan met mens en planeet. Wij zien bij private organisaties al dat de materialiteitsanalyse leidt tot het onderkennen van nieuwe thema’s die worden geïntegreerd met de strategie - een win-winsituatie.
Hoe rapporteer je evenwichtig over duurzaamheid?

Over de resultaten van het eerste ESG-Quickscanonderzoek in de publieke sector
Elke publieke instelling zal op een zeker moment te maken krijgen met eisen rondom duurzaamheid en de transparantie hierover. Deloitte ontwikkelde daarom een ESG-Quickscan en onderzocht hoe 60 grote organisaties in de publieke sector hun duurzaamheidsactiviteiten rapporteren. Juwi Liu, Senior Manager Audit Advisory en Patrick Jussen, Partner Audit Advisory, beiden werkzaam als adviseur in de publieke sector, vertellen meer.
Vanaf 2024 start de EU met het verplicht stellen van duurzaamheidsrapportages voor bedrijven, gebaseerd op de Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). Hoewel deze verplichting niet voor de publieke sector geldt, met uitzondering van de BV's en NV's, kunnen ook zij niet om duurzaamheid heen. Publieke organisaties hebben immers de maatschappelijke plicht om balans te brengen in sociale belangen, financiële resultaten en milieu. Deze transitie nodigt publieke instellingen dan ook uit om hun omgang met kansen en risico’s op het gebied van duurzaamheid in kaart te brengen.
Download het ESG rapport
Om die reden ontwikkelden jullie de ESG-Quickscan met daarin 28 vragen. Met welk doel is deze tool ontwikkeld?
Liu: “De Quickscan kan organisaties en ons inzicht geven in hun duurzaamheidsinspanningen op basis van de manier waarop ze hierover rapporteren. Het is bewust geen uitgebreide scan geworden, omdat duurzaamheidsrapportage nog een nieuw onderwerp is. Veel organisaties bevinden zich nog in een beginstadium, en deze Quickscan geeft inzicht in waar ze zich bevinden en welke vervolgstappen kunnen worden genomen.”
Welke instellingen waren bij jullie onderzoek betrokken?
Jussen: “In het onderzoek hebben we 60 grote instellingen uit de publieke sector onder de loep genomen, waaronder ziekenhuizen, ouderenzorg- en GGZ-instellingen, gehandicaptenzorg, universiteiten en gemeenten.”
Liu: “We bestudeerden jaarverslagen en jaarrekeningen van 2022 en andere openbare data zoals begrotingen en milieuverslagen. Het was een bewuste keuze om alleen openbare gegevens te gebruiken (en bijvoorbeeld geen interviews af te nemen), omdat de duurzaamheidsverantwoording draait om transparantie over waar je staat in de duurzaamheidstransitie.”
Jullie hanteren vier niveaus voor de ESG-Quickscan, van ‘Exploring Sustainability’ tot 'Being Sustainable'. Welke organisaties scoorden het hoogst, welke het laagst?
Liu: “Zoals verwacht, scoorde geen enkele organisatie veel hoger dan niveau 2: Doing Sustainable. De GGZ-sector rapporteert het minst over duurzaamheid en bevindt zich nog op het niveau Exploring Sustainability. Universiteiten, gemeenten en ziekenhuizen scoren vooral op het niveau Doing Sustainable. Dit was te verwachten, omdat deze organisaties iets meer met duurzaamheid bezig zijn, bijvoorbeeld door zich te committeren aan de Green Deal Duurzame Zorg of al duurzaamheidsdoelstellingen hebben opgenomen.”
"Publieke instellingen hebben een belangrijke voorbeeldfunctie te vervullen.”
Wat zijn jullie belangrijkste bevindingen?
