Stay in the know on all smart updates of your favorite topics.
Demoday #28: From Policy to Practice: Inclusive Design Ambitions of the Amsterdam Transport Authority

On the 5th of June, during the 28th Knowledge and Demo Day, we explored the topic of Inclusive Design in the context of mobility projects together with a diverse group of network partners. Iris Ruysch introduced the theme on behalf of the Amsterdam Transport Authority (Vervoerregio), while David Koop and Lotte de Wolde from our knowledge partner Flatland facilitated the session format, moderation and visual notes.
The ambition of the Amsterdam Transport Authority
The Amsterdam Transport Authority is responsible for public transport across fourteen municipalities in the region and is working towards a mobility system that enables people to travel quickly, safely and comfortably by public transport, bicycle or car. In addition to organising and funding public transport and investing in infrastructure, the Authority actively contributes to broader societal goals such as sustainability, health and inclusivity.
Inclusive mobility is one of the key themes within the wider mobility policy. The central principle is that everyone – regardless of age, income, disability, gender or background – should be able to travel well and comfortably throughout the region. This calls for a mobility system that is accessible, affordable, appropriate, socially safe and welcoming.
The aim of the session on 5 June was to work with the network towards an initial action plan for applying inclusive design principles in mobility projects. Iris is keen to ensure that the ambitions around inclusivity are not only stated in policy and vision documents but are truly embedded in the organisation – from policymakers to implementation teams.
Session set-up
After an introduction by Iris on the context and ambitions within the Transport Authority, we got to work. In small groups, participants explored the profile of the implementing civil servant (using a persona canvas) and considered desirable changes in approach; in terms of attitude, skills and collaboration.
We then used the Inclusive Design Wheel to examine how existing programme components of the Authority could be made more inclusive. In pairs, we tackled themes such as accessible travel information, social safety at stations (specifically for women), and improving bicycle parking facilities.
The Inclusive Design Wheel is an iterative process model that supports the structural integration of inclusivity into design and policy projects. The model emphasises collaboration, repetition, and continuous learning. It consists of four phases:
- Explore: Gather insights about users, their needs, and potential exclusion.
- Create: Develop ideas, concepts, and prototypes that address inclusive needs.
- Evaluate: Test whether the designs are inclusive, collect feedback, and make improvements where necessary.
- Manage: Ensure shared understanding, set goals, engage stakeholders, and embed the process.
Outcomes and insights
While the persona profiles were being developed, I observed the group discussions and noted several important insights to take forward in the development of the action plan:
- Awareness and concrete translation: Implementation teams often already have an intrinsic motivation to contribute to inclusivity goals set in policy. However, they may not always realise how their day-to-day work can support those goals. It’s important to continuously ask the question ‘How, exactly?’. Tools like checklists, templates and practical examples can support this translation from policy to practice.
- Flexible guidelines and not ‘extra work’: Given the differences in scale, pace and content of projects, guidelines need to be flexible. There must also be sufficient room in terms of time and budget. Most importantly, these guidelines and action plans should feel supportive, not like extra rules or bureaucracy. Too many rigid frameworks can backfire.
- Interaction between policy and implementation: There is a need for more two-way communication. Implementation teams want to be involved early in policy development, especially when they will be the ones carrying it out. They also want opportunities to reflect with policymakers on whether policy is being implemented as intended. This allows for timely feedback and course-correction based on real-world experience.
- An Inclusive Design mindset: Beyond sharpened policy documents and a stronger focus on the end user, Inclusive Design also requires a mindset – one that is inquisitive and reflective. Embedding this within the organisational culture will require more than just an action plan.
What’s next
Iris collected valuable input to kick-start the development of the action plan, and participants gained a better understanding of the Amsterdam Transport Authority, the principles of Inclusive Design, and what it takes to move from policy to implementation. This summer, a trainee will start at the Transport Authority to further develop this topic and the action plan. The session, this report, and Flatland’s visual notes provide a strong foundation to build on. We’ll be meeting with Iris and David to explore how we can support this follow-up.
Would you like to learn more about any of the topics or developments mentioned in this report? Feel free to email pelle@amsterdaminchange.com.
Apply for The Next 750 and attend TNW Conference

Your talent, recognized
LET'S CELEBRATE YOU!
The Next 750 builds upon the legacy of our renowned T500 program, expanding our recognition platform in honor of <strong>Amsterdam's 750th anniversary</strong>.
This is a celebration of exceptional talent in tech and entrepreneurship, showcasing individuals who are shaping the future across three categories:
- <strong>Rising Stars</strong>: Talents under 30 redefining innovation
- <strong>Inclusion Champions</strong>: Diverse individuals driving change through unique perspectives
- <strong>Amsterdam Changemakers</strong>: Local pioneers making an impact in the Amsterdam community
TNW Conference is proud to use its platform to honor and empower these 750 incredible talents.
Tech moves fast, but it’s powered by people. That’s why we’re giving The Next 750 access to TNW Conference 2025 — to connect them with the visibility, tools, and networks they need to thrive.
We’re shining a spotlight on the movers, makers, and game-changers shaping what’s next. Their contributions deserve to be celebrated, their potential amplified. Together, we’re not just building the future of Amsterdam—we’re shaping the future of the world.
A panel of judges will carefully review applications based on the following criteria: relevant (work) experience, side projects, and personal accomplishments to find the best candidates.
Applications are <strong>now open.</strong> This program is a great opportunity to connect with some of the most talented individuals in the digital tech industry, and you don't wanna miss it!
Stream the Amsterdam Forever Young Programme on Eye Film Player

Discover the Amsterdam Forever Young program on the Eye Film Player, a diverse programme that explores the dynamic, ever-evolving spirit of Amsterdam. This collection of films highlights how the city’s unique identity has been shaped by its past, present, and future. Hence, we place a special focus on the intersection of urban development and planning, offering a look at how the city’s architectural and cultural transformations have intertwined in, both, historical films, as well as more contemporary filmic undertakings. Thus, our collection of films, such as Where the Rats are King, A Photographer Films Amsterdam and Amsterdam Global Village, shed light on the living conditions in Amsterdam, the urban communities witihin Amsterdam and, even, films as Jenny and Amsterdam on Film that shed light on how the canals have shaped Amsterdam more than aesthetically e.g., with its focus on ecology and care for our climate. Through, both, monetized and free to watch films, we aim to share the rich history of our city, whilst aiming for a dynamic space for creativity, inclusivity, and sustainability in the future, too that we hope this knowledge and collection will inspire.
All in all, Amsterdam Forever Young invites you to reflect on the city's evolution and its commitment to being a centre of modernity, without losing the essence of its heritage. Available on the Eye Film Player, to watch from your bedroom, this "digital" exhibition celebrates Amsterdam as the city of urban transformation that, at the same time, stay true to its historical roots.
Dissemination conference of our EU funded project AnthroAction: increasing employability and societal impact of action researchers.

