Stay in the know on all smart updates of your favorite topics.
Are you interested in the experiences of others working in smart city projects and organizations? The Smart City Academy provides available knowledge about smart city projects and can help you with project development. This Smart City Academy page provides you with information and researches about the impact and conditions of smart city projects. Professors, teachers and students study the initiation, management, collaboration and scaling of smart city projects and would like to share these results with you. They do so by organizing events and masterclasses, by developing smart city tools and methodologies and by making research and outcomes accessible. You can find everything here. And the good news is.... You can add your knowledge too! Are you working on Smart City research? Please feel free to share your knowledge in the Academy section, under ‘Other research and theses’. The Smart City Academy is powered by the Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences. If you have any questions, you can contact smartcityacademy@hva.nl
Red Light District Relocation: What do you think? 🤷🤦♀️

Amsterdam is set to relocate its iconic Red Light District from De Wallen to Europaboulevard, marking a significant shift in the city's approach to sex work and urban development.
This move aims to create a more structured and safe environment for sex workers while addressing concerns about over-tourism and its impact on local communities. We analyzed available data online to understand the hottest topics from affected groups.
<strong>See data insights on Playground Journal. Or listen to a short 5-minute podcast on this here.</strong>
This is your opportunity to engage in the conversation. Your insights and opinions matter in shaping a future that respects the city’s rich history while addressing the challenges and hopes of its diverse inhabitants.
The significance of this relocation lies in its potential to reshape Amsterdam's cultural and social landscape. It reflects the city's commitment to balancing the needs of residents, tourists, and sex workers, ensuring that the new Erotic Centre aligns with contemporary values while preserving the district's historical essence.
As this transformation unfolds, community input is vital. Residents, business owners, and other stakeholders are encouraged to contribute their thoughts and ideas to help shape the future of the new Red Light District. Your insights can influence the new facility's design, amenities, and safety features.
While communities can influence many aspects—such as building design, types of amenities, and community engagement processes—certain elements are fixed. The location of the new RLD has already been determined, as are existing laws and regulations governing sex work. Additionally, the core concept of the Erotic Centre and project timelines remain unchanged.
Let’s ensure that the new Red Light District reflects the values and aspirations of all who call Amsterdam home. Your voice matters!
Building local mini-economy within planetary boundaries

Scroll naar beneden voor de Nederlandse versie
Growth is an end in itself, dictates the current economic model. For only growth would keep our economy going and be indispensable to further sustainability. At the same time, our planet is being depleted by this drive for green growth.
Is it time to abandon economic growth as a social ideal? And then what are workable, more social alternatives?
More and more business owners are opting for sustainable operations. They settle for less financial gain to do valuable work with positive social and environmental impact. The rise of the commons movement, housing-, energy- and food cooperatives, as well as social initiatives in health and welfare, show that people want to stand together for values other than financial gain.
Achievable and real alternatives
New economic models offer different perspectives for considering the economy as part of a society. They offer tools to make that economy more equitable and sustainable. Yet the new economic thinking is still often dismissed as unrealistic and unachievable. Only by trying out these theories in practice can we demonstrate that these are real alternatives.
New economic thinking, New economic acting
To experiment with new economic theory and models in practice, the Amsterdam Economic Board has started the New Economic Models exploration. In April, we introduced the living lab project “New Economic Thinking, New Economic Acting” at the Marineterrein in Amsterdam. In this we work on socio-economic experiments, together with AMS Institute, AHK Culture Club, And The People, Bureau Marineterrein, Kennisland, The Next Speaker and the knowledge coalition ‘Art, Tech & Science’.
The Marineterrein is the ideal place to do this because it is an official experiment site. Moreover, companies located here are often already working on circular and social projects. Cultural institutions and organisations at the Marineterrein, in turn, can represent what thriving without economic growth could look like and fuel our desire for a new economy.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Bouwen aan lokale mini-economie binnen planetaire grenzen
Groei is een doel op zich, dicteert het huidige economische model. Want alleen groei zou onze economie draaiende houden en onmisbaar zijn om verder te verduurzamen. Tegelijkertijd raakt onze planeet uitgeput door die drang naar groene groei.
Wordt het tijd om economische groei als maatschappelijk ideaal los te laten? En wat zijn dan werkbare, socialere alternatieven?
Steeds meer ondernemers kiezen voor een duurzame bedrijfsvoering. Zij nemen genoegen met minder financiële winst om waardevol werk te kunnen doen, met positieve sociale en ecologische impact. De opkomst van de commons-beweging, woon-, energie- en voedselcoöperaties en maatschappelijke initiatieven in zorg en welzijn, laten zien dat mensen zich samen sterk willen maken voor andere waarden dan financieel gewin.
Haalbare en reële alternatieven
Nieuwe economische modellen bieden andere perspectieven om de economie als onderdeel van een samenleving te beschouwen. Ze bieden handvatten om die economie rechtvaardiger en duurzamer in te richten. Toch wordt het nieuwe economisch denken nog vaak weggezet als onrealistisch en niet haalbaar. Alleen door deze theorieën in de praktijk uit te proberen kunnen we aantonen dat dit reële alternatieven zijn.
Nieuw economisch denken, Nieuw economisch doen
Om te kunnen experimenteren met nieuwe economische theorie en modellen in de praktijk, verkent Amsterdam Economic Board deze in de verkenning Nieuwe economische modellen. In april introduceerden we het proeftuinproject ‘Nieuw economisch denken, Nieuw economisch doen’ op het Marineterrein in Amsterdam. Hierin werken we aan sociaaleconomische experimenten, samen met AMS Institute, AHK Culture Club, And The People, Bureau Marineterrein, Kennisland, The Next Speaker en de kenniscoalitie ‘Art, Tech & Science’.
Het Marineterrein is de ideale plek om dit te doen, omdat het een officieel ‘experimentterrein’ is. Bovendien zijn de hier gevestigde bedrijven vaak al bezig met circulaire en sociale projecten. Culturele instellingen en organisaties op het Marineterrein kunnen op hun beurt verbeelden hoe bloei zonder economische groei er uit kan zien en ons verlangen aanwakkeren naar een nieuwe economie.
Kennisland-podcast #1: geen vernieuwing zonder ongemak

