Stay in the know on all smart updates of your favorite topics.
People get more connected and technology becomes part of our daily life. Between 2014 and 2015 there was a 27% growth of internet traffic in Amsterdam. Eleven out of fifteen Trans-Atlantic data cables are connected with or go through Amsterdam and the AMS-IX is the second largest internet exchange point in the world. In 2016 Amsterdam was ranked second in the European Digital City Index. Do you work on a smarter city? Share your technologies here!
Exploring the Future of Data in the Circular Economy: Highlights from Data Dilemma’s!

Amsterdam, a city with an ambitious goal of becoming fully circular by 2050, envisions a future where materials are continuously reused, waste is minimized, and resource cycles are closed. Achieving this vision hinges on the availability and analysis of data, which allows us to assess the extent to which materials are used, reused, or wasted. However, this data is often elusive, complex to analyse, and, in some cases, not even recorded. These challenges surrounding circular data were the focal point of our recent event, "Data Dilemma's: Collecting Data for the Circular Economy."
During Data Dilemma's, we explore the possibilities for using data and new technologies to address urban and societal challenges, with a focus on responsible digitalization. The goal is to use data to make cities more safe, clean and accessible. But what happens to all the data that is collected? Which dilemmas do we encounter when we collect (personal) data to improve the city.
Apparently, the topic of this edition of Data Dilemma’s was not only of interest to the Amsterdam Smart City team, since this event was completely sold out. This was no surprise, with the three incredible speakers we had lined up: Mersiha Tepic (municipality of Amsterdam), Maarten Sukel (Picnic), and Joris Bouwens (Metabolic).
Mersiha Tepic: Circular Economy Monitor Amsterdam
Mersiha Tepic, Senior Researcher at the Research & Statistics department of the Municipality of Amsterdam, demonstrated the Circular Economy Monitor Amsterdam. This essential tool tracks Amsterdam's progress towards a circular economy and identifies areas requiring further attention.
The monitor gives interesting insights. For instance, it shows that the environmental impact of food is four times as big as the impact of the built environment, even though the amount of materials used in the built environment is four and a half times larger than for food.
It reveals that food has a very high environmental per kilogram compared to materials from the built environment. This is interesting because it makes the total environmental impact of food much higher than the impact of the built environment, even though the built environment uses four times as much mass in materials than food.
For more information on the circular monitor and all its insights, you can check out their (Dutch) website.
During her presentation, Mersiha also delved into the data dilemma she faces in this project—the scarcity of data from significant commercial entities operating within the city. The lack of data from these key players poses a considerable challenge to Amsterdam's circular ambitions, and Mersiha's work sheds light on the importance of bridging these data gaps.
Maarten Sukel: Data-Driven Precision at Picnic
Our second speaker, Maarten Sukel, a Data Scientist at Picnic Technologies, showcased how the online supermarket Picnic leverages data. He presented an innovative approach that combines traditional data sources with images, written descriptions, and geographical information to predict customer preferences accurately. By doing so, Picnic not only optimizes its supply chain but also minimizes waste, aligning with the circular economy's core principles.
Maarten's insights provided a glimpse into how data-driven precision can be a game-changer in the pursuit of sustainability and waste reduction, and he also gave a convincing sales pitch on why you should be a customer of Picnic.
Joris Bouwens: The Promise of Digital Product Passports
Closing the event was Joris Bouwens, a Project Manager and Senior Consultant at Metabolic's Circular Industries team. Joris shed light on Digital Product Passports and their potential to revolutionize the circular economy. These passports offer a comprehensive digital record of a product's lifecycle and environmental impact, empowering consumers to make informed choices and encouraging responsible consumption and recycling.
Joris's presentation highlighted the immense opportunity presented by Digital Product Passports in getting as much value from used products as possible. To fully illustrate the potential of Digital Product Passport, Metabolic has created a visualization of the data flows in four sectors: Electronics, Chemicals, Apparel, and Construction. You can find these visualizations here.