Namla and Univerzita Pardubice Anthropology Department are hosting a one time mini conference next week on the results of our project in Erasmus Plus called AnthroAction: increasing employability and societal impact of action researchers. (https://erasmus-plus.ec.europa.eu/projects/search/details/2023-2-NL01-KA210-ADU-000180400)
We have been running the project since March 2024 and just wrapped up our pilot course for graduates of anthropology in Czech Republic and Netherlands; where the graduates learned to combine rapid ethnography and design thinking to tackle a real-world problem, suggested by real NGOs.
The NGOs that contributed to the project were:
-Czech Blind United (https://www.sons.cz/) with the question: how can we attract more younger members to our organisation?
-Junak - Czech Scouts (https://www.skaut.cz/) with the question: what do today’s teenagers want in leadership training?
-De Meevaart Community Centre (https://meevaart.nl/) with the question: how can we start a blue zone in Indische Buurt in Amsterdam?
-The Really Healthy School (https://www.skutecnezdravaskola.cz/) with the question: how can we reach more primary schools with our programme?
The participants in the course were coming from all over Czech Republic, and Amsterdam.
In the conference, we will discuss what happened in the course, how it went, what we can learn from the pilot. Also a number of professors in Anthropology from different parts of Europe (such as Laurens Bakker, Ana-Isabel Afonso), applied anthropologists from Czech Republic (such as Karolina Kania, PhD, Socionaut, z.s.), as well as organisations in our network will share reflections on how what we did here fits into a wider context.
Please register here before January 22nd: https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSfGfI-vtCTk3XdaGpZvlK37y2VKqZqIV1LUfUiJhsD0OqFlxg/viewform
and join the conference at this Zoom link:
Zoom link: https://us02web.zoom.us/j/89954251812?pwd=78KpFxVY3rXY682mEbErjDl7woYVnR.1#success
Meeting ID: 899 5425 1812
Password: 514987
Zero Emission Urban Logistics Challenge

From January 1 2025, a zero-emission zone will be introduced in the centre of Amsterdam, with the aim of improving air quality and making the city healthier and more liveable. This policy helps achieve climate goals and supports the ambition of becoming climate neutral by 2050. It encourages zero-emission urban logistics, which contributes to reduced pollution, noise, and traffic congestion. And cleaner air also has positive effects on the health and well-being of residents. With this initiative, Amsterdam - and other Dutch cities implementing such zones this year - aim to set an example for other cities and stimulate innovation in sustainable mobility. The so-called "zero-emission zone" is therefore an essential measure in the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable city.
This transition will only succeed through collaboration. Therefore, considerable attention is being paid to the experiences and needs of small business owners in the city. Think of; market vendors, house painters, and local greengrocers. What kind of support do they need to transition to zero-emission vehicles, and how do entrepreneurs creatively adapt to the transition and new rules? Other cities and municipalities are closely observing and there is a strong need for knowledge sharing. It is important that the experiences and lessons learned from Amsterdam, as one of the pioneers, are well-documented and shared on a national and international scale.
Smart Dublin presenteert haar Active Mobility Dashboard en vraagt jullie mening!

Hallo allen! Ik deel graag de uitnodiging voor een online webinar van EIT Urban Mobility. Op woensdag 𝟐𝟕 𝐧𝐨𝐯𝐞𝐦𝐛𝐞𝐫 organiseert EIT Urban Mobility samen met Smart Dublin een interessant webinar over ‘actieve mobiliteit in de stad’.
💡 Ze presenteren een nieuwe, innovatieve oplossing die recent in Dublin in gebruik is genomen en gaan in op ideeën en uitdagingen rond Actieve Mobiliteit – een thema dat natuurlijk past binnen de slimme stad.
🏙️✨ Zeker de moeite waard om bij te zijn!
ℹ️ Het webinar is in het Engels. Doe je mee? 👉 Meld u aan voor deze webinar via : https://kennislab.typeform.com/to/J8Ef0Vd8
Data Dilemmas Recap: Using Data and AI for an Accessible Amsterdam