Geen vernieuwing zonder ongemak. Maar durven vernieuwers het ongemak zelf in de bek te kijken? En wat kunnen we daarvan leren? In deze podcastserie ter ere van 25 jaar Kennisland gaan we in gesprek met sociale vernieuwers over scheve machtsverhoudingen, schijnparticipatie, gebrek aan diversiteit, preken voor eigen parochie, haperende verdienmodellen, de paradox van vernieuwing en andere olifanten in de kamer waar wíj het juist wel graag over willen hebben. In deze eerste aflevering gaat Marieke van Doorninck in gesprek met Tofik Dibi.
Eerste gast: Tofik Dibi
Tofik is een Marokkaans-Nederlandse oud-politicus, schrijver, activist en sinds 2018 bestuursadviseur van het stadsdeel Nieuw-West in Amsterdam. Hij richt zich onder andere op het vergroten van kansen van jongeren in grote steden. Tofik staat bekend om zijn gedrevenheid en is niet bang om de knuppel in het hoenderhok te gooien. Regelmatig zorgt hij met scherpe tweets voor reuring op X. Hij is bovendien lid van onze Raad van Advies. Marieke van Doorninck, directeur van Kennisland, gaat met hem in gesprek over ongemak en vernieuwing.
> “De realiteit vraagt soms om een bittere toon.”
Ongemak inzetten en toch verbinden
Ze praten over hoe je ongemak kunt inzetten om de status quo te bevragen en de gevestigde orde uit te dagen. Belangrijk daarbij is om tegelijkertijd comfort te bieden. Ongemak werkt het beste in een veilige setting. Hoe kun je de confrontatie aangaan zonder de ander te verliezen?
Luister de podcast (28 minuten) via onderstaande link.
2Ping 20 juni spreker op event Amsterdam Smart City
Korte samenvatting 2Ping in Zuidoost
Wij maken ons sterk voor de lokale economie. Dat willen we doen met het introduceren en ontwikkelen van een complementaire lokale munt 2Ping voor Zuidoost. Purpose en waarde gedreven. Inclusief en met impact voor iedereen.
Aanleiding
'Wij maken ons zorgen hoe onze huidige economie werkt en geloven dat het anders kan'
Wij ondernemen, wonen, werken, zorgen en leren in Zuidoost. Een stadsdeel met pioniers uit alle windstreken. Zuidoost heeft een sterke en lokale identiteit: de combinatie van onze pioniersgeest, creativiteit en saamhorigheid maakt ons uniek. Zuidoost is trots, eigengereid en ademt diversiteit. Deze unieke waarden en innovatiekracht willen we benutten om de tendens van sociale ongelijkheid te keren, door anders met ons geld om te gaan en bij te dragen aan de transitie naar een donut economie. In Zuidoost is ook veel armoede en ongelijkheid. Het geld wat vanuit de multinationals worden verdiend vloeit weer even snel de wijk uit als dat het binnenkomt zonder dat bewoners en lokale ondernemers hiervan profiteren.
Vanuit de Collectieve Ruimte Grubbehoeve in het stadsdeel Zuidoost en in samenwerking met het ZZP Cafe Hartje Bijlmer en het stadsdeel Zuidoost zijn we vanaf januari 2020 intensief bezig met de voorbereidingen voor Lokaal Geld. We hebben hiervoor Bottom up draagvlak gecreëerd, wat resulteerde in een Manifest en dat door verschillende partijen is getekend (zie bijlage).
Met lokaal geld maken we nieuwe verbindingen tussen bedrijven, netwerken en bewoners met een win-win-win voor iedereen: people, planet én profit. Zodat ons stadsdeel zich inclusief en duurzaam door ontwikkelt met sterke ondernemers en eerlijke kansen voor iedereen. Dit sluit aan bij de principes van Community Wealth Building. We hebben hierover sinds februari 2020 contact met Dirk de Jager (bestuurder stadsdeel Zuidoost) naar aanleiding van zijn oproep voor ideeën voor de lokale wijkeconomie. Sindsdien hebben we nauw contact hem waarin we de nut en noodzaak van Lokaal Geld voor Zuidoost hebben uitgediept en wat voor raakvlakken dit heeft met Community Wealth Building.
Waarom lokaal geld en voor wie?
'Wij willen dat geld en onze inzet waarde schept voor onze communities en leefomgeving'
Met lokaal geld maken we bewuste keuzes met wie we de waarden, onze energie, aandacht en kracht willen uitwisselen. Geld is niet alleen 'een algemeen aanvaard en geaccepteerd ruilmiddel' (Willem Opmeer), maar ook ‘een middel dat sociale relaties creëert en waarde toekent’ (Kate Raworth). We zien dat het neoliberale systeem, waar ons huidig economisch systeem op gebouwd is, niet meer functioneert. Van Kate Raworth, Katherine Trebeck tot onze eigen Kees Klomp laten zien dat het systeem steeds meer is gaan werken voor de happy few.
Complementair geld is met name van betekenis zijn voor perifere gebieden (regio's, wijken) die kampen met economische, sociale achterstand en werkloosheid. Het stimuleert de transitie naar een sociale, duurzame of circulaire economie door het tijdelijk uit de wind houden van kleine initiatieven en waarden te geven aan zaken die nu niet zichtbaar zijn. Met lokaal geld maken we nieuwe verbindingen tussen bedrijven, netwerken en bewoners met een win-win-win3 voor iedereen: people, planet én profit.
De pijnpunten en integrale waarden waar we een bijdrage aan willen leveren zijn: Armoede; gelijke kansen, financiële inclusiviteit, gezond voedsel betaalbaar maken; meer lokale klandizie; veiligheid; lokale productie; betaalbaar vastgoed; goede invulling geven aan Social Return; korte ketens maken; verbinding formele en informele economie; zichtbaarheid maken van impact & witwassen voorkomen.
Voor wie we het doen:
- De kleine en middelgrote ondernemer uit Zuidoost (ZZP’er, Toko-eigenaar, etc)
- De sociale, lokale en/of informele netwerken
- De huishoudens met een smalle beurs
Met wie:
´Pioniers die geloven dat het anders kan, met een droom voor Zuidoost´.
Wij zijn een open consortium (samenwerkingsverband) waar we onze kennis, talenten en krachten bundelen om een lokale munt voor Zuidoost te ontwikkelen. Onze kracht is diversiteit en gelijkwaardigheid: lokale ondernemers, maatschappelijke instellingen, lokale overheid, kennisinstellingen en bewoners. Wij zien onszelf als pioniers die vanuit verschillende rollen gezamenlijk bouwen aan een andere economie. Met de consortium partners hebben we samen een manifest geschreven wat ondertekend is door 23 organisaties, individuen en bedrijven.
Concrete integrale maatschappelijke doelen en resultaten:
Een lokale munt ontwikkelen en laten groeien die leidt tot een veerkrachtige donut economie in Zuidoost: inclusief, sociaal en duurzaam.
Het bevorderen en registreren van impact op sociaal, economisch en duurzaam gebied door co-creatie met bestaande initiatieven gerelateerd aan 4 categorieën:
De lokale economie versterken
Dat doen wij door geld langer in de wijk houden en vaker te laten circuleren zodat de onderlinge handel en ruil bevorderd wordt en lokale netwerken opbloeien. Zo maken we lokaal en inclusief ondernemerschap sterker en kansrijk. We sluiten aan bij gebiedsontwikkelingen (ArenAPoort en Amstel III) en Community Wealth Building.
- 1.000 kaarten uitgeven
- 100 bestedingsposten zijn actief
- 5% absolute waarden van de totale omzet on Zuidoost zit in het systeem
- Munten moeten minimaal 5 x circuleren
- 5% omzetverhoging
- 5 nieuwe banen worden er geschapen?
De sociale waarden activeren
Dat doen we door ons te richten op uitwisseling van diensten, op de inzet van vrijwilligers en door te bouwen aan inclusieve communities en een inclusieve economie. We sluiten ons aan bij het
“Masterplan Zuidoost“ en het “Social Pact”, ondernemers- en buurtplatfoms. We betrekken actief bedrijven met hun Social Return verplichtingen en zoeken aansluiting bij hun Maatschappelijk Verantwoord Ondernemen (MVO) doelen.
- 1.000 burgers doen mee
- 100 vrijwilligers worden gevalideerd
- 5 burgerinitiatieven doen mee
- De burgers zijn gelukkiger en minder eenzaam
De toekomst duurzaam maken
We willen de voetafdruk die ons handelen heeft op de natuur en het klimaat verkleinen. Door het stimuleren van lokale productie en handel, met minder vervoersbewegingen, geven we prioriteit aan duurzame initiatieven. We belonen gedrag dat een duurzame en gezonde levensstijl en een nieuwe circulaire economie bevordert. Hierbij staan centraal de minder draagkrachtige bedrijven, organisaties en bewoners.
- De munt ondersteunt het programma Community Wealth Building en het Masterplan
- 5 duurzaamheids initiatieven worden in de lokale munt beloond
- Impact is meetbaar
Welk effect willen we zien na een jaar:
In samenwerking met Overheid, Burgers, Bedrijven en Kennisinstellingen experimenteren, creëren en innoveren om de transitie naar een lokale donut economie te bewerkstelligen.’
Onze droom is dat 2Ping over 5 jaar zo vanzelfsprekend is dat je het vrijwel overal in Zuidoost kunt uitgeven met regionale en internationale aantrekkingskracht. Het sociaal en economisch kapitaal dat wordt gecreëerd in Zuidoost blijft ook grotendeels in Zuidoost. Netwerken tussen bedrijven, zzp-ers, organisaties, bewoners en initiatieven zijn verstevigd. Vanuit de gezamenlijke waarde die we creëren ontstaat er een overvloed aan kansen en mogelijkheden. Het stelt ons in staat om sociale, economische en duurzame doelen te realiseren. Dat de lokale munt:
De lokale economie is versterkt door geld lokaal te laten stromen
- De lokale munt is geïntroduceerd in de Bijlmer, met behulp van bestaande software van Stro/Cyclos (Een digitaal systeem waar iedereen zich veilig bij voelt)
- Social return is lokaal ingezet
- lokale inkoop is gestimuleerd
De sociale waarden zijn geactiveerd
- Vrijwilligerswerk wordt vergoedt
- De sociale, lokale netwerken zijn versterkt
Lokaal geld heeft bijgedragen aan de toekomst meer duurzaam maken
- CO2 reductie is meetbaar gemaakt doordat lokaal transport en productie tot stand is gekomen ipv grote afstanden
- Energietransitie is gestimuleerd via projecten
Integrale resultaten
- Waarde: sociaal, in ruil en in geld zichtbaar en meetbaar maakt via een dashboard
- Er is minimaal 1 experiment uitgevoerd vanuit het Living Lab waar actiegericht leren en experimenteren centraal staat en een kennisinstelling is actief aangehaakt
- Lokaal Geld Zuidoost is iIngebed is bij het programma “Community Wealth Building en het Masterplan van de gemeente Zuidoost.
- Er is een implementatie plan ontwikkelt over hoe de vervolg stappen vorm te geven. Te denken valt aan het opschalen/uitbreiden van het experiment, het starten van nieuwe experimenten, het aanpassen van de aanpak, etc. Onderdeel van het implementatie plan is dat we kijken naar het software systeem en of we vanuit dit systeem blijven opereren of ons eigen systeem gaan ontwikkelen met behulp van lokale experts.
- De lokale munt wordt breed gedragen door diverse gemeenschappen en netwerken in Zuidoost, o.a. door de inzet van ambassadeurs en het uitrollen van onze campagne. Hierdoor ontstaat een brede en representieve community van gebruikers
- Een kennisinstelling is actief aangehaakt bij het Living Lab
Communicatie
Bij al onze activiteiten maken we gebruik van lokale media kanalen zoals Zuidoost TV, Radio Mart, Razo, New Metropolis Zuidoost, facebook en whatsapp groepen. Dit is van belang om draagvlak te creëren bij de bevolking van Zuidoost. Maar ook om het consortium uit te breiden met nieuwe partners. Ook via het verspreiden van flyers en nieuwsbrieven willen we zoveel mogelijk onze impact bekend maken. Hier zijn de links waar dit initiatief via social media in de spotlight staat: https://amsterdam.groenlinks.nl/podcast/aflevering10
https://www.dezwijger.nl/programma/cinema-klimaattafel
Meerwaarde tov andere vormen van lokaal geld. Wat voegt dit toe op de bestaande lokaal geld vormen:
Geld is een afspraak van wederzijds vertrouwen, maar geld is ook energie die pas waarde genereerd als het stroomt. Het is daarom essentieel om te kijken naar de bedding, het ecosysteem waarin het geld blijft stromen. Hoe geef je het een dienende rol? Experimenten in Nederland vonden voornamelijk plaats in bedrijfsnetwerken tussen bedrijven (United, Utrechtse Euro) en in communities waarbij individuen diensten uitwisselen (Lets, Makkies). Al deze initiatieven zijn tot nu beperkt gegroeid, maar nooit opgebloeid en een marginale rol blijven spelen. We gaan met lokaal geld 4 helixen verbinden (Overheid, Burger, Bedrijfsleven en kennisinstituten) waardoor de munt makkelijker blijft stromen en steeds weer waarde kan creëren. We omarmen daarbij bestaande initiatieven en ook bestaande munten kunnen meedraaien in het geheel.We willen het wiel niet opnieuw uitvinden, maar leren van bestaande initiatieven zoals de Noppes, de Makkie, de Ecocoin, Circulair geld van Stro, Tijdsparen. Ook innovaties op het gebied van fintech, tokens en blockchain willen wij op implementatie mogelijkheden onderzoeken. Fintech en blockchain bieden de mogelijkheid te leren van de routing die het lokaal geld aflegt.
Kernwaarden en spelregels
Met elkaar bepalen we de spelregels die voortkomen uit onze gezamenlijke kernwaarden: inclusief, verbindend, transparant, gelijkwaardig, wederkerig en duurzaam. Met bottom-up projecten stimuleren we de waardecreatie en (mede)eigenaarschap. Daarnaast ondersteunt het bedrijven om de transitie slag te maken naar een duurzame, toekomstbestendige en purposedriven onderneming. Rechtvaardigheid in plaats van ongelijkheid. Impact in plaats van onhoudbare groei. Overvloed in plaats van schaarste. We hebben oog voor veiligheid, wetgeving en privacy.
Samenwerken aan transitievraagstukken; wat is er nodig? - Opbrengsten van het Amsterdam Smart City partnerdiner 2024