We extend our gratitude to our amazing speakers for their invaluable contributions and to our engaged audience for their active participation in the discussion.
In the next edition of Data Dilemma’s we will delve into the fascinating world of the underground. What cables, tubes, and other assets can be found there, how is the data on these assets shared, and how can we improve collaboration? We hope to see you there on the 26th of October.
Do you have any suggestions for which Data Dillema's we should uncover next? Let us know in the comments below.
10. Health
Most important causes of death worldwide (Source: The Lancelet, le Monde)
This is the 10th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. In this post, I mainly focus on health problems which are directly related to the quality of the living environment
Are cities healthy places?
According to the WHO's Global Burden of Diseases Study, 4.2 million deaths worldwide each year are caused by particulate matter. The regional differences are significant. Urban health depends on the part of the world and the part of the city where you are living. More than 26 million people in the United States have asthma and breathing problems as a result. African-American residents in the US die of asthma three times as often as whites. They live in segregated communities with poor housing, close to heavy industry, transportation centers and other sources of air pollution.
Globally, the increasing prosperity of city dwellers is causing more and more lifestyle-related health problems. Heart disease, and violence (often drug-related) has overtaken infectious diseases as the first cause of death in wealthy parts of the world.
The Netherlands
Very recently, Arcadis published a report on 'the healthy city'. This report compares 20 Dutch cities based on many criteria, divided over five domains. The four major cities score negatively on many aspects. In particular: healthy outdoor space, greenery, air quality, noise nuisance, heat stress and safety. Medium-sized cities such as Groningen, Emmen, Almere, Amersfoort, Nijmegen, and Apeldoorn, on the other hand, are among the healthiest cities.
In Amsterdam, the level of particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) in 2018 exceeded World Health Organization standards in many streets. The GGD of Amsterdam estimates that 4.5% of the loss of healthy years is the result of exposure to dirty air.
Collaborative measuring air quality
In various cities, groups of concerned citizens have started measuring the quality of the air themselves. A professional example is the AiREAS project in Eindhoven. An innovative measuring system has been developed together with knowledge institutions and the government. Sensors are distributed over the area of the city and the system provides real-time information. The AiREAS group regularly discusses the results with other citizens and with the city government. The measurement of the quality of the air is supplemented by medical examination. This research has confirmed that citizens in the vicinity of the main roads and the airport have an increased risk of mortality, reduced lung function and asthma.
The AiREAS project is linked to similar initiatives in other European cities. Occasionally the data is exchanged. That resulted in, among other things, this shocking video.
Future?
Could the future not be that we are busy doing the obvious things for our health, such as walking, cycling, eating good food and having fun and that thanks to wearables, symptoms of diseases are watched early and permanently in the background, without us being aware of it? The local health center will monitor and analyze the data of all patients using artificial intelligence and advise to consult the doctor if necessary. An easily accessible health center in one's own neighborhood remains indispensable.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
9. Road safety

This is the 9th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Casualties in traffic are main threats to the quality of the living environment. ‘Vision zero’ might change this.
Any human activity that annually causes 1.35 million deaths worldwide, more than 20 million serious injuries, damage of $1,600 billion and is a major cause of global warming would be banned immediately. Except for the use of the car. This post describes how changes in road design will improve safety.
The more public transport, the safer the traffic
Researchers from various universities in the US, Australia and Europe have studied the relationship between road pattern, other infrastructure features and road safety or its lack. They compared the road pattern in nearly 1,700 cities around the world with data on the number of accidents, injuries, and fatalities. Lead researcher Jason Thompsonconcluded: <em>It is quite clear that places with more public transport, especially rail, have fewer accidents</em>. Therefore, on roads too public transport must prioritized.