Liu: “Het goede nieuws is dat we zien dat de meeste organisaties in meer of mindere mate met duurzaamheid bezig zijn. Er zijn veel initiatieven en daarover wordt ook gerapporteerd. Tegelijkertijd constateren we dat deze rapportage nog enorm versnipperd is. Bedrijven rapporten in verschillende documenten over hun duurzaamheidsactiviteiten. Niet alleen in jaarverslagen, maar ook in milieurapportages, roadmaps, op hun website of in afzonderlijke duurzaamheidsverslagen. Die versnippering maakte het voor ons, en dus ook voor hun stakeholders, moeilijk om een compleet en integraal beeld te krijgen.”
Jussen: “Daarbij zien we dat er nauwelijks tot geen eenduidige spelregels worden gehanteerd in de verslaglegging. Er wordt bijvoorbeeld zelden concreet gemeld wat de beoogde doelstelling is en in hoeverre deze is bereikt. Ook is vooral zichtbaar welke activiteiten wél worden uitgevoerd, en het is onduidelijk welke activiteiten niet worden benoemd en dus niet uitgevoerd. Dit maakt de informatie moeilijk te interpreteren en roept vragen op over hoe transparantie over duurzaamheidsaspecten wordt geborgd.”
Dat lijkt me een eyeopener...
Liu: “Absoluut, en nu rijst de vraag hoe we in de publieke sector meer kunnen toewerken naar bruikbare informatie over de duurzaamheidstransitie.”
Hebben jullie daar al ideeën over?
Liu: “Zorg voor één integraal document per organisatie waarin je over alle duurzaamheidsactiviteiten rapporteert. Beschrijf daarin je ambities en doelstellingen, wat daarvan is gerealiseerd en wat je nog niet hebt gedaan."
Jussen: “En zorg voor een eenduidige manier van rapporteren. Dat maakt de informatie goed interpreteerbaar.”
Liu: “Eenduidig rapporteren én alle duurzaamheidsactiviteiten in één document weergeven is bovendien ook van belang voor alle stakeholders in je keten. Financiële instellingen zoals verzekeraars en banken hebben een verplichting om over de CSRD te rapporteren, en daarbij niet alleen naar hun eigen activiteiten te kijken, maar ook naar die van bijvoorbeeld hun leveranciers. Bereid je dus voor op vragen hierover in de nabije toekomst: één duidelijk en evenwichtig verslag voor de diverse stakeholders bespaart veel tijd.”
"Zie rapporteren als een kans om je te onderscheiden, je strategie te bepalen en sturing te geven aan de duurzaamheidstransitie.”
Tot slot: De rapportageverplichting wordt door bedrijven nogal eens ervaren als een administratieve verzwaring die niet gelegen komt in deze tijd van zwakke economische groei. Hoe zien jullie dat?
Jussen: “Als we bij onze klanten aan tafel zitten, merken we dat zij uiteraard geen behoefte hebben aan een verplichting, maar wél aan gezamenlijke actie om tot een duurzamere en inclusievere wereld te komen. Evenwichtig rapporteren is een middel om dat te bereiken. En juist publieke instellingen hebben hierin een belangrijke voorbeeldfunctie te vervullen.”
Liu: “Wie duurzaamheid prominent opneemt in zijn strategie springt eruit in de strijd om nieuw talent. De nieuwe generatie werknemers is veel meer bezig met thema's als diversiteit, inclusiviteit en de werk-privébalans. Met andere woorden: zie het rapporteren als een kans om je als organisatie te onderscheiden, je strategie te bepalen en sturing te geven aan de duurzaamheidstransitie.”
Demoday #22: Data Commons Collective

In the big tech-dominated era, data has been commercially exploited for so long that it is now hard to imagine that data sharing might also benefit the community. Yet that is what a collective of businesses, governments, social institutions and residents in Amsterdam aim to do. Sharing more data to better care for the city. On behalf of the Data Commons Collective, Lia Hsu (Strategic Advisor at Amsterdam Economic Board) asked the Amsterdam Smart City network for input and feedback on their Data Commons initiative on the last Demoday of 2023.