Als Amsterdam Smart City netwerk bijten we ons vast in complexe stedelijke transitievraagstukken. Ze zijn complex omdat doorbraken nodig zijn; van kleine doorbraakjes, tot grotere systeem doorbraken. Denk aan bewegingen rond; organisatie-overstijgend werken, domein-overstijgend werken, en van competitief naar coöperatief. Als netwerk zetten we samenwerkingsprojecten op waarin we gaandeweg ondervinden met wat voor barrières we te maken hebben en wat voor doorbraken er nodig zijn.
Tijdens ons jaarlijkse Partnerdiner op 2 april, hadden we het samen met eindverantwoordelijken van onze partnerorganisaties over de strategische dilemma’s die spelen bij transitievraagstukken. Als gespreksstarters gebruikten we onze lopende onderwerpen van 2024: De coöperatieve metropool, de ondergrond, de circulaire metropool en drijvende wijken. De gesprekken aan tafel gingen echter over wat er aan de basis staat van het werken aan transitievraagstukken. Zo ging het bijvoorbeeld over; het samenwerken aan visies en scenario’s, leiderschap, burgerlijke ongehoorzaamheid en de kracht van coöperaties. In dit artikel bespreek ik beknopt een aantal onderwerpen die onder de aandacht werden gebracht door onze gasten.
Belangen en visie organiseren
Bij een vraagstuk of onderwerp als de ondergrond, gaan we het al snel hebben over de data en de oplossingen. Dat is ‘te makkelijk’. Technisch gaat het allemaal wel kunnen, maar als we daar te snel beginnen met de oplossing lopen we over een aantal jaar weer vast. Het is belangrijk om eerst een stapje terug te doen en een gedeeld belang en gedeelde visie te organiseren.
Hoe je belanghebbenden verzamelt, en de methode om tot een gedeelde visie te komen, dat is wat meer aandacht verdient. Neem het ondergrond vraagstuk als voorbeeld. Op welke schaal organiseer je daarvoor de belanghebbenden? Aan de oppervlakte hebben we Gemeentelijke en Provinciale grenzen, maar in de ondergrond liggen netwerken van kabels en leidingen die op andere schaal zijn geïnstalleerd en hebben we te maken met bodemtypologieën met verschillende behoeften.
Samen voorstellen en voorspellen
Dat waar je naartoe wilt werken, dat moet van iedereen voelen. Het is belangrijk om een setting te creëren van gedeeld eigenaarschap, waarin iedereen zich ook gehoord voelt, en dat je voelt dat de mensen met wie je gaat samenwerken ook voor jouw belangen op zullen komen. Om samen tot een visie te komen, is het belangrijk om te werken aan scenario’s en die samen te doorleven. Je moet het dan niet alleen hebben over waar je heen wilt, maar ook uitwerken wat er gebeurt als je niets doet of als het helemaal verkeerd uitpakt.
De scenario’s zouden op waarden moeten rusten. Het beeld wat bij de scenario’s hoort is veranderlijk, maar de waarden niet. Samen ben je continu in samenspraak over wat de waarden betekenen voor het verhaal dat je creëert.
Leiderschap en een interdisciplinaire werkwijze
Transitievraagstukken en bovenstaande aanpakken verdienen een bepaald soort leiderschap. Zo zou een leidinggevende bijvoorbeeld een veranderlijke en faciliterende houding moeten tonen, en moet hij/zij vanuit waarden werken die inspireren en verbinden. Het zou meer moeten gaan over het faciliteren van doeners, het stimuleren van doelgericht samenwerken in plaats van taakgericht en ruimte bieden voor menszijn en persoonlijke expertises. Met dit laatste wordt verwezen naar een stukje burgerlijke ongehoorzaamheid. Om dingen die we belangrijk vinden in gang te zetten moeten we soms even los kunnen denken van onze organisatiestructuren en functies. We zouden wel wat vaker mogen appelleren aan ons menszijn.
Meer faciliteren en minder hiërarchie helpt ons om beleid en praktijk dichter bij elkaar te brengen, en om van competitief naar meer coöperatief te bewegen. Als je naar de uitvoering gaat mag de kracht verplaatsen naar de uitvoerders. De machtsverschuivingen tussen leidinggevenden en de doeners, met specifieke rollen en expertises, mag in een constante wisselwerking rond gaan.
Ook interdisciplinair samenwerken aan transitievraagstukken zal nog meer moeten worden gestimuleerd, en misschien wel de norm moeten worden. Bij overheden en bestuurders bijvoorbeeld, zijn transitie thema’s verdeeld over domeinen als energie, mobiliteit, etc. maar de vraagstukken zelf zijn domein overstijgend. Als voorwaarde zou je kunnen stellen dat je altijd twee transities aan elkaar moet koppelen. We zouden meer inspirerende voorbeelden moeten laten zien waarbij verschillende domeinen en transities aan elkaar worden gekoppeld, door bijvoorbeeld overheden.
Publiek-privaat-civiel
Publieke, private en civiele partijen zouden nog meer naast elkaar aan tafel mogen, in plaats van tegenover elkaar. Bedrijven kunnen verzuild zijn, of zich zo voelen, en zouden nog meer om zich heen kunnen kijken en samenwerken. Niet alleen met overheden, maar ook met civiele organisaties. Er zijn vaak meer gezamenlijke belangen dan we denken.
In een beweging naar niet-competitief samenwerken kunnen coöperaties een belangrijke factor zijn. Wanneer je meer autoriteit bij coöperaties neerlegt, weet je zeker dat er in de basis voor een wijk, een stad, haar inwoners, een publiek belang wordt gewerkt. Er liggen dan ook veel kansen bij een faciliterende houding vanuit de overheid naar coöperaties toe, en in de samenwerking tussen bedrijven en coöperaties.
Er zijn tijdens dit diner veel onderwerpen aan bod gekomen waar we met het netwerk mee aan de slag kunnen in onze programmering. De input wordt gebruikt voor onze lopende vraagstukken en we gaan de komende tijd in gesprek met partners om te kijken of we van start kunnen met verdiepende sessies of het ontwikkelen van methoden op (enkele van) deze onderwerpen.
<em>Wil je doorpraten over deze onderwerpen, met ons - of een van onze partners? Mailen kan naar pelle@amsterdamsmartcity.com*</em>
Demoday #23: Mobility Injustices and the creative mind.