The growing risk of pedestrians and cyclists
Most accidents occur in developing and emerging countries. Road deaths in developed countries are declining. In the US from 55,000 in 1970 to 40,000 in 2017. The main reason is that cars always better protect their passengers. This decrease in fatalities does not apply to collisions between cars and pedestrians and cyclists, many of which are children. Their numbers are increasing significantly, in the US more than in any other developed country. In this country, the number of bicycle lanes has increased, but adjustments to the layout of the rest of the roads and to the speed of motorized traffic have lagged, exposing cyclists to the proximity of speeding or parking cars. SUVs appear to be 'killers'and their number is growing rapidly.
Safe cycling routes
In many American cities, paint is the primary material for the construction of bike lanes. Due to the proximity of car traffic, this type of cycle routes contributes to the increasing number of road deaths rather than increasing safety. The Canadian city of Vancouver, which doubled the number of bicycle lanes in five years to 11.9% of all downtown streets, has the ambition to upgrade 100% of its cycling infrastructure to an AAA level, which means safe and comfortable for all ages and abilities. Cycle paths must technically safe: at least 3 meters wide for two-way traffic; separated from other traffic, which would otherwise have to reduce speed to less than 30 km/h). In addition, users also need to feel safe.
Street design
Vision Zero Cities such as Oslo and Helsinki are committed to reducing road fatalities to zero over the next ten years. They are successful already now: There were no fatalities in either city in 2019. These and other cities use the Vision Zero Street Design Standard, a guide to planning, designing, and building streets that save lives.
Accidents are often the result of fast driving but are facilized by roads that allow and encourage fast driving. Therefore, a Vision Zero design meets three conditions:
• Discouraging speed through design.
• Stimulating walking, cycling and use of public transport.
• Ensure accessibility for all, regardless of age and physical ability (AAA).
The image above shows a street that meets these requirements. Here is an explanation of the numbers: (1) accessible sidewalks, (2) opportunity to rest, (3) protected cycle routes, (4) single lane roads, (5) lanes between road halves, (6) wide sidewalks, (7) public transport facilities, (8) protected pedestrian crossings, (9) loading and unloading bays, (10) adaptive traffic lights.
Enforcement
Strict rules regarding speed limits require compliance and law enforcement and neither are obvious. The Netherlands is a forerunner with respect to the infrastructure for bikes and pedestrians, but with respect to enforcement the country is negligent: on average, a driver of a passenger car is fined once every 20,000 kilometers for a speeding offense (2017 data). In addition, drivers use apps that warn of approaching speed traps. Given the risks of speeding and the frequency with which it happens, this remissing law enforcement approach is unacceptable.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
De stad van de toekomst bouwen ze in Almere in Minecraft

Met een spetterende kick-off door Justin Edwards, Director of Learning Programmes van Microsoft, zijn 200 studenten van hogeschool Windesheim Flevoland vandaag in teams gestart met het in Minecraft bouwen van het nog te realiseren stadsdeel Pampus. Bijzonder omdat Almere als tweede stad na London start met een Minecraft challenge voor de realisatie van een nieuwbouwopgave. Het winnende studententeam van Windesheim mag haar concept van 7 – 9 november presenteren in het Holland paviljoen tijdens de Smartcity Expo World Congres in Barcelona.
De komende anderhalf jaar biedt Almere honderden jongeren tussen de 8 en 21 jaar op deze unieke manier de kans om zelf op de stoel van de architect te zitten en zo mee te denken over grote maatschappelijke vraagstukken. Basisschoolleerlingen en studenten bouwen op hun eigen niveau aan een virtueel Almere Pampus. Dit als plek waar zij in de toekomst zelf willen wonen. Dit stadsdeel bouwen ze met een speciale versie van Minecraft Education Edition.
Wethouder Maaike Veeningen van Almere (Economische ontwikkeling, hoger onderwijs): ‘we dagen leerlingen tot 21 jaar uit om met oplossingen te komen voor vraagstukken op het gebied van duurzaam, energiezuinig en inclusief bouwen. Op deze manier leren zij bijvoorbeeld over het gebruik van Artificial Intelligence (AI), Virtual Reality (VR) en robotisering bij het ontwikkelen van een nieuw stadsdeel. Zo betrekken we onze toekomstige inwoners bij het bouwen aan de ideale stad van de toekomst.’