On September 26th, our community gathered in the AHK Culture Club at Marineterrein Amsterdam for our Datadilemma’s series. This edition focused on the use of Data and AI to create a more accessible Amsterdam. This article presents some of the key highlights and insights from the afternoon.
Together with the three speakers, Vishruth Krishnan, Hans Voerknecht, Michiel Bontenbal, and our audience we discussed how data and AI can help make our city more accessible for all. Which dilemma’s do we encounter when we use new technologies for an accessible city? How can data help to get more understanding of unequal access to mobility in the country? And what about sounds and noise pollution; how can data help make te city more livable?
What the three speakers had in common; a personal motivation to get away from the surface and dive deeper into the data, attempting to get closer to people’s experiences and perceptions. From an ordinary routeplanner, to one paying specific attention to challenges for people in weelchairs. From generic accesibility data for the region, to data highlighting the unequal distribution of access to mobility. And from recording noise levels, to measuring and classifying all different sounds in urban settings. In the paragraphs below, I will delve deeper into the different speakers and their topics.
Visruth Krishnan – Personalized Route Planner for People in a Wheelchair
To help individuals with limited mobility navigate the city more easily, the city’s innovation department has developed a prototype route planning tool. This route planner maps out the most accessible routes based on personal needs, considering preferences like maximum curb height at crossings, minimum sidewalk width, and whether to prioritize sidewalks or bike paths.
Visruth Krishnan, Data Scientist at the Innovation Department of the Municipality of Amsterdam, explained how data helps facilitate travel from point A to point B. However, to ensure route planning tools address the challenges faced by wheelchair users, we must feed these systems with data drawn from real-world experiences. A person’s journey might present specific challenges, such as detours, improperly parked bicycles, slopes, and narrow footpaths.
Working with a group of wheelchair users, Visruth studied the obstacles and experiences they encountered on their routes. This research generated precise data to feed the route planner, enabling it to provide personalized route suggestions that account for each individual’s freedom of movement.
Visruth presented several dilemmas encountered during the project:
- Subjectivity in the data: How busy is a sidewalk or intersection perceived to be? Are cyclists at a certain point fast and aggressive, or is that just a feeling?
- Minimal vs. comprehensive data collection: How much data should be gathered? While more data might provide deeper insights, it could also increase privacy risks.
- Accurate vs. timely data: Timely data may not always be accurate, and accurate data may not always be available in time for critical decision-making. Consider issues like illegally parked bikes, construction work, and terraces that vary in size and location depending on the season.
- Transparency vs. complexity: How transparent should data-driven processes be, especially when the algorithms or analytics behind them are complex? AI is often seen as a "black box"—people don’t understand how it works or how data is processed, which can lead to less trust from the start.
To address these challenges, Visruth and his team maintain an ongoing dialogue with the target audience. It’s an iterative process, and they keep the ‘human in the loop.’ The prototype is now ready, and hopefully, it can be further developed!
Hans Voerknecht – Unequal Accesibility and Data to Support The Narrative
Hans Voerknecht, strategist for sustainable accessibility at Een Nieuwe Kijk, presented the Integrated Perspective on Accessibility method, which he developed to get a deeper understanding of people’s accessibility. This method assists in collecting data and analyzing the severity of current inequalities and the effects of policy measures. The method has already been applied in nearly twenty projects, including four in the Amsterdam region, such as the Multimodal Future Vision of the Metropoolregio Amsterdam (MRA).
IKOB stands for "Integrale Kijk Op Bereikbaarheid" (Integrated Perspective/view on Accessibility). IKOB examines the travel time and costs that people face to reach their workplace by bike, car, or public transport and it visualizes how many jobs people can access from a specific area.
IKOB uses 'distance decay curves<strong>,'</strong> meaning that jobs located closer are given more weight than those further away. Travel time and costs are adjusted depending on the target group. Factors considered include income, access to a car, travel cost reimbursement, public transport options, and preference for a mode of transport (car, public transport, or bike). For people with a lower income, costs weigh more heavily than for those with higher incomes.
Throughout his talk, Hans discussed how data can be used to support a narrative, either consciously or unconsciously. Regional research on the state of mobility can quickly paint a positive picture if you're working with averages and fail to examine differences between people. There are groups that experience less access to mobility, and for whom this issue carries more weight due to financial constraints. The way data is researched and how deeply you investigate determines to what extent this group and their challenges are brought into focus.
One of the dilemmas Hans mentioned was the fact that poor accessibility is a personal experience. It’s subjective, and there can be a lot behind it. Regardless of the detail and quality of your data, you can never be completely sure if it truly reflects the human experience it’s supposed to represent.
Michiel Bontenbal – The Urban Sounds Sensor
Our third and final speaker discussed sounds and noise pollution in an urban environment. It may not seem to immediately fit with the rest of the speakers, but urban sound is also important to consider when creating an accessible and liveable city. Michiel Bontenbal, lecturer in business and IT courses at the Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences, told us more about the Urban Sounds sensor, developed in collaboration with the volunteer organization Sensemakers. He explained us more about the challenges they face with this AI-driven solution and raised some dilemmas in his work.
The Urban Sounds Sensor project was developed in response to the need for evidence of nighttime noise disturbances. It was crucial to be able to distinguish between different types of sounds, such as music, mopeds, alarms, doors, car noises, and honking.
Together with the volunteers from Sensemakers, Michiel designed the sensor in such a way that the recorded sounds are neither stored nor released. The microphone registers the sound, and the algorithm in the sensor immediately categorizes it within the device. This approach ensures privacy by design.
Training the sensor is still an ongoing process. Achieving high accuracy is challenging, as even humans sometimes have trouble identifying certain sounds. And, while measuring noise disturbances is definitely getting more attention in the city now. However, this specific method of distinguishing between sound categories is still lagging behind in both development and interest from government authorities.
Michiel concluded his presentation by discussing his dilemmas with the audience. One of his dilemmas, as expected, was about placing microphones in public spaces; how desirable is that, really? It's important to talk about ethics and privacy when measuring in public spaces, especially with a sound sensor that isn’t visible. His second point focused on the experience of city sounds. How you perceive sounds depends on personal experiences and preferences. Some people enjoy urban sounds, like the noise of a tram or ringing bike bells. People may have associations with certain sounds that determine whether they find them annoying, don't even notice them, or actually enjoy them. This is a factor that a sound sensor and the data it collects have difficulty accounting for.
Panel Discussion
After the presentations, we brought the speakers together for a panel discussion. Led by Chris de Veer, programme manager Mobility at Amsterdam InChange, there was an engaging conversation with the audience. To wrap things up, I’d like to highlight three key statements made by the speakers in response to some critical questions from the audience:
- "We often try to objectify the world with data, but there is no objective truth. However, diving deep into data can give you a better and more diverse understanding of an issue or region." – Hans
- "Data is always messy. If the data we input is messy, the outcome will also be messy. Garbage in, garbage out." – Michiel
- “The Route Planner method and platform could be of great use in gaining a better overview of building accessibility throughout the city.” - Visruth
Thanks to the speakers for their stories and to the audience for the lively discussions afterwards. Want to join us for our next Data Dilemmas event? The next edition of this series of open events will be announced soon. We’re also always open to new themes and topics for this series; we’re curious to hear about the data dilemmas you encounter in your work!
Using AI for All Amsterdammers

Modern technologies can be used in various ways to make life easier. But if we’re not careful, these possibilities will mainly benefit people who already have it easy. What can technology mean for people who, for one reason or another, have a harder time in society, for example, because they are hard of hearing, have little money, or are immigrants?
The EU project CommuniCity encourages the development of tech solutions for and with various marginalized and/or vulnerable groups. This afternoon, we will present serveral of the pilots that were carried out over the past year, demonstrating how artificial intelligence and other technologies can contribute to the well-being of various residents of Amsterdam.
De Interdisciplinaire Afstudeerkring - Mobiliteitsrechtvaardigheid. HvA x PNH x ASC

