Stay in the know on all smart updates of your favorite topics.
Lezing generatieve AI en deepfakes (Dutch)

Kun je nog weten wat betrouwbaar is in tijden van generatieve AI en deepfakes?
Deze Nederlandstalige lezing is bedoeld voor iedereen die meer wil weten over de risico’s van deepfakes (denk aan stemklonen, plaatjes en chatgpt).
Wat is de globale werking, waar kom je het tegen, wanneer moet je extra voorzichtig zijn en wat kun je doen om jezelf te beschermen en manipulaties te doorzien.
Everything Urban 001_Interactive Talk for students and young professionals

Everything Urban 001 (LinkedIn Event) is the first in the Interactive Talk series for students and young professionals interested in Urban Affairs i.e. urban planning, urban management, architecture, sustainability, smart cities, to name some. Feel Free to attend it on September 4, 2025. More details in the link.
Demoday #28: From Policy to Practice: Inclusive Design Ambitions of the Amsterdam Transport Authority

On the 5th of June, during the 28th Knowledge and Demo Day, we explored the topic of Inclusive Design in the context of mobility projects together with a diverse group of network partners. Iris Ruysch introduced the theme on behalf of the Amsterdam Transport Authority (Vervoerregio), while David Koop and Lotte de Wolde from our knowledge partner Flatland facilitated the session format, moderation and visual notes.
The ambition of the Amsterdam Transport Authority
The Amsterdam Transport Authority is responsible for public transport across fourteen municipalities in the region and is working towards a mobility system that enables people to travel quickly, safely and comfortably by public transport, bicycle or car. In addition to organising and funding public transport and investing in infrastructure, the Authority actively contributes to broader societal goals such as sustainability, health and inclusivity.
Inclusive mobility is one of the key themes within the wider mobility policy. The central principle is that everyone – regardless of age, income, disability, gender or background – should be able to travel well and comfortably throughout the region. This calls for a mobility system that is accessible, affordable, appropriate, socially safe and welcoming.
The aim of the session on 5 June was to work with the network towards an initial action plan for applying inclusive design principles in mobility projects. Iris is keen to ensure that the ambitions around inclusivity are not only stated in policy and vision documents but are truly embedded in the organisation – from policymakers to implementation teams.
Session set-up
After an introduction by Iris on the context and ambitions within the Transport Authority, we got to work. In small groups, participants explored the profile of the implementing civil servant (using a persona canvas) and considered desirable changes in approach; in terms of attitude, skills and collaboration.
We then used the Inclusive Design Wheel to examine how existing programme components of the Authority could be made more inclusive. In pairs, we tackled themes such as accessible travel information, social safety at stations (specifically for women), and improving bicycle parking facilities.
The Inclusive Design Wheel is an iterative process model that supports the structural integration of inclusivity into design and policy projects. The model emphasises collaboration, repetition, and continuous learning. It consists of four phases:
- Explore: Gather insights about users, their needs, and potential exclusion.
- Create: Develop ideas, concepts, and prototypes that address inclusive needs.
- Evaluate: Test whether the designs are inclusive, collect feedback, and make improvements where necessary.
- Manage: Ensure shared understanding, set goals, engage stakeholders, and embed the process.
Outcomes and insights
While the persona profiles were being developed, I observed the group discussions and noted several important insights to take forward in the development of the action plan:
- Awareness and concrete translation: Implementation teams often already have an intrinsic motivation to contribute to inclusivity goals set in policy. However, they may not always realise how their day-to-day work can support those goals. It’s important to continuously ask the question ‘How, exactly?’. Tools like checklists, templates and practical examples can support this translation from policy to practice.
- Flexible guidelines and not ‘extra work’: Given the differences in scale, pace and content of projects, guidelines need to be flexible. There must also be sufficient room in terms of time and budget. Most importantly, these guidelines and action plans should feel supportive, not like extra rules or bureaucracy. Too many rigid frameworks can backfire.
- Interaction between policy and implementation: There is a need for more two-way communication. Implementation teams want to be involved early in policy development, especially when they will be the ones carrying it out. They also want opportunities to reflect with policymakers on whether policy is being implemented as intended. This allows for timely feedback and course-correction based on real-world experience.
- An Inclusive Design mindset: Beyond sharpened policy documents and a stronger focus on the end user, Inclusive Design also requires a mindset – one that is inquisitive and reflective. Embedding this within the organisational culture will require more than just an action plan.
What’s next
Iris collected valuable input to kick-start the development of the action plan, and participants gained a better understanding of the Amsterdam Transport Authority, the principles of Inclusive Design, and what it takes to move from policy to implementation. This summer, a trainee will start at the Transport Authority to further develop this topic and the action plan. The session, this report, and Flatland’s visual notes provide a strong foundation to build on. We’ll be meeting with Iris and David to explore how we can support this follow-up.
Would you like to learn more about any of the topics or developments mentioned in this report? Feel free to email pelle@amsterdaminchange.com.
A Lab Open Huis. Met exposities, pitches voor een positieve toekomst, live muziek, dans en theater, workshops en meer!