In a world where moving yourself from point A to point B is becoming much more crucial than ever, there are people out there who cannot experience such a luxury at the flick of a wrist, or perhaps the clack of an ankle? It is hard to imagine sometimes, but there are those who cannot move around as easily as others; be it because of financial, physical, vehicular, or other reasons. A community that can go about as they please without any issues is a happy community that is beneficial to society – For a collective of governments and businesses it is in their best interests to ensure citizens can experience freedom and liberty in their mobility. The question of how to achieve this freedom in mobility and how to deter against injustices regarding mobility remains a hot topic, however. On behalf of Provincie Noord Holland and in collaboration with Amsterdam Smart City and Amsterdam Centre of Expertise, a group of graduating students tackled this topic on the latest Demoday of 2024.
Starting the voyage : What are mobility injustices?
A value workshop led by Jackie Ippel and Jade Salomons engaged the participants in a fun, creative wave of brain-crackling activities. Participants were presented with a question of whether they knew what mobility injustices, or as we call it in Dutch “Mobiliteits Armoede”, was. An explanation of which followed suit soon after. Mobility Injustices, as described by the KiM organization, explains the inability or difficulties people experience in terms of reaching activity locations due to inadequate transport options, combined with socio-economic and spatial conditions in which people find themselves. As a result, they are often hindered in their participation in social life, which negatively affects their quality of life.
It is important to think about the definition of what exactly mobility injustices entail, as it helps us find a better understanding in finding a creative series of solutions that will solve this complex jigsaw puzzle.
Like a ball of yarn : unraveling theorems.
In order to stimulate the brain of each participant and to get the blood pumping through their legs, each participant was asked to stand in the middle of the room. As was once quoted in the horror thriller Saw; “Wanna play a game?”. Participants were presented with a series of theorems in which they had to make a choice that’d question their liberal thoughts; either stand on one side of the room for one answer or on the other side for the other – No in-betweens. Being forced to make ultimatums proved to be both challenging for the participants yet fun, as it was met with bountiful heaps of enthusiasm. In the first theorem, participants were presented with a question of whether or not mobility should be a fundamental right for each and every citizen. While agreed one did not, but can their minds be changed? A flurry of other theorems were presented, each of which dove deeper into the depths of dilemmas one may encounter when attempting to solve the puzzle of mobility inequality. Like who is more important, those who have low incomes or those who suffer from physical and mental disabilities which hinder their day-to-day lives? Brief discussions flowed forth after each and every theorem, after each voting round, reasons were given as to why one can choose one over the other. After which another second voting session followed. Perhaps new insights would change one’s opinion on the subject? It actually did once or twice! Such is the power of dialogue.
Embarking into the abyss : Worst Idea Possible.
“How ba-a-a-ad can I be? I’m just doing what comes naturally-“ -such were the words Onceler sung in Dr. Seuss’s ‘The Lorax’. While people do not like the idea of being bad or thinking of bad ideas sometimes this way of thinking can actually bring plentiful new insights never thought of before. The group split itself in two, each of which under the guidance of either Jackie Ippel or Jade Salomons. Participants were asked to come with their most horrid, ludicrous ideas that’d actually make mobility injustices worse. After which they had to decide what element made this a bad idea. Example, if public transport were to be described, the element that’d make the idea bad would be less alternatives for traveling. The final and third part of this exercise required something rather unique however. Does your mind already wonder what? Well, it’s quite simple really, now participants had to come up with what would be the opposite of their bad idea! So what would their idea be in reverse, an actual solution to the problem they created. If your bad solution was to make everything only scannable by QR-codes its reverse solution would be… using solely physical text! For a solid 20 minutes participants racked their heads and discussed until their times were down to only 5 minutes left. The last of those minutes left were spent discussing and laughing about their ideas – A method met with confusion at first was appreciated with loads of enthusiasm by the end where only time was the fun killer.
A creative view found in madness: Crazy Eight.
The creativity cannot just end after one session. Holding the thought of the previous session, participants were asked to gather in a circle around a table. With each given a paper and asked to fold it so that 8 separate square spaces would form on the sheet the Crazy Eight exercise was explained. Participants were asked to draw their solution one of their 8 square. For each drawing they had a minute per square, a total of 8 minutes until all were filled. Of course with so little time there was little room for thinking, imagination had to pull the cart here, which led to both silly and unique drawings. The longer the session went on the more difficult it became – the participants were truly pushed to their creative limits. A well-trained eye could even notice how some participants still tried to finish their previous drawing before moving onto the next despite the time. You could feel the atmosphere in the room shift to a hectic, almost crazy aura, thus doing its name of ‘Crazy Eight’ truly justice.
At the end of the session it was only natural that people presented their top 3 drawings. One after another each participant proudly showed off their creative drawings like a trophy to the rest of the group. Turns out, despite not communicating with one another during the drawing sessions there were lots of similarities in the elements used in each drawing. The bus, the civil servant, and the elderly were commonly used elements seen back in almost everyone’s drawing. Via these sources of inspiration it became clear just where the solutions may lie.
An journey’s end : Results.
At the end of the session we didn’t just start talking about what we had done. No, instead we At the end of the session, we didn’t just start talking about what we had done. No, instead we went back and looked at the very first theorem everyone was presented with; “Should mobility be a fundamental right for each and every citizen?”. Last time everyone answered all but one was in favor of this theorem, now participants were asked to revise their statement and see if they still agreed with what they said at the beginning. As said before, dialogue can change the outlook we have on the world and so someone did change their stance – The one person that disagreed with the theorem now actually agreed that mobility should be a fundamental right. A full 100% score! Only after this a talk about what we had done started. Opinions were asked and each participant shared the emotion they had experienced during this work session and to leave it behind on a post-it.
· Fun and insightful: The gamification of thinking is taking the design world by storm, and on this Demoday, it has proven that this form of design thinking can not only be effective in bringing brand new insights but also can be fun.
· Enthusiasm: What started off with an iffy approach ended with tons of enthusiasm. Idea generating doesn’t just have to be sitting at a table and talking in your own bubble; it can become so much more effective when the mood is changed from serious and gloomy to frivolous and enthusiastic..
· Creativity: A creative way of thinking actually helps in generating ideas. Using playful thinking such as considering a bad idea first and then the opposite helps find solutions to problems in a much more efficient way.
During this Demoday, we as a group of graduating students got to know the thought process behind those who work within the field of mobility. While we hope that we brought them plenty of insights and, above all, a fun day, it is sufficient to say that we too learned an abundance of information. The insights made during the Demoday will be used by us in writing our final report for the Provincie Noord Holland regarding a detailed consult on how to improve the mobility of the citizens of the province of Noord-Holland and how to tackle the injustices surrounding mobility. Demoday’s are fun and can inspire even the most closed-minded people. If we could, we would do it all over again. And, if you are still on the fence about joining a Demoday, then I hope that column will ignite that curiosity.
New article "Guidelines for a participatory Smart City model to address Amazon’s urban environmental problems"
Dear Amsterdam Smart City Managers and Members,
As a member of your digital platform, I would like to sincerely thank you for the insightful emails and contents you provide to members like myself throughout the year.
I am delighted to share with you my latest published article, "Guidelines for a participatory Smart City model to address Amazon’s urban environmental problems," featured in the December 12, 2023 issue of PeerJ Computer Science.
The article can be fully accessed and cited at:
da Silva JG. 2023. Guidelines for a participatory Smart City model to address Amazon’s urban environmental problems. PeerJ Computer Science 9:e1694 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.1694
I welcome you to read my publication and share it with fellow members who may find the digital solutions for the Amazon region useful. Please let me know if you have any feedback or ideas to advance this work.
Sincerely (敬具)
Prof. Jonas Gomes ( 博士ジョナス・ゴメス)
www.jgsilva.org
UFAM/FT Industrial Engineering Department (Manaus-Amazon-Brazil)
The University of Manchester/MIOIR/SCI/AMBS Research Visitor 2020/2023
Amsterdam Region’s Insights on Local Green Deals during COP28
Participating in a COP28 side event organized by the European Commission, the Amsterdam Region delved into Local Green Deals as instrument for achieving the green transition. The primary goal for the session was to uncover actionable strategies and prerequisites essential for fostering public-private collaboration to realize the sustainability transition. Marja Ruigrok, vice-mayor for the municipality of Haarlemmermeer, represented the Amsterdam Region alongside political and business leaders from Braga (Portugal), Aalborg (Denmark) and Skelleftea (Sweden).
Commencing the session, Valentina Superti, DG for Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship, and SMEs at the European Commission, highlighted Europe's ambition to become the first climate-neutral continent by 2050. This necessitates a transformative shift towards sustainability, digitalization, and resilience, which is why the Commission is introducing critical legislation like the Net-Zero Industry Act and the Critical Raw Materials Act.
Ruigrok shared insights from the Amsterdam Metropolitan Region’s efforts in establishing Local Green Deals, emphasizing her role as political ambassador and champion for the Green Deal Bikes initiative. She stressed the importance of cycling, explaining that despite its reputation as a cycling paradise, approximately 20% of young people in the Amsterdam Region can not ride a bike: “If you don’t learn to ride a bike at a young age, you are also much less likely to use a bike for commuting later in life. That’s why in this Green Deal, we stimulate young people to learn to ride bikes, and encourage employers to support commuting by bike. This is crucial because employees who bike take on average 2.5 fewer sick days compared to those who don’t bike.”
Reflecting on success factors, Ruigrok emphasized the need for political commitment, and clear project ownership: "From a political point of view, you need long term commitment, and you have to create ownership. Someone has to take ownership and say ‘this is my project.’ This might be a governmental agency, a company, a knowledge institution, or civil society organisation - but someone has to take the lead. Otherwise, you will continue to talk, and nothing will happen."
Throughout the session, participants provided practical insights and recommendations for fostering successful public-private collaborations in general, and Local Green Deals in specific:
- Lasse Frimand Jensen, mayor of the City of Aalborg, emphasized the necessity of accountability mechanisms: “Mutual commitment is necessary and there must be mechanisms in place to keep each other accountable.”
- Ricardo Rio, mayor of City of Braga and Member of the European Committee of the Regions, highlighted the role of local authorities in mobilizing capacity and engaging stakeholders: “Local authorities need to have the spirit to engage stakeholders and shape partnerships. We also need governance models that tranced political cycles, and that allow people to participate and hold us accountable.”
- Jens Broberg, representing the business sector, emphasized the urgent need for appropriate incentives: “Governments must use policy frameworks to incentivize and regulate businesses and industry towards a green economy.”
- Evelina Fahlesson, vice-mayor of Skelleftea Municipality emphasized the need for open and honest dialogue: “As a municipality, you have to be open about your challenges and willing to start a dialogue with your citizens and companies. Use procurement and new financing models as tools to implement a shared vision.”
- David Nordberg, from Skanska Sweden, encouraged business leaders to align their business models with sustainability ambitions: "Be brave: try new ways of doing business and work in collaborations. In the long term, there is no conflict between sustainability and the economy."
The session highlighted the pivotal role of collaborative multi-stakeholder partnerships in achieving the green transition, emphasizing sustained political commitment, robust governance structures transcending political timelines, and policy frameworks incentivising sustainable businesses.
In the context of COP28, the true challenge lies in replicating these successful approaches on a wider scale, extending beyond the relatively affluent European context to a global landscape with more limited resources. In many regions, the urgent and acute impacts of climate change are already pervasive, amplifying the need for swift, comprehensive action. This necessitates a global and concerted effort of nations and industries, to surmount the hurdles posed by resource scarcity and varying levels of socio-economic development. This calls for collaboration not only within regions but across continents, fostering knowledge-sharing, technology transfer, and collective efforts in tackling climate challenges. The urgency of the climate crisis demands a united global front, where the lessons learned and successes achieved in Local Green Deals can serve as guiding principles towards a more sustainable and resilient future for all.
ICC Phase 2: Kick off in Brussels