ENGLISH BELOW
Gedurende de eerste helft van 2024 werkten we samen met vier studenten van de Hogeschool van Amsterdam (HvA) op het thema Mobiliteitsrechtvaardigheid. Samen met de provincie Noord-Holland waren we als opdrachtgevers onderdeel van een primeur: De eerste interdisciplinaire afstudeerkring van de Hogeschool van Amsterdam. De afstudeerders kwamen vanuit verschillende opleidingen. De groep van vier bestond uit twee Bestuurskunde studenten (Jade Salomons en Timo van Elst), een student Toegepaste Psychologie (Jackie Ippel), en een student Communicatie en Multimedia Design (Merel Thuis).
De HvA wilt haar studenten al vroeg bekend maken met interdisciplinair samenwerken en onderzoeken. Een domein-overstijgend en complex vraagstuk als Mobiliteitsrechtvaardigheid, wat al langere tijd binnen het Amsterdam Smart City netwerk wordt behandeld, bleek een mooi onderwerp voor hun eerste afstudeerkring. Voor zowel de HvA en de opdrachtgevers was er veel nieuw aan dit project en waren er veel onzekerheden, maar vanuit onze waarde ‘leren door te doen’ gingen we samen aan de slag!
Resultaten
Na een kick-off met de leden van de Mobiliteitsrechtvaardigheid werkgroep en verkennende interviews met specialisten van Provincie Noord-Holland vormden de studenten concrete onderzoeksvragen. Na een brede introductie en vraagstelling hebben de studenten een deelonderwerp eigen gemaakt en hun afstudeeropdracht daarop ingericht. Bij deze licht ik kort toe wat de verschillende onderwerpen en resultaten waren. Bij vervolgvragen kunnen jullie mij of Bas Gerbrandy (PNH) een berichtje sturen.
- Timo keek naar het grotere plaatje en bestudeerde hoe het mobiliteitsbeleid in Noord-Holland nu is ingericht, met name met betrekking tot Mobiliteitsarmoede. Ook keek hij hoe participatiemethoden hier nu een rol in had. Hij schreef een advies waarin hij bijvoorbeeld pleit voor het installeren van participatie experts per domein/sector, in plaats van het als een apart team beschouwen.
- Jackie verdiepte zich nog meer in hoe ambtenaren zich verhouden tot de doelgroep die mobiliteitsarmoede kan ervaren. Zij onderzocht de bereidheid van ambtenaren om in gesprek te gaan met de doelgroep. Een belangrijk onderdeel wat velen nog een spannend idee vinden. Ook hielp Jackie mee met Jade’s focusgroep en kwalitatieve onderzoek.
- Jade ging namelijk het veld in. Ze sprak ouderen in Purmerend over hun reiservaringen en wat voor belemmeringen ze ervaren. Haar onderzoek bewees hoe belangrijk dit onderdeel is. Ze lichtten bijvoorbeeld uit dat ouderenvervoer goed geregeld is, maar dat ze angstig kunnen zijn tijdens hun reisbewegingen. Slechte kwaliteit van voetpaden en het snelle optrekken van een bus is waar ze het veel over wilden hebben.
- Ten slotte ging Merel aan de slag met een multidevice ontwerp. Ze creëerde een tool waarmee belevingen van inwoners op persoonlijk niveau uitgevraagd kunnen worden. Vervolgens wordt hierin inzichtelijk en tastbaar gemaakt wat beleidsrisico’s en -kansen zijn voor de sector Mobiliteit van de provincie. Het dient zo als gesprekstool en brug tussen de persoonlijke ervaringen van inwoners en de abstractere en strategische niveau van de beleidsmedewerkers.
Interdisciplinair en organisatie-overstijgend samenwerken
Het is een intensieve periode geweest waarin we het de studenten, en hun afstudeerbegeleiders, niet altijd makkelijk hebben gemaakt. Het project stelde namelijk bloot hoe de afstudeertrajecten en -eisen verschillen per studie en faculteit binnen de HvA. De studenten en docenten gingen hier uiteindelijk soepel mee om, maar dit was zeker wennen voor ze tijdens de start van de afstudeerkring. Ook voor de opdrachtgevers en begeleiders was het een leerproces waarin we samen in een iteratief proces onze werkwijze en opdrachten moesten aanpassen.
Bij veel van de vraagstukken die langskomen in het Amsterdam Smart City netwerk gaat het over het belang van domein overstijgend werken en hoe veel moeite grote (overheids)organisaties hier mee hebben. Juist daarom kijken we tevreden en trots terug op dit proces. Op deze manier hebben we de studenten voor de start van hun carrière al laten kennismaken met het samenwerken op maatschappelijke vraagstukken, met anderen, die vanuit hun eigen expertise, achtergrond en creativiteit naar problemen en oplossingen kijken.
Hogeschool van Amsterdam is op zoek naar een nieuw vraagstuk!
Ook komend jaar (start 2025) gaan we weer met veel enthousiasme aan de slag met een vraagstuk voor een nieuwe lichting afstudeerders. Om het onderwerp verder te brengen en om samen nog meer te leren over interdisciplinair samenwerken aan maatschappelijke vraagstukken. Samen met de HvA zijn we daarom op zoek naar een nieuw maatschappelijk vraagstuk voor de volgende groep afstudeerders. We zijn op zoek naar een onderwerp, maar ook een organisatie die, in combinatie met een ASC collega, als mede-opdrachtgever en begeleider zal optreden. Dit kan uiteraard in samenwerking met andere ASC partners.
Het onderwerp zal eind september bekend moeten zijn. In de weken die daarop volgen, zal de (groeps)opdracht gefinetuned worden en start de werving van geschikte studenten die in 2025 afstuderen.
Voor meer informatie kun je contact opnemen met Marije Poel (m.h.poel@hva.nl), Nora Rodenburg (n.m.rodenburg@hva.nl) of mij (pelle@amsterdamsmartcity.com)
________________________________________
ENGLISH:
During the first half of 2024, we collaborated with four students from the Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences (HvA) on the theme of Mobility Justice. Together with the Province of North Holland, we had the privilege of being part of a pioneering project: the first interdisciplinary graduation circle at the HvA. The graduates came from different programmes, and the group of four included two Public Administration students (Jade Salomons and Timo van Elst), a student Applied Psychology (Jackie Ippel), and a Communication and Multimedia Design student (Merel Thuis).
The HvA aims to familiarise its students early on with interdisciplinary collaboration and research. A complex, cross-domain issue like Mobility Justice, which has been a topic of focus within the Amsterdam Smart City network for some time (LINK), proved to be an excellent subject for their first graduation circle. For both the HvA and the commissioners of the topic, this project was new and presented many uncertainties, but driven by our value of ‘learning by doing,’ we embarked on this journey together!
Results
Following a kick-off with members of the Mobility Justice working group and exploratory interviews with specialists from the Province of North Holland, the students began to formulate concrete research questions. After a broad introduction and question formulation, each student chose a specific sub-topic to focus on for their graduation project. Below, I briefly outline the different topics and results. For further questions, feel free to contact me or Bas Gerbrandy (PNH, bas.gerbrandy@noord-holland.nl).
- Timo looked at the bigger picture, studying how mobility policy is currently structured in North Holland, particularly concerning Mobility Poverty. He also examined the role of participation methods in this context. In his advisory report, he advocates, for example, the installation of participation experts per domain/sector, rather than considering it as a separate team.
- Jackie delved deeper into how civil servants relate to the target group that may experience mobility poverty. She investigated the willingness of civil servants to engage in dialogue with this group, an essential aspect that many still find daunting. Jackie also assisted with Jade's focus group and qualitative research.
- Jade took to the field, speaking with the elderly in Purmerend about their travel experiences and the barriers they face. Her research highlighted the importance of this issue. For instance, she found that while transport services for the elderly are well-organised, they often feel anxious during their journeys. Poor pavement conditions and the sudden acceleration of buses were frequent topics of concern.
- Finally, Merel worked on a multi-device design. She created a tool that can be used to gather personal experiences from residents. This tool then makes the policy risks and opportunities for the Mobility sector in the province more visible and tangible. It serves as a discussion tool and a bridge between the personal experiences of residents and the more abstract, strategic level of policy officers.
Interdisciplinary and Cross-Organisational Collaboration
It has been an intensive period in which we didn’t always make it easy for the students and their graduation supervisors. The project revealed how graduation trajectories and requirements vary across programmes and faculties within the HvA. The students and lecturers eventually handled this smoothly, but it was certainly an adjustment for them at the start of the graduation circle. It was also a learning process for the supervisors, where we had to iteratively adapt our working methods and assignments together.
Many of the issues that arise in the Amsterdam Smart City network relate to the importance of cross-domain collaboration and the difficulties that large (government) organisations often face with this. That’s why we look back on this process with satisfaction and pride. We have introduced the students to the practice of working on social issues, with others who bring their own expertise, background, and creativity to the table, before the start of their careers.
Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences is Looking for a New Topic!
Next year (start of 2025), we will again enthusiastically tackle a new topic with a fresh group of graduates, to further advance the subject and learn even more about interdisciplinary collaboration on social issues. Together with the HvA, we are therefore looking for a new social issue for the next group of graduates. We are searching for a topic, as well as an organisation that, in combination with an ASC colleague, will act as a co-client and supervisor. This can, of course, be in collaboration with other ASC partners.
The topic should be finalised by the end of September. In the weeks after, the (group) assignment will be fine-tuned, and the recruitment of suitable students graduating in 2025 will begin.
For more information, you can contact Marije Poel (m.h.poel@hva.nl), Nora Rodenburg (n.m.rodenburg@hva.nl), or me (pelle@amsterdamsmartcity.com).
Demoday #24: Exploring the public transport of the future with Amsterdam’s Mobility Radar (2024)