Laat je nieuwsgierigheid de vrije loop tijdens het <strong>A Lab Open Huis</strong>. Een creatief en innovatief festival voor alle nieuwsgierige Amsterdammers die in deze turbulente tijden waarde hechten aan kunst & cultuur, duurzaamheid en sociale innovatie.
Kom kijken hoe meer dan 350 members in onze broedplaats werken aan een positieve toekomst. Met een programma vol exposities, live muziek, kunst, pitches, theater, fotoreportages, workshops, interessante ontmoetingen en meer! Kinderen? Neem ze vooral mee, het is voor iedereen een feestje!
Ontdek nieuwe ideeën, ontmoet makers en verken het live programma. Dwaal rond en laat je verrassen door wat je tegenkomt, of volg een van de inspirerende routes die speciaal zijn samengesteld langs de thema’s waar A Lab members aan werken. Er is een (digitale) kunst & cultuurroute, een duurzaamheidsroute, een sociaal maatschappelijke innovatieroute en ga voor een mix van activiteiten in de kidsroute.
Bekijk het volledige programma met timetables komende tijd op de website, maar een sneak peek is natuurlijk altijd leuk. Laat je meevoeren door livemuziek – van opkomend raptalent tot jazzy klanken – en ontdek unieke ervaringen zoals een levende algenexpo, verticale dans op de binnentuinmuur en interactieve datavisualisatie. Luister naar korte, inspirerende talks over een zelfredzame toekomst, stap in een Kanta vol verhalen over Amsterdam Noord, of scoor iets moois in de A Lab pop-up store. Geniet van wereldse smaken van de restaurants van het nieuwe Maritim Hotel, bewonder kunst van o.a. jonge makers, draai aan een meteorologisch rad of ga zelf aan de slag in een escape room of met je eigen digitale kunst. En voor filmliefhebbers: struin door Izzy’s Videotheek voor verborgen parels die je nergens kunt streamen.
Het event is gratis, maar reserveer wel je gratis ticket via deze link.
Digital Society School - Transformation Learning Programme Info session

Call to all aspiring leaders!
Are you looking for the next step in advancing your leadership and management skills in alignment with your current role?
Join our upcoming info session on June 11th to learn more about the Transformation Leadership Programme (TLP) – Digital Society School’s part-time programme designed for professionals ready to lead change in the digital and sustainable transition.
We’re looking for Netherlands-based professionals with a Master’s degree and at least 2 years of relevant work experience, particularly with skills in project and team management.
During the info session we will be joined by former Transformation Owners from the TLP track who will share their own experiences during the programme.
The info session will take place online on June 11th 16:00 CET. See you then!
Neem je werk en je uitdagingen mee naar buiten en vier Outdoor Office Day in het Amsterdamse Bos

De stedelijke natuur als jouw werkplek.
Dit jaar in het Amsterdamse Bos waar iedereen duurzame leiders, toekomstdenkers & doeners kan ontmoeten. Zij staan klaar om met jou een rondje Amsterdamse Bos te lopen. Boek een één-op-éen wanderwalk om jouw onderwerp of uitdaging te bespreken.
Of neem jouw overleg mee naar buiten of kom met je laptop het bos in. Inspirerende ‘collega’s’, frisse lucht vers van de bomen en natuurlijk een duurzame barista. Het grote buitenkantoor is 12 juni ingericht met buiten werkplekken & inspiratie.
Outdoor Office Day 2025