What is a (data) common?
Commons are natural resources that are accessible to everyone within a community. Water. Fertile soil. Clean air. Actually everything the earth has given us. We as humanity have increasingly begun to exploit these commons in our pursuit of power and profit maximisation. As a result, we risk exhausting them.
Data is a new, digital resource: a valuable commodity that can be used to improve products and services. Data can thus also be used for the common good. However there are two important differences between a common and a data common: data in commons never runs out, and data in commons is not tied to any geographical location or sociocultural groups.
Four principles for Data Commons
The Data Commons collective is currently working on different applied use cases to understand how data commons can help with concrete solutions to pressing societal problems in the areas of energy, green urban development, mobility, health and culture. Each data commons serves a different purpose and requires a different implementation, but there are four principles that are always the same:
- The data common is used to serve a public or community purpose
- The data common requires cooperation between different parties, such as individuals, companies or public institutions
- The data common is managed according to principles that are acceptable to users and that define who may access the data commons under what conditions, in what ways they may be used, for what purpose, what is meant by data misuse
- The data common is embedded to manage data quality, but also to monitor compliance with the principles and ensure that data misuse is also noticed and that an appropriate response (such as a reprimand, penalty or fine) follows.
The Data Commons Collective is now in the process of developing a framework, which provides a self-assessment tool to guide the formation of Data Commons initiatives by triggering consideration of relevant aspects for creating a data commons. It is a means of reflection, rather than prescription, to encourage sustainable and responsible data initiatives.
Energy Data Commons case and Value Workshop by Waag