Yuki Tol and Joaquim Moody, trend watchers for Smart Mobility at the Innovation Department of the Municipality of Amsterdam, delivered the Mobility Radar on future public Transport.Twee 'moonshots' geven je een,van zo'n 11 jaar) this March. In this first edition, the Amsterdam Smart Mobility program delves deeper into the city's mobility challenges. Will staff and funding shortages, the energy transition, and a growing demand for (accessible) transport options continue to impact the city's future public Transport system? Two 'moonshots' give us a glimpse into the future, showing what public Transport might look like in 2050.
The new concession for public Transport in Amsterdam is nearly ready and will commence in 2025 for a period of approximately 11 years. This is a good time to engage in discussions about the steps that need to be taken to achieve the goals and ambitions set for 2050. It is also crucial to determine what measures are necessary to address the developments that public Transport will face in the future. If the current system is continued, we are only one or two concessions away from 2050. Therefore, now is the time to start working on developments, innovations, and concepts that we want to include in the concessions for the 2030s and 2040s.
Exploring the future together
The Radar team has developed a workshop to engage with various organizations, experts, residents, and enthusiasts to discuss the Mobility Radar. In this workshop, participants jointly explore the trends and developments that can influence the future of mobility. It is a great way for participants to practice this way of thinking, and such a session also brings up topics and discussion points that the Municipality of Amsterdam can incorporate into its future explorations and concessions.
During our 24th Knowledge and Demo Day, Joaquim Moody hosted a work session for a diverse group of participants various organizations and domains. In three groups, we analysed an emerging public Transport challenge using the Mobility Radar approach and creatively thought about solutions. In the following paragraphs, I summarize what we discussed with the group.
Method
The starting point is a number of current challenges in public Transport: staff shortages, funding shortages, accessibility, the energy transition, and the growing demand for public Transport.
Each group selects one of the challenges and then 'dissects' it. Using a worksheet, you look at the following topics: What basic need underlies this challenge? What are examples of how or where you see this challenge currently? What macro changes play a role in the emergence of this challenge – in the long and short term? And how do these macro changes affect which basic needs are important and how they are fulfilled?
Next, you start creating a solution for this challenge and trend. Examples of solutions are: a service, a product, a regulatory adjustment, or an informative campaign. You also need to consider how you would deploy it and who exactly the target audience is.
Results
Accessibility
One of the groups analysed the challenge of public transport accessibility. This needs to be adequate for everyone, now and in the future. Accessibility involves affordability, the digital skills required, travel costs, and physical accessibility. This challenge mainly revolves around the basic needs of connectedness, independence, and control. The macro changes playing a role are migration (increasing number of people to be transported) and aging (more people wanting to travel independently but requiring extra assistance – particularly in digital and physical aspects). Therefore, more space and special assistance will be needed for a growing group of travellers.
The group proposed focusing more on 'micro public transport' and 'on-demand public transport' and making bus and train compartments more flexible. This would make people less dependent on a rigid system and travel environment. The group argued that air travel can serve as an example, where you can specify exactly where you want to sit, whether you need extra space, and if you require extra assistance. These needs deserve more attention in public transport as well. This can be tested with prototypes in train cars and buses and is intended for the target groups: the elderly, people with disabilities, and parents with young children.
Staff Shortages in Public transport
The challenge of 'staff shortages in public transport' is reflected in developments such as cancelled schedules, high work pressure, high absenteeism, strikes, and less social control in public transport (due to less staff). The basic needs affected by this challenge are the need for social status, financial security (for the driver), and a pleasant, healthy workplace. Macro changes playing a role include the large number of job opportunities in other sectors, increasing aggression and hardening in society, worsening public perception of public transport, and aging. As a result, working in public transport has become less prestigious, less safe, relatively less well-paid, and there is little influx of new, young employees.
The group proposed a campaign to improve the image of working in public transport. Currently, too few people choose this profession. However, with campaigns similar to those by the Defense Department, it could be made trendy and attractive again. Influencers or famous Dutch people could also play a role in this. The target audience to be enthused includes young starters and people considering a career switch.
The Growing Demand for public transport
Finally, the third group presented their worksheet regarding the challenge of the growing demand for public transport (and the decline in public transport investments). This is reflected in the decline in service quality, travel options, and the fact that less equipment is available. This affects the basic needs of comfort, connection, and being able to be oneself). Macro changes exacerbating these challenges include the decreasing space for mobility, individualization as a societal development, and increasing travel costs. This leads to a kind of public transport anxiety, aversion, and aggression, which is already happening and is only getting worse, the group noted.
The group proposed recognizing the societal role of public transport more, which would lead to more respect and funding. We should also further 'de-peak' travel times by better aligning telecommuting days or departure times for employees. This can be tested with pilots in specific (travel) areas or with large employers. The target audience can be seen as all travellers together.
Follow-Up
Joaquim will use the presented analyses and solutions as inspiration for further research and use the feedback on the method and workshop to improve such sessions in the future. Enthusiastic participants also wanted to use this method for sessions with students and international delegations, illustrating its success!
During the upcoming Knowledge- and Demo Day, we will have another session on mobility with a similar approach, but this time we will work with the scenario studies made by the Province of North Holland. Thinking about the future using trends, scenarios, and moonshots is essential in every domain, especially when done with a diverse group and maintaining connection.
Trainee Event Slimme en Schone Mobiliteit