On June 12th 2025 we will celebrate the 7th edition of the international Outdoor Office Day. It’s an open invitation to take your work outside, reconnect with the surrounding urban nature around your office.
This year’s theme is 'Connecting with each other’: with your direct colleagues, colleagues from other departments, neighbours, or external relations. Please join the growing network of individuals and companies that take their work outside more and more often. Get inspired whilst you spend time surrounded by urban nature. This enhances new and meaningful relationships, stimulates the flow of good ideas and supports the forging of valuable collaborations.
Please meet our partners and participants:
https://www.outdoorofficeday.nl/participants
If in Amsterdam we invite for wanderwalk with sustainable leaders. Join us in Amsterdamse Bos to discuss your dilemma's, learn from each other and connect.
Sensemakers #IoTDay celebration: Easter Workshop

For the 15th year we're celebrating International IoTDay, it's all about sharing knowledge about how to create your own projects and connecting with people in the process!
We’re excited to share a fun and engaging project with you! Join the Easter workshop, creating a beautiful personalized ornament that you can lasercut and program yourself! (of course we'll help!)
More information on the project can be found here:
https://sensemakersams.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/Sensemakers-XMas2024-Project.pdf
There is a fee involved, but we have 2 'Pay-It-Forward' kits available for those low on budget this holiday season. Just dm Manon if you want one of those!
And of course we'll have some free alternatives like experimenting with 3D printing your own Easter-buddy:-)
Apply for The Next 750 and attend TNW Conference

Your talent, recognized
LET'S CELEBRATE YOU!
The Next 750 builds upon the legacy of our renowned T500 program, expanding our recognition platform in honor of <strong>Amsterdam's 750th anniversary</strong>.
This is a celebration of exceptional talent in tech and entrepreneurship, showcasing individuals who are shaping the future across three categories:
- <strong>Rising Stars</strong>: Talents under 30 redefining innovation
- <strong>Inclusion Champions</strong>: Diverse individuals driving change through unique perspectives
- <strong>Amsterdam Changemakers</strong>: Local pioneers making an impact in the Amsterdam community
TNW Conference is proud to use its platform to honor and empower these 750 incredible talents.
Tech moves fast, but it’s powered by people. That’s why we’re giving The Next 750 access to TNW Conference 2025 — to connect them with the visibility, tools, and networks they need to thrive.
We’re shining a spotlight on the movers, makers, and game-changers shaping what’s next. Their contributions deserve to be celebrated, their potential amplified. Together, we’re not just building the future of Amsterdam—we’re shaping the future of the world.
A panel of judges will carefully review applications based on the following criteria: relevant (work) experience, side projects, and personal accomplishments to find the best candidates.
Applications are <strong>now open.</strong> This program is a great opportunity to connect with some of the most talented individuals in the digital tech industry, and you don't wanna miss it!
Online course Just Sustainability Transitions

Across six interactive online sessions, this course offers the tools, knowledge, and inspiration needed to support just and sustainable transformations – grounded in action research, critical reflection, and peer learning.
We are offering the course for the third time, this year in collaboration with Dina Lupin from University of Southampton.
We have made the programme a bit more compact to make it more affordable, and as always offer it at a variable rate (€1,775.00 for well-paid professionals and €1,245.00 for those with more limited financial means) to make it as accessible as possible.
Stream the Amsterdam Forever Young Programme on Eye Film Player

Discover the Amsterdam Forever Young program on the Eye Film Player, a diverse programme that explores the dynamic, ever-evolving spirit of Amsterdam. This collection of films highlights how the city’s unique identity has been shaped by its past, present, and future. Hence, we place a special focus on the intersection of urban development and planning, offering a look at how the city’s architectural and cultural transformations have intertwined in, both, historical films, as well as more contemporary filmic undertakings. Thus, our collection of films, such as Where the Rats are King, A Photographer Films Amsterdam and Amsterdam Global Village, shed light on the living conditions in Amsterdam, the urban communities witihin Amsterdam and, even, films as Jenny and Amsterdam on Film that shed light on how the canals have shaped Amsterdam more than aesthetically e.g., with its focus on ecology and care for our climate. Through, both, monetized and free to watch films, we aim to share the rich history of our city, whilst aiming for a dynamic space for creativity, inclusivity, and sustainability in the future, too that we hope this knowledge and collection will inspire.
All in all, Amsterdam Forever Young invites you to reflect on the city's evolution and its commitment to being a centre of modernity, without losing the essence of its heritage. Available on the Eye Film Player, to watch from your bedroom, this "digital" exhibition celebrates Amsterdam as the city of urban transformation that, at the same time, stay true to its historical roots.
Sensemakers knowledge sharing: Deepfakes & Digital Humans
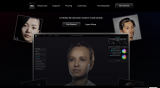
This Wednesday we have 2 speakers introducing you to the latest on synthetic media (deepfakes) and digital humans.
Manon den Dunnen
Introducing you to the latest developments in synthetic media (deepfake, LLM's)Mao Lin Liao (Reblium)
Introducing the challenges and possibilities of customized digital humans (avatars) and their various applications.
Looking forward to seeing you! Presentations are in Engels, maar we spreken ook Nederlands!
Dissemination conference of our EU funded project AnthroAction: increasing employability and societal impact of action researchers.