The Intelligent Cities Challenge (ICC) is one of the European Commission’s largest city support initiatives supporting European cities in their green and digital transitions. ICC delivers knowledge and support services to cities and their local economies to address two major challenges: making the transition to a net-zero economic model, while enabling social inclusion and sustainable development for every EU citizen.
Cities learn how to address these challenges through Local Green Deals: integrated, multi-disciplinary action plans to lead the green and digital transition across sectors from the built environment, urban mobility and renewable energy systems to tourism or small retailers. Cities become members of a vibrant network, gain access to advisory services, innovation and sustainability management techniques, cutting-edge technology and training and get inspiration and advice from peers and mentor cities.
Building on the success of the previous edition of the ICC programme (2020-22) and Digital Cities Challenge (2017-19), the ICC will now enter Phase 2!
Amsterdam as a Mentor City
Like previous years, Amsterdam has been selected to join the support programme as a mentor city. The city will play a leading support role by guiding the 64 core cities as they embark on their two year journey to create impactful strategies and develop innovative solutions that will place the cities at the forefront of the green and digital twin transition through Local Green Deals. A nice compliment, allowing the Amsterdam Region to share their experiences and learnings from setting up Local Green Deal initiatives over the past years.
The Intelligent Cities Challenge Strategy City Lab: Accelerating the Twin Transition (November 2023)
On 23 and 24 November 2023, over 200 people - a mix of Intelligent Cities Challenge (ICC) core and mentor cities, political leaders and representatives from European institutions gathered for the first time in-person to discuss the status quo of Twin Transition. Through examples and best practices, attendees had the honour to hear from over 30 speakers as they shared insights into collaboration methods, Local Green Deals, climate ambitions, digital transitions and more across the course of 20 sessions.
Amsterdam Smart CIty's Leonie van den Beuken travelled to this gathering in Brussels as one of the representatives of the Amsterdam Region. She summarized her trip as follows:
This EU program helps cities from north to south, east and west to connect, share and learn. A much needed interaction, as we all try to improve the quality of life of our citizens. We all struggle with the ever rising cost of living. And we all want to get our cities to become more sustainable.
None of this comes easy, but we all know that local collaboration plays a key role. Building local coalitions between government, businesses and citizens is one thing, but how do we make sure these so called coalitions of the willing actually become coalitions of the doing?
Some of the learnings we shared from the Amsterdam Region are; the need for political support and the importance of trust and respect.
Local political leadership will inspire and guide society and entrepreneurs to invest and contribute. However, make sure pilotical support doesn’t evolve into political ownership. When that happens, societal parties and businesses tend to step out the coalition.
Take the importance of trust and respect seriously. You need to show long term commitment, take time to create understanding between parties. Take competition between participating SME’s serious and define together how to handle this together. Create a workflow in which smaller parties are allowed to participate less intense but sill feel incorporated.
We'll keep you up to date on our participation in future gatherings and results from ICC Phase 2. Want to know more? Check https://www.intelligentcitieschallenge.eu/
CTwalk Map

What opportunities for social cohesion do cities provide?
Is your neighbourhood park frequented by a homogenous or diverse mix of people? How many hashtag#amenities can you reach within a short hashtag#walking distance? And do you often encounter people from different walks of life?
I am very excited to introduce to you CTwalk Map, a web tool that seeks to highlight the social cohesion potential of neighbourhoods while also unmasking local access hashtag#inequities. CTwalk maps opportunities that different age groups can reach within a 5 or 15-minute walk.
🚶♀️🚶♂️ It uses granular population, location, and pedestrian network data from open sources to estimate how many children, adults, and elderly hashtag#citizens can reach various destinations in a city within a short walk.
🌐 It offers a simple and straightforward understanding of how the 5 and 15-minute walking environments are shaped by the street network.
➗ It estimates the degree of pedestrian co-accessibility of various hashtag#city destinations.
CTwalk Map is now available for the five largest cities in The Netherlands.
Take a look at the web tool:
https://miliasv.github.io/CTwalkMap/?city=amsterdam
... learn more about CTwalk Map at this link:
[currently does not support mobile phones or tablets]
...and let us know what you think!
Hoe creëer je Levende Lerende Netwerken die impact hebben?

Hoe maak je de stap van gezamenlijk leren, naar samen echt dingen doen? Er is al veel over gezegd en geschreven... Communities of practice, smeden van allianties, enz enz... Vaak blijft het dan een beetje hangen bij het organiseren van een toffe sessie, vast met veel energie. En daarna gaat iedereen - als het goed is met nieuwe ideeën en inspiratie - weer verder met waar 'ie al mee bezig was. Vaak is dat al genoeg, maar zeker in transities wil je eigenlijk een stapje verder komen.
Is eigenlijk al wel voldaan aan een aantal belangrijke condities om het netwerk levend te maken en te houden?
Reflecterend op onze eigen praktijk, ontdekten we een aantal kenmerken die belangrijk en beïnvloedbaar zijn bij het bouwen van impactvolle levende lerende netwerken. Amsterdam Smart City zelf is zo'n voorbeeld, waarin we voortdurend met elkaar op zoek zijn naar hoe we onze samenwerking van betekenis kunnen laten zijn voor de duurzame transities in onze regio. De Green Deal Circular Festivals, het MRA Platform Smart Mobility, Sail Amsterdam, en het Initiatief Bewust Bodemgebruik zijn enkele andere voorbeelden van levende lerende netwerken. Ook hier zagen we telkens dat de volgende kenmerken van belang zijn om verder te komen, en om de stap te maken van samen leren, naar samen doen:
(1) Wederzijdse afhankelijkheid tussen deelnemers
(2) Beweging door gedeelde energie
(3) Diversiteit daagt uit
(4) Persoonlijke ontwikkeling, empathie, ego overstijgend
(5) Veilige ruimte om te leren en ontwikkelen
Op basis van onze ervaringen in de praktijk, hebben we onze kijk op het ontstaan, de kenmerken en het begeleiden van Levende Lerende Netwerken opgeschreven in een whitepaper. Wil je meer weten, dan kun je die downloaden via onderstaande link (naar beneden scrollen naar de download knop van de Levende Lerende Netwerken Whitepaper).
Tijdens het PGM Open Congres op 26 september organiseren we hierover een workshop voor programmamanagers (https://lnkd.in/gcRPv4V8). En, je kunt me natuurlijk altijd een berichtje sturen als je meer wilt weten!
Science-based targets for nature: Setting ambitious and effective goals for biodiversity

Preserving and reviving nature plays a crucial role in addressing climate change and biodiversity loss. But determining the starting point and measuring progress can be challenging.
Science-based targets offer a starting point to take concrete actions toward a sustainable future.
Setting SBTs enables companies to transform vague intentions into specific commitments. Imagine going from "We should do something with water" to "We aim to reduce water consumption in high-stress regions by 25% before 2030 through rainwater catchment and increased reuse." Science-based targets provide a clear direction and roadmap for achieving such goals.
If you’re interested in learning more about how science-based targets can drive positive change and contribute to a sustainable future, check out Metabolic's latest article. We explore SBTs and their impact on biodiversity and nature.
#Sustainability #ScienceBasedTargets
How to live with global warming larger then 3 degrees C
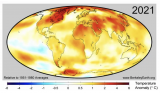
In my previous post (in Dutch) I summarized the main conclusions of the IPCC's Final Report: The probability that the world will have warmed by more than three degrees by 2100 is much greater than that we hold it at 1 1/2 degrees Celsius. In this post I will discuss the consequences of this for the world, whether there is still a way out and what the consequences are for Dutch policy.
eBooks on how to create better streets, neighborhoods and cities

Each of the ebooks I've compiled from my blog posts and other publications contains essays on how to make our environment more livable and humane. Anyone can download these ebooks for free. There are also print-friendly versions available and most are available in English and Dutch. Below you will find an overview with links to all of them:
New and free e-book: Better cities and digitization