Intro
Op woensdag 19 juni 2024 vond het trainee event Smart Mobility plaats bij AMS. Verschillende prominente organisaties waren aanwezig, waaronder de provincies Noord-Holland en Utrecht, de Metropoolregio Amsterdam (MRA), het MRA platform Smart Mobility, de Vervoerregio Amsterdam (VRA), en de gemeente Utrecht. Het evenement richtte zich op verschillende thema’s binnen de slimme en schone mobiliteit.
Doelen van het Evenement
Het evenement had drie hoofddoelen:
· Kennis vergaren: Inzicht krijgen in de nieuwste ontwikkelingen en uitdagingen op het gebied van slimme mobiliteit.
· Netwerken: Verbinding maken met professionals uit verschillende regio’s en sectoren.
· Teamwork: Samenwerken aan oplossingen voor actuele mobiliteitsvraagstukken.
Sprekers
Daniël van Motman (VRA en MRA-platform Smart Mobility)
Daniël van Motman gaf een uitgebreide presentatie over de huidige stand van zaken in de woningbouw, de schaarste aan mensen en grondstoffen, en het belang van duurzame samenwerking. Hij benadrukte dat, ondanks technologische vooruitgang, de mens nog steeds de slimste factor blijft in slimme mobiliteit.
Sander Oudbier (AMS)
Sander Oudbier presenteerde verschillende projecten die momenteel lopen binnen AMS, zoals City Flows, Smart Hubs en Code the Streets. Hij besprak ook educatieve initiatieven zoals MaaS for Elderly en het autovrije marine terrein. Een bijzonder project dat werd uitgelicht was de ontwikkeling van Roboat, dat zal worden ingezet tijdens de Olympische Spelen in Parijs. Daarnaast werd het project Digitale Regie op de Openbare Ruimte (DRO) besproken, dat de komende vijf jaar zal lopen vanuit DMI.
Pelle Menke (Amsterdam Smart City)
Pelle Menke presenteerde de thema’s mobiliteitsrechtvaardigheid en CO2-vrij reizen naar de JC ArenA. Hij benadrukte dat mobiliteit voor veel mensen moeilijker wordt en specifieke subgroepen unieke wensen hebben. Een werkgroep onderzoekt mogelijke oplossingen door kennisdeling en samenwerking met overheden. Ook werd een challenge besproken om CO2-vrij naar de JC ArenA te reizen door fiets, openbaar vervoer en deelvervoer te promoten. Samenwerking met vervoerders, evenementenorganisaties zoals Ajax, en gebiedsontwikkelaars is essentieel, evenals gedragsverandering en aanpassing van reisgewoontes.
Workshop: Crowdmanagement voor Sail 2025
De workshop werd verzorgd door Wouter en Maarten van het MRA-platform Smart Mobility.
“Hoe verzorgen we een goed crowdmanagement tijdens Sail 2025?”
De eerste stap in dit proces was het nadenken over ons eigen reisgedrag. We kregen per persoon een modaliteit aangewezen. De vraag was: als je om 12:00 op een bepaalde plek hebt afgesproken met je groep vrienden, wat heb je dan nodig om daar te komen?
Dit zorgde ervoor dat we nadachten over alle voorzieningen zoals (fiets)parkeerplekken en openbaar vervoer. Voor deze voorzieningen heb je data nodig, zoals inzicht in de beschikbaarheid van parkeerplekken en de status van het openbaar vervoer. Ook vanzelfsprekende dingen, zoals het checken van het weer met bijvoorbeeld Buienradar, zijn belangrijk omdat het weer een grote impact heeft op ons reisgedrag.
Daarna stapten wij in de rol van verkeersmanager. We bedachten welke middelen we konden inzetten om bezoekers zo goed en gemakkelijk mogelijk op hun bestemming te krijgen. We dachten aan elementen zoals éénrichtingsverkeer en het aantrekkelijker maken van het openbaar vervoer en de fiets. Dit konden we bewerkstelligen door bijvoorbeeld entertainment in het OV of het verzamelen van tokens op fietsroutes naar het evenement, die je kon inwisselen voor een gratis drankje. Ook kwamen er vragen naar voren zoals: hoe zorg je dat alles toegankelijk is voor iedereen? Hoe zorg je ervoor dat mensen met een beperking ook gemakkelijk naar het event kunnen komen? Hoe zorg je ervoor dat mensen die niet digitaal vaardig zijn, ook alle informatie kunnen krijgen?
Wat vond ik ervan?
Al met al was ik zeer te spreken over dit evenement. Ik heb geleerd dat de wereld van slimme en schone mobiliteit zeer breed is. Er is veel werk te doen in de komende jaren om ervoor te zorgen dat we anders gaan kijken naar mobiliteit. Een belangrijk punt dat ik heb meegenomen, is de filosofie dat de mens nog steeds de slimste factor is in Smart Mobility en dat we de mens echt centraal moeten stellen. Daarnaast is het uiterst belangrijk dat we ervoor zorgen dat de wensen en behoeften van minderheidsgroepen goed worden meegenomen en dat Smart Mobility niet alleen voor de grootste groep mensen is, maar voor iedereen.
Data Dilemma’s: Data and AI for an accessible Amsterdam

This event is postponed to September 26 (was first scheduled on July 16)
We often take daily activities such as commuting to work, independently taking public transport, grocery shopping or going to a restaurant for granted. Unfortunately, not everyone has this privilege. For people with reduced mobility (e.g., wheelchair users), getting around Amsterdam can be tricky. There are a lot of obstacles, such as narrow or bumpy pavements and high curbs.
The municipality of Amsterdam wants to be a free, just and sustainable city for all. For which the accessibility of the city is essential. With the Amsterdam for All initiative, the municipality of Amsterdam researches and experiments with how data and AI can be leveraged to ensure accessibility for its residents. How can the data and AI help to make our city more accessible for all? And which kind of dilemma’s does the city come across?
To help people with less mobility move around the city more easily, the city’s innovation department has created a prototype route planning tool. This route planner maps out the best accessible route for each person based on what they need. It considers preferences like maximum curb height when crossing the road, minimum sidewalk width, and a preference for using sidewalks or bike paths. Vishruth Krishnan, Data Scientist at the Innovation department of the municipality of Amsterdam, will tell you all about this route planner, the necessary data and the dilemma’s faces while using the data.
Hans Voerknecht, strategist for sustainable accessibility at Een Nieuwe Kijk, will speak about the Integrated Perspective on Accessibility method, which he developed to improve accessibility for people. This method assists in collecting data and analyzing the severity of current inequalities and the effects of policy measures. The method has already been applied in nearly twenty projects, including four in the Amsterdam region, such as the Multimodal Future Vision of the Metropoolregio Amsterdam (MRA).
Additionally, Michiel Bontenbal (Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences) tells us more about the Urban Sounds sensor, developed in collaboration with the volunteer organization Sensemakers. He takes us through the challenges they face with this AI-driven solution and presents his question: How can this technical solution best be used around the issue of accessibility?
Agenda
- 15:45 – 16:00 Walk-in
- 16:00 – 16:10 Welcome and introduction by Amsterdam InChange (formerly known as Amsterdam Smart City)
- 16:10 – 16:25 Demo of the Route Planner by Vishruth Krishnan (municipality of Amsterdam)
- 16:25 – 16:35 Hans Voerknecht, strategist for sustainable accessibility, on the Integrated Perspective on Accessibility method.
- 16:35 – 16:45 Michiel Bontenbal from Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences about the Urban Sounds sensor.
- 16:45 – 17:15 panel discussion
- 17:15 – 18:00 drinks
Location
The Culture Club, Amsterdam
About the Data Dilemma’s series
Data Dilemmas is a collaboration between Amsterdam InChange and the City of Amsterdam’s Data Lab. Four times a year we explore the possibilities for using data and new technologies to address urban and societal challenges, with a focus on responsible digitalization. The goal is to use data to make cities more safe, clean and accessible. But what happens to all the data that is collected? Which dilemmas do we encounter when we collect (personal) data to improve the city? These questions are important for everyone: governments, knowledge institutions, companies, and civil society. Amsterdam InChange would like to explore with you which decisions are needed for responsible use of data.
Join AMS Institute's Scientific Conference, hosted by TU Delft, Wageningen University & Research, MIT and the City of Amsterdam.