Namla and Univerzita Pardubice Anthropology Department are hosting a one time mini conference next week on the results of our project in Erasmus Plus called AnthroAction: increasing employability and societal impact of action researchers. (https://erasmus-plus.ec.europa.eu/projects/search/details/2023-2-NL01-KA210-ADU-000180400)
We have been running the project since March 2024 and just wrapped up our pilot course for graduates of anthropology in Czech Republic and Netherlands; where the graduates learned to combine rapid ethnography and design thinking to tackle a real-world problem, suggested by real NGOs.
The NGOs that contributed to the project were:
-Czech Blind United (https://www.sons.cz/) with the question: how can we attract more younger members to our organisation?
-Junak - Czech Scouts (https://www.skaut.cz/) with the question: what do today’s teenagers want in leadership training?
-De Meevaart Community Centre (https://meevaart.nl/) with the question: how can we start a blue zone in Indische Buurt in Amsterdam?
-The Really Healthy School (https://www.skutecnezdravaskola.cz/) with the question: how can we reach more primary schools with our programme?
The participants in the course were coming from all over Czech Republic, and Amsterdam.
In the conference, we will discuss what happened in the course, how it went, what we can learn from the pilot. Also a number of professors in Anthropology from different parts of Europe (such as Laurens Bakker, Ana-Isabel Afonso), applied anthropologists from Czech Republic (such as Karolina Kania, PhD, Socionaut, z.s.), as well as organisations in our network will share reflections on how what we did here fits into a wider context.
Please register here before January 22nd: https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSfGfI-vtCTk3XdaGpZvlK37y2VKqZqIV1LUfUiJhsD0OqFlxg/viewform
and join the conference at this Zoom link:
Zoom link: https://us02web.zoom.us/j/89954251812?pwd=78KpFxVY3rXY682mEbErjDl7woYVnR.1#success
Meeting ID: 899 5425 1812
Password: 514987
🚀 Oproep voor organisaties in de publieke sector! Draag bij aan de ontwikkeling van ethische mobiele innovatie! 🌍

Wil jij de status quo uitdagen en bijdragen aan een mobiel ecosysteem dat privacy, duurzaamheid en ethische technologie vooropstelt?
💡 Bij Waag Futurelab zijn we vastbesloten om alternatieven te verkennen voor de datahongerige apps en apparaten die momenteel de techwereld domineren. Via ons onderzoeksproject Mobifree nodigen we organisaties in de publieke sector uit om een open-source Murena-smartphone te testen en samen met ons de toekomst van ethische, open-source mobiele technologie in Europa vorm te geven.
Dit is jouw kans om:
✅ Als organisatie Murena-smartphones te testen, voorzien van open-source apps.
✅ Feedback te geven die direct invloed heeft op de volgende generatie mobiele oplossingen.
✅ Bij te dragen aan een duurzaam, veilig en inclusief alternatief voor Big Tech.
🔍 Wat kun je verwachten?
- Doe mee aan een pilot van twee maanden (februari–oktober 2025) en verken hoe open-source tools jouw werk- en persoonlijke behoeften kunnen ondersteunen.
- Test baanbrekende technologie terwijl je pleit voor ethische en duurzame softwareontwikkeling.
- Maakt deel uit van een community die een privacy gerichte en Big Tech-vrije toekomst vormgeeft!
🙌 Wie kan deelnemen?
We een groep van maximaal 30 deelnemers om de volgende kerngebieden te verkennen:
- Besturingssystemen
- Messaging-apps
- Appstores
- Cloudservices
📩 Hoe kun je je aanmelden?
Stuur een e-mail naar bente[at]waag[dot]org met de naam van je organisatie, het aantal deelnemers, gekozen categorieën en een korte motivatie om mee te doen. Vervolgens zullen wij contact met je opnemen!
Doe met ons mee om mobiele technologie opnieuw vorm te geven voor een betere, privacy-respecterende Europa 🌟
Digital Society School Showcase