Toekomstige leefomgeving
Het toekomstige Almere Pampus wordt in het zuidwesten van Almere gebouwd, met meer dan 30.000 woningen en 16.000 arbeidsplaatsen. Projectdirecteur Almere Pampus en senior stedenbouwkundige bij de gemeente Almere Paola Huijding over de Minecraft Challenge: “Deze leerlingen zijn misschien de toekomstige bewoners van Pampus. Hiermee bouwen we aan woon- en werkplekken omringd door water en groen. Het is daarom zo mooi dat juist de toekomstige generatie nu meedenkt over hun leefomgeving.”
Digitaalvaardig
De speciale editie van Minecraft die de studenteams gebruiken is ontwikkeld door Iamprogrez. Het gebruik ervan moet op een speelse en laagdrempelige manier bijdragen aan een digitaal vaardige samenleving. Scholieren krijgen zo inzicht in de banen van de toekomst. Ook kunnen zij in een buddysysteem ouderen meenemen in hun digitale kennis en vaardigheden.
Fleur van Beem, Executive Director bij VodafoneZiggo: “Het vooruithelpen van twee miljoen mensen in de samenleving willen wij bereiken door initiatieven als Online Masters, een online lesprogramma voor scholen over de digitale wereld. De Minecraft Challenge sluit hierop naadloos aan en het is natuurlijk fantastisch om dankzij gamification jongeren digitaalvaardig te krijgen.”
Bouwen aan innovatieve concepten
De leerlingen kunnen alleen of in teams werken aan de challenge en krijgen hiervoor een digital skills-certificaat. Na de ontwerpfase, kunnen zij hun toekomstige visie op Pampus uploaden op de website van de Green Innovation Hub (GIH). Een groep experts kiest de winnaar. Danny Frietman, Projectdirecteur van de GIH: “De winnende uitkomsten van de Minecraft Challenge vormen de basis voor ons om start-ups en scale-ups uit te dagen om de concepten van de scholieren daadwerkelijk in de praktijk te brengen.”
“Hoe ziet het er dan uit”
Kijk HIER naar de video aankondiging van de eerder gehouden Minecraft-challenge in Londen. Daarin zie je duidelijk hoe de challenge werkt en welke mogelijkheden Minecraft hiervoor biedt.
Fotografie Daan Klunder, Almere City Marketing
8. Polycentricity
This is the 8th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. The question is whether a distribution of services over the whole area contributes to the quality of the urban environment.
The central parts of cities like Siena, Amsterdam and Barcelona are overrun by visitors and tourists. Partly because Airbnb has increased its overnight capacity by withdrawing homes from their actual destination. As a result, these cities see their real estate prices rise ans residents leave, making room for expensive apartments, boutique hotels and corporate headquarters. Eventually, old city centers will become amusement parks that offer twenty-four hours of entertainment.
The need for distributed centers
There are no objections against visiting nice cities. The underlying problem is that many of these cities have few other places of interest left, partly due to destruction in the Second World War and their rapid expansion afterwards. Therefore, some cities are in urgent need to create additional attractive places and become polycentric. This aligns with the intention of cities to become a 15-minute city. The figure above is a model developed for this purpose by the council of Portland (USA).
Because of this policy, the prospect is that residents can buy their daily necessities close to home. At the other hand, tourists will be spread. What attractive neighborhood centers look like will be discussed in a subsequent post.
Ancillary centers
Cities without an inordinate number of tourists and visitors also observe a steady grow in the number of events, all competing for the same locations. For this reason, it is advisable that cities have a few ancillary centers each with one or two crowd pullers that divide the stream of visitors. An example is the Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao and its newly developed public space around. In world cities such as London and New York, such centers have existed for years, but they are sometimes difficult to find because they are spread over a large area.