After the introduction to the Data Commons Collective and Framework by Simone van der Burg (Waag) and Roos de Jong (Deloitte), the participants engaged in a value workshop led by Simone. The case we worked with: we’re dealing with a shortage of affordable and clean energy. Congestion issues are only expected to get worse, due to increased energy use by households en businesses. An energy Data Commons in neighbourhoods can have certain benefits. Such as preventing congestion issues, using clean energy sources more effectively, becoming self-sufficient as a neighbourhood and reducing costs. But under what circumstances would we want to share our energy data with our neighbours? What are the values that we find important when it comes to sharing our energy data?
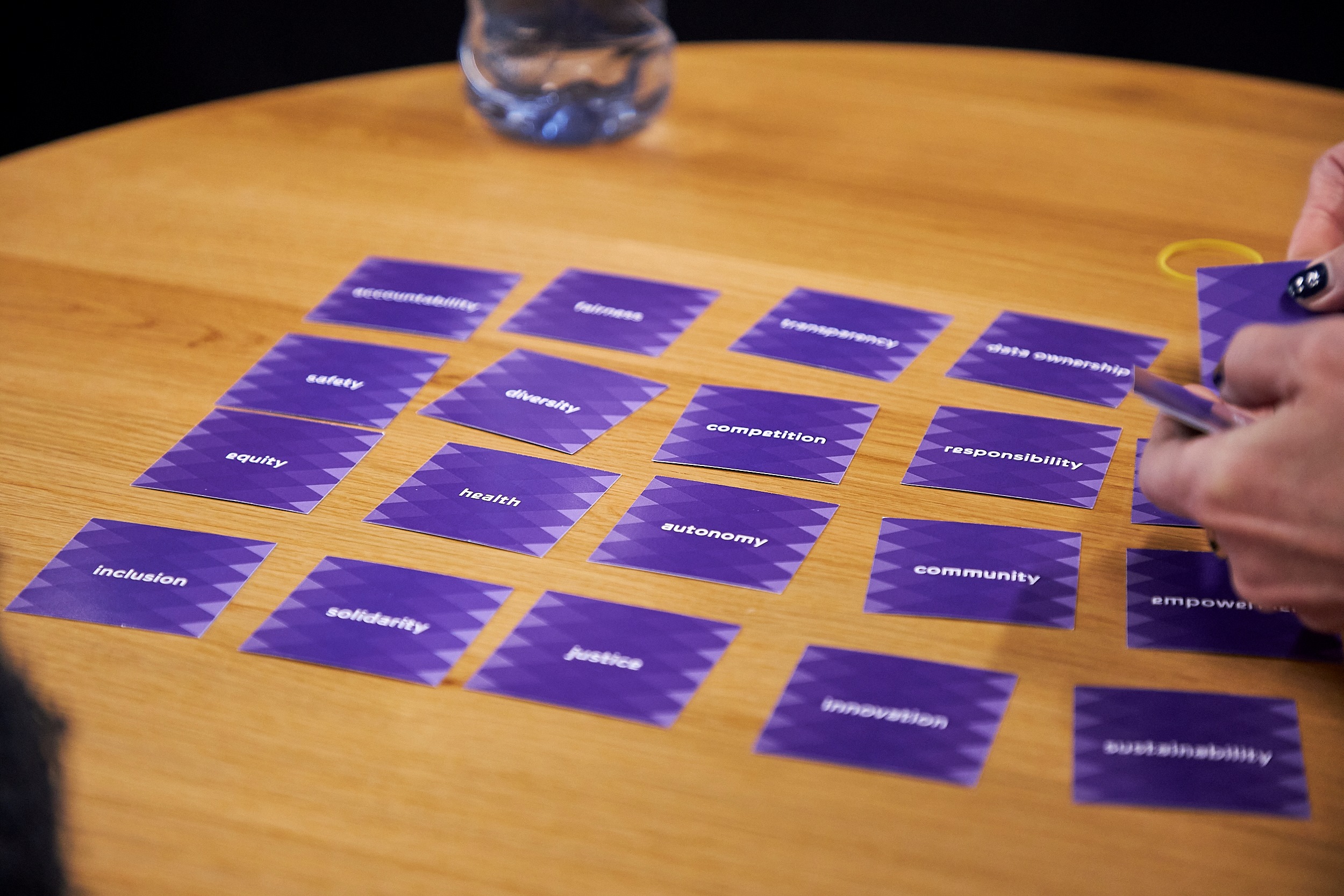

Results: Which values are important when sharing our energy data?
In smaller groups, the participants discussed which values they found important for an energy data common using a value card deck from Waag. Some values that were mentioned were:
- Trustworthiness: It is important to trust one another when sharing our energy data. It helps when we assume that everyone that is part of the common has the right intentions.
- Fun: The energy Data Commons should be fun and positive! The participants discussed gamification and rewards as part of the common.
- Knowledge: One of the goals of sharing data with each other is to gain more knowledge about energy consumption and saving.
- Justice and solidarity: If everyone in the common feels safe and acknowledged, it will benefit the outcome. Everyone in the common should be treated equally.
- Inclusion and Community-feeling: It is important that people feel involved in the project. The Data Commons should improve our lives, make it more sustainable but also progress our social relations.
During this Demoday, we got to know the Data Commons collective and experienced which values we find important when sharing our data with others. Amsterdam Economic Board will remain involved in the Data Commons Collective in a coordinating role and work on use cases to understand how data commons can work for society.
Would you like to know more about the Data Commons Collective or do you have any input for them? Please feel free to reach out to me via sophie@amsterdamsmartcity.com or leave a comment below.
Recap of Demoday #22

On Thursday December 14th, Amsterdam Smart City partners concluded 2023 with an afternoon full of inspiration, exchange and connections at our 22nd Demoday! Our partner Deloitte welcomed our network in The Garage, where their ‘Deloitte Studios’ department is located. In this article, we’ll give you a quick overview of the Knowledge Session, Work Sessions and Pitches. Interesting in learning more? Read the full reports by our Programme Managers Noor, Pelle and Sophie (linked below).