Makers’ playground for better futures
Ever felt that spark of creativity, that urge to build something meaningful, but didn’t know where to start? Is your organisation on the path for transformation and you seek inspiration for the next step?
On January 22 (17:00 – 20:00), dive into our Showcase where our trainee teams from the Digital Transformation Intensive Programme will exhibit their impactful work on challenges from our partners. Experience firsthand how repeated iterations and bold experimentation shaped their innovative solutions.
Beyond the exhibition, our talk show will feature inspiring speakers who pave the road for change, embracing alternative approaches to design for transformation.
Whether you’re a seasoned maker or just beginning to explore how to meaningfully use your creative potential, join our community of resilient innovators. Connect with like-minded individuals and organisations in our Clubhouse or tune in via [our YouTube channel](https://www.youtube.com/live/Swkf13n32aA?feature=shared "https://www.youtube.com/live/Swkf13n32aA?feature=shared").
So, mark your calendars and be part of this celebration of maker courage and persistence!






PROGRAMME
We have prepared an exciting programme for you:
17:00 – 17:30 Walk-in & welcome
17:30 – 18:30 Talk Show
Our Talk Show will shed light on alternative approaches to design for transformation. Speakers announced in December
18:30 – 20:00 Networking & drinks
There will be plenty of opportunities to connect with the trainees, partners and the extended Digital Society School community, so don’t miss out!
Research Interviews Request for PhD Dissertation!
My name is Pınar Ebe-Güzgü, a PhD student at İzmir Katip Çelebi University, Turkey, currently conducting research at the University of Twente. My doctoral research focuses on social justice and disadvantaged groups in the context of smart city applications, with a particular emphasis on the mobility of elderly people (defined by WHO as people over the age of 65).
As part of my research, I conduct in-depth interviews with residents (aged 65+) of Amsterdam, caretakers of elderly individuals, and those working on (or with expertise in) smart city initiatives. The goal is to explore the mobility experiences of 65+ people in Amsterdam and develop policy recommendations to enhance social justice in urban management.
If you would like to share your experiences, your participation in this research would be invaluable. All interviews will be conducted at a time and format that suits you.
Thank you for your time and consideration. Your insights will greatly contribute to our understanding of how smart city applications impact the mobility and quality of life of older individuals.
If you are interested in participating, please reach out to me via the email address below:
p.ebe-guzgu@utwente.nl
Best regards,
Pınar Ebe-Güzgü
Just.City.Amsterdam.2024

Op 21 november 2024 vindt de tweede editie van Just.City.Amsterdam plaats. Dit jaar richten we ons op een belangrijk thema: rechtvaardigheid in de praktijk brengen. Waar we tijdens de eerste editie verschillende perspectieven op rechtvaardigheid onderzochten, gaan we nu aan de slag met de vraag: Hoe doen we dat?
Wat kun je verwachten?
Vanuit het A Lab in Amsterdam Noord gaan we de wijk in om rechtvaardigheid van dichtbij te ervaren. Samen bezoeken we lokale initiatieven die actief werken aan meer rechtvaardigheid. We kijken naar wat er gebeurt, wat werkt, en wat misschien anders kan. Daarnaast denken we samen na over wat jij zelf kunt bijdragen aan een rechtvaardige stad.
Tijdens Just.City.Amsterdam.2024 ervaar je hoe rechtvaardigheid in de stad wordt toegepast. Sluit je aan bij één van de excursies waarin lokale gemeenschappen hun projecten en uitdagingen delen, en leer meer over hun inzet voor rechtvaardigheid en verandering. Of kies voor een workshop waarin je dieper ingaat op hoe creatieve en praktische methodes bijdragen aan een eerlijker Amsterdam.
Bekijk het aanbod hieronder, meld je aan en doe mee aan het gesprek over een rechtvaardige stad!
- Excursie: Inkijkjes in de Energietransitie - met Tessa Steenkamp
- Workshop: School voor Strijders - met Massih Hutak
- Excursie: Red Amsterdam Noord - met Eva Bollen en Esmee Barel
- Workshop: De maatschappelijke impact van documentaires - met Ester Gould
- Excursie: De Rechtvaardige Stad en Community Wealth Building - met Floris Bremen
- Excursie: Van wie en voor wie is de buurt - Met Bart Stuart
👇 💜 🤩 Co-Creation Opportunity 👇 💜 🤩