For 23 weeks I have published weekly episodes of the series Better Cities. The role of digital technology on this site. I have edited and compiled these episodes in an e-book (88 pages). You can download this for free via the link below. The book has 17 chapters that are grouped into six parts:
1. Hardcore: Technology-centered approaches
2. Towards a humancentric approach
3. Misunderstanding the use of data
4. Ethical considerations
5. Embedding digitization in urban policy
6. Applications (government, mobility, energy and healthcare)
7. Wrapping up: Better cities and technology
23. Epilogue: Beyond the 'Smart City'

In the last episode of the Better cities: The contribution of digital technology-series, I will answer the question that is implied in the title of the series, namely how do we ensure that technology contributes to socially and environmentally sustainable cities. But first a quick update.
Smart city, what was it like again?
In 2009, IMB launched a global marketing campaign around the previously little-known concept of 'smart city' with the aim of making city governments receptive to ICT applications in the public sector. The initial emphasis was on process control (see episode 3). Especially emerging countries were interested. Many made plans to build smart cities 'from scratch', also meant to attract foreign investors. The Korean city of Songdo, developed by Cisco and Gale International, is a well-known example. The construction of smart cities has also started in Africa, such as Eko-Atlantic City (Nigeria), Konzo Technology City and Appolonia City (Ghana). So far, these cities have not been a great success.
The emphasis soon shifted from process control to using data from the residents themselves. Google wanted to supplement its already rich collection of data with data that city dwellers provided with their mobile phones to create a range of new commercial applications. Its sister company Sidewalk Labs, which was set up for that purpose, started developing a pilot project in Toronto. That failed, partly due to the growing resistance to the violation of privacy. This opposition has had global repercussions and led in many countries to legislation to better protect privacy. China and cities in Southeast Asia - where Singapore is leading the way - ignored this criticism.
The rapid development of digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence, gave further impetus to discussion about the ethical implications of technology (episodes 9-13). Especially in the US, applications in facial recognition and predictive police were heavily criticized (episode 16). Artificial intelligence had meanwhile become widespread, for example to automate decision-making (think of the infamous Dutch allowance affair) or to simulate urban processes with, for example, digital twins (episode 5).
This current situation - particularly in the Netherlands - can be characterized on the one hand by the development of regulations to safeguard ethical principles (episode 14) and on the other by the search for responsible applications of digital technology (episode 15). The use of the term 'smart city' seems to be subject to some erosion. Here we are picking up the thread.
Human-centric?
The dozens of descriptions of the term 'smart city' not only vary widely but they also evoke conflicting feelings. Some see (digital) technology as an effective means of urban growth; others see it as a threat. The question is therefore how useful the term 'smart city' is still. Touria Meliani, alderman of Amsterdam, prefers to speak of 'wise city' than of 'smart city' to emphasize that she is serious about putting people first. According to her, the term 'smart city' mainly emphasizes the technical approach to things. She is not the first. Previously, Daniel Latorre, place making specialist in New York and Francesco Schianchi, professor of urban design in Milan also argued for replacing 'smart' with 'wise'. Both use this term to express that urban policy should be based profoundly on the wishes and needs of citizens.
Whatever term you use, it is primarily about answering the question of how you ensure that people - residents and other stakeholders of a city - are put in the center. You can think of three criteria here:
1. An eye for the impact on the poorest part of the population
There is a striking shift in the literature on smart cities. Until recently, most articles focused on the significance of 'urban tech' for mobility, reduction of energy use and public safety. In a short time, much more attention has been paid to subjects such as the accessibility of the Internet, the (digital) accessibility of urban services and health care, energy and transport poverty and the consequences of gentrification. In other words, a shift took place from efficiency to equality and from physical interventions to social change. The reason is that many measures that are intended to improve the living environment led to an increase in the (rental) price and thus reduce the availability of homes.
2. Substantial share of co-creation
Boyd Cohen distinguishes three types of smart city projects. The first type (smart city 1.0) is technology- or corporate-driven. In this case, companies deliver instruments or software 'off the shelf'. For example, the provision of a residential area with adaptive street lighting. The second type (smart city 2.0) is technology enabled, also known as government-driven. In this case, a municipality develops a plan and then issues a tender. For example, connecting and programming traffic light installations, so that emergency services and public transport always receive the green light. The third type (smart city 3.0) is community-driven and based on citizen co-creation, for example an energy cooperative. In the latter case, there is the greatest chance that the wishes of the citizens concerned will come first.
A good example of co-creation between different stakeholders is the development of the Brain port Smart District in Helmond, a mixed neighborhood where living, working, generating energy, producing food, and regulating a circular neighborhood will go hand in hand. The future residents and entrepreneurs, together with experts, are investigating which state-of-the-art technology can help them with this.
3. Diversity
Bias among developers plays a major role in the use of artificial intelligence. The best way to combat bias (and for a variety of other reasons, too) is to use diversity as a criterion when building development teams. But also (ethical) committees that monitor the responsible purchasing and use of (digital) technologies are better equipped for their task the more diverse they are.
Respecting urban complexity
In his essay The porous city, Gavin Starks describes how smart cities, with their technical utopianism and marketing jargon, ignore the plurality of the drivers of human behavior and instead see people primarily as homo economicus, driven by material gain and self-interest.
The best example is Singapore – the number 1 on the Smart City list, where techno-utopianism reigns supreme. This one-party state provides prosperity, convenience, and luxury using the most diverse digital aids to everyone who exhibits desirable behavior. There is little room for a differing opinion. A rapidly growing number of CCTV cameras – soon to be 200,000 – ensures that everyone literally stays within the lines. If not, the culprit can be quickly located with automatic facial recognition and crowd analytics.
Anyone who wants to understand human life in the city and does not want to start from simplistic assumptions such as homo economicus must respect the complexity of the city, try to understand it, and know that careless intervention might have huge unintended consequences.
The complexity of the city is the main argument against the use of reductionist adjectives such as 'smart', but also 'sharing', circular, climate-neutral', ‘resilient' and more. In addition, the term smart refers to a means that is rarely seen as an aim as such. If an adjective were desirable, I prefer the term 'humane city'.
But whatever you name a city, it is necessary to emphasize that it is a complex organism with many facets, the coherence of which must be well understood by all stakeholders for the city to prosper and its inhabitants to be happy.
Digitization. Two tracks
City authorities that are aware of the complexity of their city can best approach digitization along two tracks. The first aims to translate the city's problems and ambitions into policy and consider digital instruments a part of the whole array of other instruments. The second track is the application of ethical principles in the search for and development of digital tools. Both tracks influence each other.
Track 1: The contribution of digital technology
Digital technology is no more or less than one of the instruments with which a city works towards an ecologically and socially sustainable future. To articulate what such a future is meaning, I introduced Kate Raworth's ideas about the donut economy (episode 9). Designing a vision for the future must be a broadly supported democratic process. In this process, citizens also check the solution of their own problems against the prosperity of future generations and of people elsewhere in the world. Furthermore, policy makers must seamlessly integrate digital and other policy instruments, such as legislation, funding, and information provision (episode 8).
The most important question when it comes to (digital) technology is therefore which (digital) technological tools contribute to the realization of a socially and ecologically sustainable city.
Track 2: The ethical use of technology
In the world in which we realize the sustainable city of the future, digital technology is developing rapidly. Cities are confronted with these technologies through powerful smart city technology marketing. The most important question that cities should ask themselves in this regard is How do we evaluate the technology offered and that we want to develop from an ethical perspective. The first to be confronted with this question—besides hopefully the industry itself—is the department of the Chief Information or Technology officer. He or she naturally participates in the first track-process and can advise policymakers at an early stage. I previously inventoried (ethical) criteria that play a role in the assessment of technological instrument.
In the management of cities, both tracks come together, resulting in one central question: Which (digital) technologies are eligible to support us towards a sustainable future in a responsible way. This series has not provided a ready-made answer; this depends on the policy content and context. However, the successive editions of this series will have provided necessary constituents of the answer.
In my e-book Cities of the Future. Always humane, smart if helpful, I have carried out the policy process as described above, based on current knowledge about urban policy and urban developments. This has led to the identification of 13 themes and 75 actions, with references to potentially useful technology. You can download the e-book here:
New e-book: Kennisdossier Zonne-energie

I updated and put together 75 posts and articles about the energy transition in a new e-book (in Dutch) 'Kennisdossier Zonne-energie' (120 pages). If you interested, download it for free with the link below.
22. Two '100 smart city missions'- Twice an ill-advised leap forward