About our Demodays
The Demodays are one of the tools we use to stimulate innovation and encourage connection between our partners and community. The purpose of the Demodays is to present the progress of various innovation projects, ask for help, share dilemmas and involve more partners to take these projects to the next level. More information about the Demodays can be found here.
Knowledge Session: Change in the here and now, with Theory U
To kick-off our final Demoday of 2023, our brand-new partner Hieroo led an inspiring knowledge session about the change method they use for social innovation in the city: Theory U. Dorien Schneider and Maartje Krijnen taught us more about this methodology and how it can help us solve complex problems by shifting from ego to eco-thinking. Read the full report here.
Work sessions
After the plenary Knowledge Session we split up in different worksessions, each exploring regional innovation challenges. As always, we had set up the sessions’ topics and moderation in collaboration with our partners.
Mobility | Decision-making along the principles of Inclusive Prosperity – Jurhan Kwee (Municipality of Amsterdam)
In The Netherlands, the concept of ‘Inclusive Prosperity’ is on the rise. Policy makers are busy defining this concept, figuring out how to put this concept into practice and what it means for their decision-making process. Together with his colleagues at the Municipality of Amsterdam, Yurhan Kwee hosts sessions on decision-making along the principles of Inclusive Prosperity. With the input he gathers, he hopes to make the decisions needed for our Inclusive Prosperity ambitions more understandable and transparent, both for Amsterdam’s administrators and councillors as well as its citizens. Read Pelle’s recap article here.
Digital | Data Commons Collective: Using data for a liveable city – Lia Hsu (Amsterdam Economic Board) and Simone van der Burg (Waag)
In the big tech-dominated era, data has been commercially exploited for so long that it is now hard to imagine that data sharing might also benefit the community. Yet that is what a collective of businesses, governments, social institutions and residents in Amsterdam aim to do. Sharing more data to better care for the city. On behalf of the Data Commons Collective, Lia Hsu (Strategic Advisor at Amsterdam Economic Board) asked the Amsterdam Smart City network for input and feedback on their Data Commons initiative. Read Sophie's recap article here.
Energy | How can we continue to facilitate the homeowner in driving the energy transition? | Wouter van Rooijen (Alliander)
Wouter van Rooijen (Alliander) discussed the challenges related to grid congestion. From 2030 onwards, it is expected that a significant portion of the low-voltage network will experience both over- and under-voltage. While the network will be reinforced as quickly as possible, the lack of labour capacity is also prompting the consideration of alternative solutions.
The solution that emerged from Wouter's co-creation process was WijkWise. In this work session, Wouter aimed to validate the WijkWise concept and find parties that could contribute to its development and market implementation. Dave van Loon from Kennisland moderated the session. Read Noor’s recap article here.
Circular | Navigating eco-emotions: The impact of working in sustainability on your mental wellbeing| Marian Zandbergen (Hogeschool van Amsterdam)
This work session, led by Marian Zandbergen (CIRCOLLAB, HvA) and moderated by Mareille de Bloois (Royal HaskoningDHV), explored the challenges and opportunities associated with eco-emotions, both personally and within organizations. The key question addressed was: How can individuals and organisations constructively manage eco-emotions, and what implications does this have for organisations? Read Noor’s recap article here.
Pitches
To end this festive afternoon and the year 2023 as a whole, we invited project owners and -members to present their progress and next steps on topics brought in during our events and deep-dives throughout 2023. The following projects were presented. You can read more about these topics on their dedicated articles and project pages, linked below.
Local Energy Systems: Where we started, what we have achieved, and what are the next steps – Omar Shafqat (University of Applied Sciences Amsterdam)
Connecting the resource- and energy transition – Edwin Oskam (MRA)
ChatGPT and the government: Possibilities and impact on our work – Jeroen Silvis (Province of North Holland)
Floating urban districts: Future-proof living in the Metropolitan Region – Joke Dufourmont (AMS Institute)
Mobility Justice: Raising the topic of Mobility Poverty and the working group’s progress – Bas Gerbrandy (Province of North Holland)
Our next Demoday will take place in April. Do you have an inspiring story or project you want to pitch to the Amsterdam Smart City network? Let us know via sophie@amsterdamsmartcity.com
Demoday #22: How can we continue to facilitate homeowners in driving the energy transition?