Do you want to learn from and network with the best researchers and scientists working to tackle pressing urban challenges?
AMS Institute, is organizing the AMS Scientific Conference from April 23-25 at the Marineterrein, Amsterdam, to address pressing urban challenges. The event is organized in collaboration with the City of Amsterdam.
The conference brings together leading institutions in urban research and innovation, thought leaders, municipalities, researchers, and practitioners to explore innovative solutions for sustainable development in Amsterdam and other global cities.
Keynotes, research workshops, learning tracks, and special sessions will explore the latest papers in the fields of mobility, circularity, energy transition, climate adaptation, urban food systems, digitization, diversity, inclusion, living labs experimentation, and transdisciplinary research.
Attendees can expect to gain valuable insights into cutting-edge research and engage in meaningful discussions with leading experts in their field. You can see the full program and all available sessions here.
This year's theme is 'Blueprints for messy cities? Navigating the interplay of order and messiness'.
The program
Day 1: The good, the bad, and the ugly
Keynotes by Paul Behrens of Leiden University and Elin Andersdotter Fabre of UN-Habitat will be followed by a city panel including climate activist <strong>Hannah Prins</strong>. The first day concludes with a dinner at the Koepelkerk in Amsterdam: you're welcome to join our three-course meal with a 50 euro ticket.
Day 2️: Amazing discoveries
Keynotes by Carlo Ratti of MIT and Sacha Stolp of the Municipality of Amsterdam discuss innovation and research in cities. <strong>Corinne Vigreux</strong>, co-founder of TomTom, and Erik Versnel from Rabobank will participate in the city panel.
Day 3️: We are the city
Keynotes by Paul Chatterton of Leeds University and Victor Neequaye Kotey Deputy Director of the Waste Management Department of the Accra Metropolitan Assembly, Ghana. They discuss how we shape the future of our cities together. This will be followed by a city panel including Ria Braaf-Fränkel of WomenMakeTheCity and prof. dr. Aleid Brouwer of the Rijksuniversiteit Groningen.
To buy tickets: You can secure your conference tickets through our website.
Dinner tickets: On April 23 we’re hosting a dinner at the Koepelkerk in Amsterdam. Tickets for this can be added to your conference pass or bought separately.
Supporting Sustainable Technology Education Through E-Waste Recycling

🌍✨ Join Us in Making a Difference! ✨🌍
We're excited to launch a groundbreaking project aimed at transforming e-waste into educational opportunities! 🚀📚 As part of our commitment to sustainability and digital literacy, we're collecting smartphones, laptops, and other electronics to support vibrant educational workshops in Rwanda.
Why join us? By participating, you'll:
- 🌱 Support environmental sustainability by helping reduce e-waste.
- 📖 Contribute to enhancing digital literacy among underserved communities.
- 🤝 Be part of a global movement advocating for responsible technology use.
- 🎓 Help provide essential skills that can transform lives and foster long-term growth.
We're looking for individuals and organizations to donate devices, share expertise, or sponsor our efforts. Every contribution makes a real difference, and together, we can create a more sustainable and inclusive future. 🌟
Let's reshape the future, one device at a time. Join us in this exciting journey and be credited in our upcoming documentary that highlights the collective efforts of our incredible partners from Germany, Latvia, and the Netherlands. 🎥🌍
CONTACT US THROUGH EMAIL - madaralace1999@gmail.com
Mobiliteit als schaars goed - Denk mee: Hoe regelen we het recht om te reizen?

Mobiliteit staat voor vrijheid, maar zorgt ook voor ongelijke lasten. Tijdens deze sessie onderzoeken we samen in een interactieve simulatie een systeem dat met 'mobiliteitskrediet' werkt. Wat zijn de effecten voor de samenleving? Biedt het kansen voor een eerlijkere verdeling om maakt het de ongelijkheid alleen maar groter?
Deze avond is onderdeel van een studie van de TU Delft, in samenwerking met AMS Institute en gemeente Amsterdam. Let op: Om deel te nemen aan deze avond in Pakhuis de Zwijger, heb je een werkende smartphone nodig.
NB. Deelname aan de sessie wordt beloond met een VVV-bon ter waarde van 10-euro.
Aanmelden kan via de website van Pakhuis de Zwijger https://dezwijger.nl/programma/mobiliteit-als-schaars-goed
Wanneer: Dinsdag 23 april
Hoe laat: 19:30-21:30
Waar: Pakhuis de Zwijger, IJzaal (Piet Heinkade 179, 1019 HC Amsterdam)
Online Just Sustainability Transitions Course

Do you believe, like us, that sustainability and social justice are key to fundamental change? ‘Just Sustainability Transitions’ is a six-month online course that provides the tools and inspiration you need to create your own transition strategy. This year, we're organising a third edition!
The Just Sustainability Transitions peer-learning course draws from our latest action research insights on justice, sustainability transitions and social innovation. This is the third year we are organising this course, which brings you best practices and personal experiences we gathered during our work on transition processes in different settings and countries – in Europe and across the globe.
How can we facilitate and accelerate societal transformation? And how can we really bring in diverse allies to drive systemic change? This course helps you find answers to such questions by combining state-of-the-art research with deep critical reflection and applied action learning. We provide a diversity of perspectives that help you discover what works for you.
Special attention is given to tools and methods with which you can organise a process of transition in your area, organization or sector.
Your guides on this journey will be young and more seasoned DRIFT experts, all active in transitions research, (government) consultancy and education. They specialise in diverse domains such as climate policy, energy, agro-food, inclusiveness & participation, sustainable urbanism and the circular economy.
https://drift.eur.nl/courses/just-sustainability-transitions-course/
Illustration by Maria Fraaije
Are you an innovative entrepreneur? The In Residence Open Events program might be your chance to cooperate with Amsterdam!