Amsterdam too urgently needs one or more ancillary centers. The area between Leidseplein and the Rijksmuseum has potential but lacks unity due to the chaotic intersections of roads and tram lines. The presence of a train or metro station is an advantage, that is why the area near Station Zuid also has potential.
Peripheral centers
Next decade, many visitors will still arrive by car and the best policy is to seduce them to leave their cars at safe transfer points to continue their journey by public transport. For visitors who intend to stay longer, this solution is not optimal. Many will dismiss the perspective of carrying their luggage to the hotel by public transport, although taking a cab is an alternative, albeit expensive. The alternative is the presence of a couple of affordable hotels next to the car park and the development of these areas into attractive public space, with shops, cafes, and restaurants, as a starting point to visit places of interest in the city. These centers can also accommodate major events, such as a football stadium, a music hall, cinemas and open-air festivities, because of the presence of large scale parking facilities. The Amsterdam Arena district is developing in this direction. It used to be a desolate place, but it's getting better. There are excellent train and metro links.
And what about the old 'old' city center?
The public spaces in the old city centers must meet the same requirements as the whole city to prevent becoming an amusement park for tourists. Aside from its carefully maintained and functionally integrated cultural legacy, centers should provide a mix of functions, including housing, offices, spaces for craft and light industry and plenty of greenery dedicated to its inhabitants. The number of hotels should be limited and renting out by Airbnb prohibited. There will be shops for both residents and tourists, rents must be frozen, and the speculative sale of houses curbed. Space over shops must be repurposed for apartments.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fi/x39qvzkw687rxsjvhsrzn/overzicht-blogposts-Eng.docx?rlkey=vpf7pwlfxkildpr9r062t5gf2&dl=0
7. Accessibility

This is the 7th episode of a series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. The question is whether motorized traffic must be banned from central parts of the city to improve the quality of the urban environment.
Most cities face a choice when it comes to accessibility of their central parts: Whether they renovate the road infrastructure or they face a growing and lasting conflict between car traffic and visitors, whose numbers will decrease further as a result of prioritizing cars. This post deals with the first option.
Changing priorities in the use of road space
The starting point for this renovation is choosing the best experience for both residents and visitors. Therefore, the use of road space in all parts of cities must be under scrutiny. This also applies the connecting roads between centers and the other parts of the city. The distribution of space between pedestrians, cyclists, cars, and public transport has to be reconsidered. A good example is the Ferdinand Bolstraat in Amsterdam. Cars have been banned, the sidewalks are widened, cyclists have their own lanes and the tram uses a switch track (photo below left), just as in Leidsestraat (photo above left).
Accessibility
The rule of thumb is that the larger a city and the better public transport is functioning, the more the accessibility by car of the central parts and the residential areas as well can be reduced. Visitors who rely on the use of a car then store their vehicle in a parking on the edge of the center, preferably near supermarkets or other places where voluminous purchases can be made. From these parking spaces they enter the central area on foot. Incidentally, it is worth considering opening the entire center to cars until 11 a.m. to pick up orders.
Cyclists can be allowed deeper penetration in the central urban area, but not unlimited. They leave their bicycles in (guarded) parking facilities too.
Public transport never stops more than 300 meters from the middle of the center, where comfortable waiting areas are offered, and information is available.
Separation of traffic flows
A separation of traffic flows is required for the entire urban area. The most central streets will be exclusively intended for pedestrians, emergency services and occasionally the tram. Bicycles are allowed in streets in the center, depending on their wideness.
Public transport has always priority at traffic lights. It ensures not only transfer-free accessibility of the urban center, but also connects the most important residential and work areas with a minimum number of transfer. The possible arrival of autonomous minibuses will radically improve the flexibility of public transport (photo above right).