Grid congestion is becoming increasingly significant and will start to pose a problem in the low-voltage network in the coming years. This will prevent homeowners from transitioning away from gas, result in low efficiency for their solar panels, and could make it impossible to have a charging station at their doorstep. Alliander does not want to hinder the energy transition. Therefore, they are looking for a way to involve homeowners in the issue of grid congestion and provide solutions that are still feasible with a crowded grid.
In the energy work session on the 14th of December, Wouter van Rooijen (Alliander) discussed the challenges related to grid congestion. From 2030 onwards, it is expected that a significant portion of the low-voltage network will experience both over- and under-voltage. While the network will be reinforced as quickly as possible, the lack of labour capacity is also prompting the consideration of alternative solutions.
The solution that emerged from Wouter's co-creation process was WijkWise. In this work session, Wouter aimed to validate the WijkWise concept and find parties that could contribute to its development and market implementation. Dave van Loon from Kennisland moderated the session.
WijkWise – Understanding the neighbourhood's grid situation
The WijkWise concept focuses on three problems:
- The growth of grid congestion at low-voltage
- Homeowners' uncertainty about making sustainable investments. For instance, because they may not know if their solar panels will yield a good return.
- Homeowners' lack of awareness regarding the impact their choices have on the stability of the grid.
The proposed solution:
"With WijkWise, Alliander continues to facilitate homeowners in making their homes more sustainable. Alliander does this by providing insight into the neighbourhood's grid situation and recommending the best investment. Residents can make informed choices that contribute to payback time, comfort, and certainty. A good choice benefits both the homeowner and the grid operator."
The idea is to provide more insight into the neighbourhood's grid situation and offer tailored advice for home sustainability. This way, homeowners can determine whether they should invest in insulation, a heat pump, or solar panels.
Alliander does not want to develop this concept alone, but is seeking partners to bring this concept to market.
Discussion
After the concept presentation, a brief discussion followed. The main questions raised were:
- Can providing insight into the neighbourhood's grid situation have (negative) effects on the housing market?
→ They don't know yet; further investigation is needed. - Can this data be shared freely?
→ The data shared will be at the neighbourhood level (transformer level) and not in real-time (monthly). If there is user data involved, consent must be obtained. - What behaviour change do you expect?
→ That, during the investment moment, consideration will be given to the grid situation for the most advantageous investment.
After the discussion, we worked in groups with the Empathy Canvas from Kennisland to view the WijkWise concept from the perspective of the homeowners. This tool helped us really view the problems from the perspective of a homeowner.
Empathy Mapping
In three groups, we delved into the homeowner's situation. The recurring themes in the empathy maps were:
- A sense of unfairness for the homeowner. They invest in sustainability and are rewarded with grid congestion problems.
- A feeling of uncertainty for the homeowner. They want assurance that their investment will yield results.
- Little trust in the grid operator and the government. First, everyone had to get solar panels, and now suddenly it doesn't fit, and net metering is being discontinued (or not?)
- Limited understanding by homeowners because they find it very complicated and don't want to delve into it. It's not an urgent problem for them.
- Collaboratively seeking solutions can be very positive, but can also lead to friction.
Alliander plans to take the next steps with this concept in 2024. In 2024, they are planning to do the follow-up research, make the minimal viable product, and launch the first version of the product at the end of the year.
Do you know of any stakeholders that absolutely need to be involved, or would you like to be involved in the implementation of the WijkWise concept? Please contact Noor at noor@amsterdamsmartcity.com. Special thanks to Wouter and Dave for this interesting session.
Stay up to date
Get notified about new updates, opportunities or events that match your interests.