Want to test your innovation during an open event such as Amsterdam Pride or the Amsterdam marathon? And looking for the opportunity to cooperate with the city in the long run?
The In Residence Open Events programme might be something for you. We have 8 broad defined challenges, ranging from circular economy to safety, from mobility to extreme whether. Basically we're looking for all innovations that can have an positive impact on the city and the event of the future!
During the programme you get:
- The opportunity to pilot your solution at an open event in Amsterdam, such as Amsterdam Pride or the Amsterdam Marathon
- 15K test budget to execute this pilot
- Guidance by an experienced mentor
- Access to the large municipality network
- The opportunity for long term cooperation in case of a succesfull pilot
- Large exposure and feedback opportunities
Interested to see our programme, the challenges and opportunity this brings for you?
See our website, www.innovatiepartners.nl, or see most recent LinkedIn post: https://www.linkedin.com/posts/gemeente-amsterdam-innovatie_inresidence-amsterdam-innovatie-activity-7163881081757253632-6soh?utm_source=share&utm_medium=member_desktop
For questions or thoughts, you can reach out to Mark Stoevelaar, project manager of the In Residence programme.
- mark.stoevelaar@amsterdam.nl
- +31621193028
Urban Sky Lab - How do drones fit into the city of tomorrow?

The air space above our city is about change. Drones will soon have a profound impact on our collective future - Last year alone, the city of Amsterdam detected over 43,000 low-altitude flights over our parks, squares, and waterfronts. As this trend continues to grow year-after-year, how can we repurpose drones to create a more sustainable and livable city?
This Thursday & Friday (15-16 Feb.) we are hosting the Urban Sky Lab together with Arcam and the Amsterdam Drone Lab. For this unique event we have invited Studio To Create, INBO, and FABRICations into a two-day sprint to design a future with drones for the Western Docklands, Amsterdam Zuidoost (Amsterdamse Poort area) and RAI Amsterdam.
You are welcome to attend the presentations of the preliminary results at Hotel Casa Amsterdam on Friday afternoon 16 February.
How do higher density and better quality of life go together? 3/7

A certain degree of compactness is essential for the viability of 15-minute cities. This is due to the need for an economic threshold for facilities accessible by walking or cycling. A summary of 300 research projects by the OECD shows that compactness increases the efficiency of public services in all respects. But it also reveals disadvantages in terms of health and well-being due to pollution, traffic, and noise. The assumption is that there is an optimal density at which both pleasant living and the presence of everyday facilities - including schools - can be realised. At this point, 'densification' is not at the expense of quality of life but contributes to it. A lower density results in more car use and a higher density will reduce living and green space and the opportunity to create jobs.
The image above is a sketch of the 'Plan Papenvest' in Brussels. The density, 300 dwellings on an area of 1.13 hectares, is ten times that of an average neighbourhood. Urban planners often mention that the density of Dutch cities is much lower than in Paris and Barcelona, for example. Yet it is precisely in these cities that traffic is one of the main causes of air pollution, stress, and health problems. The benefits of compactness combined with a high quality of life can only be realised if the nuisances associated with increasing density are limited. This uncompromisingly means limiting car ownership and use.
Urban planners often seem to argue the other way round. They argue that building in the green areas around cities must be prevented at all costs to protect nature and that there is still enough space for building in the cities. The validity of this view is limited. In the first place, the scarce open space within cities can be better used for clean workshops and nature development in combination with water control. Secondly, much of the 'green' space outside cities is not valuable nature at all. Most of it is used to produce feed for livestock, especially cows. Using a few per cent of this space for housing does not harm nature at all. This housing must be concentrated near public transport. The worst idea is to add a road to the outskirts of every town and village. This will undoubtedly increase the use of cars.
Below you can link to my free downloadable e-book: 25 Building blocks to create better streets, neighborhoods and cities
The 15-minute city: from metaphor to planning concept (2/7)
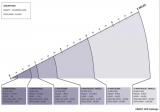
Carlos Moreno, a professor at the Sorbonne University, helped Mayor Anne Hidalgo develop the idea of the 15-minute city. He said that six things made people happy: living, working, amenities, education, wellbeing, and recreation. The quality of the urban environment is enhanced when these functions are realized near each other. The monofunctional expansion of cities in the US, but also in the bidonvilles of Paris, is a thorn in his side, partly because this justifies owning a car.
A more precise definition of the concept of the 15-minute city is needed before it can be implemented on a large scale. It is important to clarify which means of transport must be available to reach certain facilities in a given number of minutes. The list of facilities is usually very comprehensive, while the list of means of transport is usually only vaguely defined. But the distance you can travel in 15 minutes depends on the availability of certain modes of transport (see figure above).
Advocates of "new urbanism" have developed the tools to design 15-minute cities. They are based on three zones: the 5-minute walking zone, the 15-minute walking zone, which coincides with the 5-minute cycling zone, and finally the 15-minute cycling zone. These are not static concepts: In practice, the zones overlap and complement each other.
The 5-minute walking zone
This zone corresponds to the way in which most residential neighbourhoods functioned up until the 1960s, wherever you are in the world. Imagine a space with an average distance from the center to the edge of about 400 meters. In the center you will find a limited number of shops, a (small) supermarket, one or more cafes and a restaurant. The number of residents will vary between two and three thousand. Density will decrease from the centre and the main streets outwards. Green spaces, including a small neighbourhood park, will be distributed throughout the neighbourhood, as will workshops and offices.
In the case of new construction, it is essential that pedestrian areas have a dense network of paths without crossings at ground level with streets where car traffic is allowed. Some paths are wider and allow cycling within the 5- and 15-minute cycle zones. The streets provide access to concentrated parking facilities.
The 5-minute cycle zone and the 15-minute walking zone.
Here the distance from the center to the edge is about one kilometer. In this area, most of the facilities that residents need is available and can be distributed around the centers of the 5-minute walking zones. For example, a slightly larger supermarket may be located between two 5-minute walking zones. This zone will also contain one or more larger parks and some larger concentrations of employment.
This zone can be a large district of a city, but it can also be a small municipality or district of around 15 to 25,000 inhabitants. With such a population there will be little room for dogmatic design, especially when it comes to existing buildings. But even then, it is possible to separate traffic types by keeping cars off many streets and clustering car parks. The bottom line is that all destinations in this zone can be reached quickly by walking and cycling, and that car routes can be crossed safely.
The car will be used (occasionally) for several destinations. For example, for large shopping trips to the supermarket.
The 15-minute cycle zone.
This zone will be home to 100.00 or more residents. The large variation is due to the (accidental) presence of facilities for a larger catchment area, such as an industrial estate, a furniture boulevard or an IKEA, a university or a (regional) hospital. It is certainly not a sum of comparable 5-minute cycle zones. Nevertheless, the aim is to distribute functions over the whole area on as small a scale as possible. In practice, this zone is also crossed by several roads for car traffic. The network of cycle paths provides the most direct links between the 5-minute cycle zones and the wider area.
The main urban development objectives for this zone are good accessibility to urban facilities by public transport from all neighbourhoods, the prohibition of hypermarkets and a certain distribution of central functions throughout the area: Residents should be able to go out and have fun in a few places and not just in a central part of the city.
Below you can link to my free downloadable e-book: 25 Building blocks to create better streets, neighborhoods and cities.
Stay up to date
Get notified about new updates, opportunities or events that match your interests.