The 22nd and penultimate episode in the *Better cities: The contribution of digital technology-*series will discuss two ambitious ‘smart city’plans of two governments and the associated risks.
Recently, the European Commission launched a 100-city plan, the EU Mission on Climate-Neutral and Smart Cities. One hundred European cities that aspire to be climate neutral by 2030 (you read that correctly) can register and count on supplemental funding. I immediately thought of another 100-city plan, India's Smart City Mission. In 2015, Prime Minister Modi announced that in six years 100 Indian cities would become 'smart'. The official term of the project has now ended, and I will examine below whether this goal has been achieved, I discuss the two plans and then explain why I call both of them a leap forward. At the end I will make a few suggestions for how the European mission can still learn from the Indian one.
India's Smart City Mission
The problem
In India, 377 million people live in cities. In 15 years, 200 million will have been added. Already, traffic in Indian cities has come to a complete standstill, each year more than 600,000 people die from air pollution, half of the urban areas have no drinking water connection, waste collection is poor and only 3% of sewage is treated. The rest is discharged into surface water, which is also the main source of drinking water.
The mission
The Smart City Mission was intended to implement substantial improvements on all these problems in 100 cities, which together comprise 30% of the population. In the improvements digital technology had to play an important role.
The 100 cities were selected because of favorable prospects and the quality of the plans, which usually consisted of a long series of projects.
Governance
The regular city governing bodies were deemed incompetent to lead the projects. That is why management boards (‘special purpose vehicles’) have been appointed, operating under company law and led by a CEO, supported by international consultancy firms. All rights and duties of the City Council regarding the execution of the mission were delegated to the appointed boards, including the power to collect taxes! Not surprisingly, this decision has been challenged in many places. Several cities have withdrawn from 'the mission' for this reason.
Financing
To implement their projects, each city would receive $150 million over five consecutive years. This money should be seen as seed capital to be supplemented from additional sources such as public-private partnerships, commercial bank lending, external financing, loans, and foreign investment.
Area-oriented and pan-urban approach
The plans contain two components: an area-oriented and a pan-urban approach. The first aims at adapting, retrofitting or new construction and should relate to a wide range of 'smart services'. For example high-speed internet, waste facilities, parking facilities, energy-efficient buildings, but also replacement of slums by high-rise buildings. The slick 'architectural impressions' that circulated at the beginning of the planning period (see above) mainly concern the area-oriented approach.
The pan-urban approach includes at least one 'smart' facility for a larger part of the city. The choice is often made to improve the transport infrastructure, for example the construction of new roads and highways and the purchase of electric buses. No fewer than 70 cities have built a 'smart' control center based on the example of Rio de Janeiro, which I believe was rather premature.
Progress
Now that the official term of 'the mission' has ended, a first inventory can be made, although observers complain about a lack of transparency about the results. About half of all the 5000 projects that have been started have not (yet) been completed and a significant part of the government funds have not yet been disbursed. This could still happen in the coming years. This is also because attracting external resources has lagged behind expectations. These funds came mainly from governments, and large technology companies. This has had an impact on the implementation of the plans.
The slow progress of most projects is partly because most of the population was barely aware of the mission and that city councils were not always cooperative either.
Impact
It was foreseen that half of the available resources would go to area-oriented projects; this eventually became 75-80%. As a result, on average only 4% of the inhabitants of the cities involved have benefited from 'the mission' and even then it is not clear what the benefits exactly entail. The city of New Delhi covers an area of almost 1500 km2, while the area concerned is only 2.2 km2: So you're not even going to have 100 smart cities. You're going to have 100 smart enclaves within cities around the country, said Shivani Chaudhry, director of the Housing and Land Rights Network.
It soon became clear that the mission would be no more than a drop in the ocean. Instead of $150 million, it would take $10 billion per city, $1000 billion in total, to address all ambitions, according to an official calculation. Deloitte was a little more modest, calculating the need for $150 billion in public money and $120 billion from private sources.
Type of projects
The many topics eligible for funding have resulted in a wide variety of projects. Only one city has put the quality of the environment first. Most cities have initiated projects in the areas of clean energy, improving electricity supply, reducing air pollution, construction of new roads, purchasing electric buses, waste disposal and sanitation. What is also lacking, is a focus on human rights, gender, and the interests of the poorest population groups.
In some places, it has been decided to clear slums and relocate residents to high-rise buildings on the outskirts of the city. Indian master architect Doshi warns that the urban vision behind the smart city plans will destroy the informality and diversity that is the cornerstone of the country's rural and urban society. He challenges planners to shift the emphasis to rural areas and to create sufficient choices and opportunities there.
The European Mission on Climate-neutral and Smart Cities
The problem
Cities produce more than 70% of the world's greenhouse gas emissions and use more than 65% of total energy. In addition, cities in Europe only cover 4% of the total surface area and accommodate 75% of the population. The ecological footprint of the urban population is more than twice what it is entitled to, assuming a proportional distribution of the earth's resources.
The mission
On November 25, 2021, the European Commission called on European cities to express their interest in a new European mission on Climate-neutral and smart cities. The mission aims to have 100 climate-neutral and smart cities by 2030, which will act as a model for all other European cities.
The sectors involved in this transformation process are the built environment, energy production and distribution, transport, waste management, industrial processes and product use, agriculture, forestry, and other land uses and large-scale deployment of digital technology. That is why the European Commission talks of a green and digital twin, or a simultaneous green and digital transformation.
Governance
Reaching the stated goal requires a new way of working and the participation of the urban population, hence the motto 100 climate neutral cities by 2030 - by and for the citizens.
According to the plan's authors, the main obstacle to climate transition is not a lack of climate-friendly and smart technology, but the inability to implement it. The current fragmented form of governance cannot bring about an ambitious climate transition. Crucial to the success of the mission is the involvement of citizens in their various roles as political actors, users, producers, consumers, or owners of buildings and means of transport.
Funding
The additional investment to achieve the mission is estimated at €96 billion for 100 European cities by 2030, with a net positive economic benefit to society of €25 billion that will increase further in the period thereafter. The European Commission will provide €360 million in seed funding.
The overwhelming amount of funding will have to come from banks, private equity, institutional investors, and from the public sector at the local, regional and national level.
What went wrong with the Indian Mission and its follow-up
The gap between ambitions and reality
Almost all comments on 'the mission' emphasize that three necessary conditions were not met from the start, namely a widely accepted governance model, adequate funding, and involvement of the population and local government. There was an unbridgeable gap between ambitions and available resources, with the contribution of external capital being grossly overestimated.
The biggest problem, however, is the gap between the mission's ambitions and the nature of the problems that India it faces: Cities are bursting at the seams because of the millions of poor people who flock to cities every year in search of work and a place to live that find them only in the growing slums. The priorities for which the country must find a solution are therefore: improving life in rural areas, improving housing in the cities, ensuring safe drinking water, waste disposal, sanitation, and purification of wastewater, good (bus) transport and less polluting car traffic. Urgently needed is a sustainable development model that addresses ecological problems, makes urbanization manageable, controls pollution and will use resources efficiently.
Leap forward
The 'Mission' is a leap forward, which does not tackle these problems at the root, but instead seeks a solution in 'smartification'. Policymakers were captivated by the promises made by IBM and other technology companies that ICT is the basis for solving most urban problems. A view that I objected in the third episode of this series. IC solutions have been concentrated in enclaves where businesses and prosperous citizens are welcomed. The Government of India Special Rapporteur on Housing therefore notes that the proposals submitted had a predominant focus on technology rather than prioritizing affordable housing and doubts the correctness of this choice.
Instead of emphasizing the role of digital technology, the focus should have been on equitable, inclusive, and sustainable living areas for all. Not the area-oriented but the pan-urban approach should have prevailed.
Follow-up
Several authors suggest future actions consistent with the above comments:
• Setting a longer time horizon, which is much more in line with the problems as they are felt locally.
• Decentralization, coupled with strengthening local government in combination with citizen participation.
• A more limited number of large-scale pan-urban projects. These projects should have an immediate impact on all 4000 Indian cities and the surrounding countryside.
• More attention for nature and the environment instead of cutting down trees to widen motorways.
• Training programs in the field of urbanization, partly to align urban development with Indian culture.
The European mission revisited
Leap forward
Europe and India are incomparable in many ways, but I do see similarities between the two missions.
With the proclamation of the 'mission', the Indian government wanted to show the ultimate – perhaps desperate – act of determination to confront the country's overwhelming problems. I therefore called this mission a flight forward in which the image of the 'smart city' was used as a catalyst. However, the country’s problems are out of proportion to this, and the other means employed.
It is plausible that the European Union Commission also wanted to take an ultimate act. After the publication of the ambitious European Green Deal, each national governments seems to be drawing its own plan. The ‘100 cities mission’ is perhaps intended as a 'booster', but here too the feasibility of this strategy is doubtful.
Smart and green
The European Union cherishes the image of a 'green and digital twin', a simultaneous green and digital transformation. Both the Government of India and the European Commission consider digital technology an integral part of developing climate neutral cities. I hope to have made it clear in the previous 21 episodes of this series that digital technology will certainly contribute. However, the reduction of greenhouse gases and digitization should not be seen as an extension of each other. Making a city climate neutral requires way more than (digital) technology. Moreover, suitable technology is still partly under development. It is often forgotten that technology is one of the causes of global warming. Using the image of green and smart twins will fuel the tension between the two, just like it happened in India. In that case, it remains to be seen where the priority will lie. In India it was 'smart'.
Funding
Funding of the Indian mission fell short; much is still unclear about funding of the European mission. It is highly questionable whether European states, already faced with strong opposition to the costs of 'climate', will be willing to channel extra resources to cities.
Governance
The European mission wants to be by and for the citizens. But the goal has already been established, namely becoming climate neutral by 2030. A new 'bottom-up' governmental approach would have been to investigate whether there are cities where a sufficiently large part of the population agrees with becoming climate neutral earlier than in 2050 and how much sooner that could be and next, leave it to these cities themselves to figure-out how to do this.
Can Europe still prevent its mission from failing like India's? I propose to look for in the same direction as India seems to be doing now:
• Opt for one unambiguous goal: Reducing greenhouse gases significantly earlier than 2050.
• Challenge a limited number of cities each to form a broad coalition of local stakeholders that share this ambition.
• Make extra resources available, but also ask the cities themselves to make part of the necessary investments.
• Stimulate universities and industry to provide a European response to Big Tech and to make connections with the 'European Green Deal'.
My e-book Smart City Tales contains several descriptions of intended and alleged smart cities, including the much-discussed Saudi Arabian Neom. The Dutch version is here.
Risks and opportunities of digitization in healthcare