Calling all community engagement specialists shaping the future of our urban spaces! 📢
At Playground City🛝, we believe real impact happens when we build solutions together. The insights we’ve gained from incredible conversations at Placemaking Europe, World Summit AI, and soon at Smart City Expo World Congress are already shaping our roadmap—and now, we’re ready to bring in those who can help take it to the next level.
We’re building an ambassador community for dedicated community engagement professionals to join us in pioneering a platform created for (and with!) the people driving change in our cities.
As an ambassador, you’ll have early access to shape and use Playground City🛝 as it evolves, guiding its development with your insights. We’re also preparing exclusive perks just for you, like discounted pilot projects, early access to new features, and more exciting benefits (yes, also our amazing merch.. 😎).
If you’re a community engagement specialist, urban strategist, or resident leader ready to make an impact, comment “I’m in!” below, and we’ll follow up with details. We can't wait to meet you all!
Passionate about co-creation in urban spaces? Join Playground and make an impact! 🌍
#CommunityEngagement #UrbanInnovation #Placemaking #PlaygroundCity #CoCreation #AmbassadorProgram #SmartCities #UrbanImpact #PlaygroundCity
Open call: 54 tech-for-good challenges with funding available for over 60 pilots

CommuniCity's third Open Call is now launched! 🚀
We are pleased to launch the final CommuniCity Open Call round. There will be over 60 pilots running across Europe, focusing on digital inclusion and wellbeing for marginalized communities. 7 challenges are focused on citizens of Amsterdam.
In addition to the partner cities of Helsinki, Porto, and Amsterdam, the Replicator Cities are also presenting their unique challenges. The Replicator Cities are Aarhus, Bruges, Brussels, Cuneo, London, Manchester, Matosinhos, Milazzo, Plock, Prague, Sant Boi de Llobregat, Sarajevo, The Hague and Utrecht.
💡 Tech providers: Apply for grants of up to €12,500 to develop tech solutions and run real-life experiments in collaboration with the cities. The deadline for applications is October 31st, 5pm CET.
More information on the Open Call: https://lnkd.in/e-Z5EA5z
Let’s shape the future of our cities together! 💪
🔍 CIIIC zoekt een Communicatie & Community Lead!

Ben jij een ervaren communicatieprofessional met een hart voor de creatieve sector? Samen met het Ministerie van OCW, CLICKNL en vier uitvoeringspartners stelt CIIIC de creatieve industrie en contentmakers in staat om de potentie van immersive experiences te benutten.
Als Communicatie en Community Lead ben je verantwoordelijk voor het (door)ontwikkelen en implementeren van de communicatiestrategie van het CIIIC-programma. Daarnaast heb je een sleutelrol in het opbouwen en onderhouden van een betrokken en actieve community, waaronder IX-makers, kennisinstellingen, bedrijven die IX toepassen en andere relevante partijen.
📑 Lees de volledige vacature hier: https://lnkd.in/eBusnR6p
👋 Interesse? Stuur je motivatie en werkervaring naar info@clicknl.nl voor 16 september 23:59 uur.
🔗 Ken jij de perfecte kandidaat? Deel deze post!
🔍 CIIIC is looking for a Communications & Community Lead!
Are you an experienced communications professional with a love for the creative industry? Together with the Ministry of OCW, CLICKNL and four implementing partners, CIIIC enables the creative industry and content creators to harness the potential of immersive experiences.
As Communication and Community Lead, you are responsible for (further) developing and implementing the communication strategy of the CIIIC programme. You also have a key role in building and maintaining an engaged and active community, including IX makers, knowledge institutions, companies applying IX and other relevant parties.
📑 Read the full vacancy here: https://lnkd.in/eq_fE5WU
👋 Interested? Send your motivation and work experience to info@clicknl.nl before 16 September 23:59.
🔗 Do you know the perfect candidate? Share this post!
Stay up to date
Get notified about new updates, opportunities or events that match your interests.