The 21st episode of the Better cities – the contribution of digital technology-series is about priorities for digital healthcare, often referred to as eHealth.
The subject is broader than what will be discussed here. I won't talk about the degree of automation in surgery, the impressive equipment available to doctors, ranging from the high-tech chair at the dentist to the MRI scanner in hospitals, nor about researching microbes in air, water and sewerage that has exploded due to the covid pandemic. Even the relationship with the urban environment remains somewhat in the background. This simply does not play a prominent role when it comes to digitization in healthcare. The subject, on the other hand, lends itself well to illustrate ethical and social problems associated with digitization. As well as the solutions available in the meantime.
The challenge: saving costs and improving the quality of care
The Netherlands can be fortunate to be one of the countries with the best care in the world. However, there are still plenty of challenges, such as a greater focus on health instead of on disease, placing more responsibility for their own health on citizens, increasing the resilience of hospitals, paying attention to health for the poorer part of the population, whose number of healthy life years is significantly lower and, above all, limiting the increase of cost. Over the past 20 years, healthcare in the Netherlands has become 150% more expensive, not counting the costs of the pandemic. Annual healthcare costs now amount to € 100 billion, about 10% of GDP. Without intervention, this will rise to approximately €170 billion in 2040, mainly due to an aging population. In the meantime, healthcare costs are very unevenly distributed: 80% of healthcare costs go to 10% of the population.
The most important task facing the Netherlands and other rich countries is to use digitization primarily to reduce healthcare costs, while not forgetting the other challenges mentioned. This concerns a series of - often small - forms of digital care. According to McKinsey, savings of €18 billion by 2030 are within reach, if only with forms of digitization with proven effect. Most gains can be made by reducing the administrative burden and shifting costs to less specialized centers, to home treatment and to prevention.
Information provision
There are more than 300,000 health sites and apps on the Internet, which provide comprehensive information about diseases, options for diagnosis and self-treatment. More and more medical data can also be viewed online. Often the information on apps is incomplete resulting in misdiagnosis. Doctors in the Netherlands especially recommend the website Thuisarts.nl, which they developed themselves.
Many apps use gamification, such as exercises to improve memory. A good example of digital social innovation is Mirrorable, a program to treat children with motor disorders because of brain injury. This program also enables contact between parents whose inputs continuously help to improve exercises.
Process automation
Process automation in healthcare resembles in many respects automation elsewhere, such as personnel, logistics and financial management. More specific is the integrated electronic patient file. The Framework Act on Electronic Data Exchange in Healthcare, adopted in 2021, obliges healthcare providers to exchange data electronically and prescribes standards. However, data exchange will be minimal and will only take place at a decentralized level to address privacy concerns. The complexity of the organization of health care and the constant discussions about the content of such a system were also immense obstacles. That's a pity because a central system lowers costs and increases quality. Meanwhile, new technological developments guarantee privacy with great certainty. For example, the use of federated (decentralized) forms of data storage combined with blockchain. TNO conducts groundbreaking research in this area. The institution applies the principles of federated learning along with the application of multi-party computation technology. These innovative technologies enable learning from sensitive data from multiple sources without sharing this data.
Video calling
The recent eHealth monitor of the RIVM shows that by 2021 almost half of all doctors and nurses had had contact with patients with video calling, while this hardly happened in 2019. Incidentally, this concerns a relatively small group of patients. In the US there was an even larger increase, which has now been converted into a sharp decline. It seems that in the US primary health care is reinventing itself. Walgreens, the largest US drugstore chain, will begin offering primary care in 1000 of its stores. Apparently, in many cases, physical contact with a doctor is irreplaceable, even if (or perhaps because) the doctor is relatively anonymous.
Video calling is not only important for care provider, but also for informal caregivers, family and friends and help to combat loneliness. Virtual reality (metaverse!) will further expand the possibilities for this. TNO is also active here: The TNO media lab is developing a scalable communication platform in which the person involved (patient or client), using only an upright iPad, has the impression that the doctor, district nurse or visitor is sitting at the table or on the couch right in front.
Self-diagnosis
The effectiveness of a remote consultation is of course served if the patient has already made a few observations him- or herself. 8% of patients with chronic conditions already do this. There is a growing range of self-tests available for, for example, fertility, urinary tract infections, kidney disorders and of course Covid-19. There are also home devices such as smart thermometers, mats that detect diabetic foot complications, and blood pressure meters; basically, everything that doctors often routinely do during a visit. The GGD AppStore provides an overview of relevant and reliable apps in the field of health.
Wearables, for example built into an i-watch, can collect part of the desired data, store it for a longer period and, if necessary, exchange it with the care provider.
More advanced are the mobile diagnosis boxes for emergency care by nurses on location, such as ambulances. With a fast Internet connection (5G), specialist care providers can watch if necessary.
A small but growing group of patients, doctors, and researchers with substantial financial support from Egon Musk sees the future mainly in chip implants. This would allow not only more complete diagnoses to be made, but also treatments to be carried out. Neuralink has developed a brain implant that improves communication with speech and hearing-impaired people. The Synchron brain implant helps people with brain disorders perform simple movements. For the time being, the resistance to brain implants is high.
Remote monitoring
Meanwhile, all these low-threshold amenities can lead us to become fixated on disease rather than on health. But what if we never had to worry about our health again? Instead, the local health center watches over our health thanks to wearables: Our data is continuously monitored and analyzed using artificial intelligence. They are compared with millions of diagnostic data from other patients. By comparing patterns, diseases can be predicted in good time, followed by automated suggestions for self-treatment or advice to consult a doctor. Until then, we have probably experienced nothing but vague complaints ourselves. Wouldn't that be an attractive prospect?
Helsinki is experimenting with a Health Benefit Analysis tool that anonymously examines patients' medical records to evaluate the care they have received so far. The central question here is can the municipality proactively approach people based on the health risk that has come to light because of this type of analysis?
Medics participating in a large-scale study by the University of Chicago and the company Verify were amazed at the accuracy with which algorithms were able to diagnose patients and predict diseases ranging from cardiovascular disease to cancer. In a recent article, oncologist Samuel Volchenboom described that it is painful to note that the calculations came from Verify, a subsidiary of Alphabet, which not only used medical data (with patients’ consent), but also all other data that sister company Google already had stored about them. He adds that it is unacceptable that owning and using such valuable data becomes the province of only a few companies.
Perhaps even more problematic is that these predictions are based in part on patterns in the data that the researchers can't fully explain. It is therefore argued that the use of these types of algorithms should be banned. But how would a patient feel if such an algorithmic recommendation is the last straw? It is better to invest in more transparent artificial intelligence.
Implementing digital technology
Both many patients and healthcare professionals still have doubts about the added value of digital technology. The media reports new cases of data breaches and theft every day. Most people are not very confident that blockchain technology, among other things, can prevent this. Most medical specialists doubt whether ICT will reduce their workload. It is often thought of as some additional thing. Numerous small-scale pilot projects are taking place, which consume a lot of energy, but which are rarely scaled up. The supply of digital healthcare technologies exceeds their use.
Digital medicine will have to connect more than at present with the needs of health professionals and patients. In addition to concerns about privacy, the latter are especially afraid of further reductions in personal attention. The idea of a care robot is terrifying them. As should be the case with all forms of digitization, there is a need for a broadly supported vision and setting priorities based on that.
Against this background, a plea for even more medical technology in our part of the world, including e-health, is somewhat embarrassing. Growth in healthy years due to investment in health care in developing countries will far exceed the impact of the same investment in wealthy countries.
Nevertheless, it is desirable to continue deliberately on the chosen path, whereby expensive experiments for the benefit of a small group of patients have less priority in my opinion than investments in a healthy lifestyle, prevention, and self-reliance. Healthcare cannot and should not be taken over by robots; digitization and automation are mainly there to support and improve the work of the care provider and make it more satisficing and efficient.
One of the chapters in my e-book Future cities, always humane, smart if helpful, also deals with health care and offers examples of digital tools. In addition, it pays much more contextual information about the global health situation, particularly in cities. You can download by following the link below. The Dutch edition is here.
Leer over blauw-groene daken tijdens een Pakhuis de Zwijger bijeenkomst (21 maart)

Drie jaar lang werkten 9 partners aan het RESILIO project. Amsterdam is nu ruim 10.000m2 aan innovatieve, groene, waterbergende daken rijker!
Op 21 maart tijdens een WeMakeTheCityGreen event van Pakhuis de Zwijger presenteert RESILIO de onderzoeksresultaten. Daarna volgt een workshop waarin alle stappen van ambitie tot aanleg van blauw-groen in kaart worden gebracht. Welke hobbels en kansen kwamen we tegen tijdens de aanleg en realisatie? Reserveer hier voor de presentatie en hier voor de workshop.
Stay up to date
Get notified about new updates, opportunities or events that match your interests.