Intra-urban walking and cycling routes
Pedestrians’ and cyclists’ safety and amenity are improved if the connections between the central and outlying parts of the city are accessible by separate routes too. In a city whose green space penetrates deep into the central area, these routes can partly run through nature. A good example is the cycle route from the center of Utrecht to Leidsche Rijn (photo bottom right). Pedestrians need an attractive route through the built-up area for reasons of social safety.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Smart building inside and out

Day and night, 114 sensors are collecting data about the use and occupation of the facilities at H20 Esports Campus in Purmerend. Such data can be of great interest to plan work more efficiently and cost effectively. Partners of AMdEX, an Amsterdam Economic Board initiative make sure data is exchanged between trusted parties only. And that any conditions for access and use are enforced.
How many people go in and out a building throughout the day? Do they prefer specific elevators? Which toilet areas are most used? Are bins and soap dispensers full? Facility managers and cleaning companies love that type of information. Unoccupied areas do not need to be serviced as frequently as busy ones. The Esports Campus, an event location for businesses and private parties, was keen to share the sensor data in a safe and trustworthy manner. The entrepreneur reached out to the team of our AMdEX initiative, via the Data Sharing Coalition.
Ready for it
For AMdEX, the request from Esports Campus came at exactly the right time. Previously, the field lab at the Marineterrein in Amsterdam proved how environmental and liveability data can be accessed and shared in a trusted environment – after the data owner and data user had agreed on simple terms. “We were ready for a more complicated case,” says Hayo Schreijer (Dexes), one of the founding partners of AMdEX. “The case at Esports Campus is a mix of private and public data, collected in a private space and to be shared over the Internet. Also, a lot more parties would be involved than in the previous Marineterrein case.”
Endorsing partner KPN
KPN is AMdEX’ endorsing partner for connectivity and network infrastructure. KPN’s infrastructure could enable this innovative entrepreneur to collect and share this data reliably with his business partners. Carolien Nijhuis is EVP Internet of Things and Dataservices at KPN. She says: “This smart building project is next level complexity. It combines all the issues we think are important. Safe and trusted exchange of data is necessary to solve the bigger issues in our society. In this project, KPN provides interoperability and connectivity according to European standards of privacy and security.” It is tempting to think that data exchange is all about technology. It is not. “Besides being innovative, using professional technology, data exchange is very much about legal and organisational issues”, says Schreijer.
New terms and conditions
The Esports Campus pilot ran in parallel with a next phase of the field lab at the Marineterrein. Tom van Arman (Tapp), says: “At Marineterrein we measure environmental factors and occupancy of the public space: water quality, temperature, numbers of people. Esports is a private space that collects more personal and commercially sensitive data. We had to consider new terms and conditions in the agreements with all parties involved. We also included the principles of the Tada Manifesto, that prescribe safe, inclusive sharing and usage of data.” Collecting data inside a building results in whole new datasets to play with.
Prototype for all-in-one app
This summer, a milestone was reached: a prototype of Facility Apps, the all-in-one app solution for cleaning and facility management. Data from the Esports Campus is made available to the cleaning partners through this app, allowing them to plan the work more efficiently. The data in the app is contained in a ‘Solid Pod’, a decentralised data store. When data is stored in someone’s Pod, they control which people and applications can access it. The AMdEX layer verifies the identity of parties that want to access the data and authorises them to do so – if they are certified parties. Schreijer clarifies that AMdEX does not ‘see’ the data. It tells systems whether access or usage of data is allowed and makes these decisions auditable. Nijhuis also emphasises that KPN enables the technical data exchange and has no access to the actual data. The next step is to evaluate the app with the users.
Great potential for smart cities
This pilot has shown that private data can be shared reliably between private partners. Combined with the results from the public space of Marineterrein, all three partners see great potential for smart city applications. City planning based on actual data, more efficient energy management of buildings or even industrial areas, innovation in sustainable logistics. “Especially when we all work together,” concludes Nijhuis. “If you run alone, you go faster, but together you go farther.”
Text: Karina Meerman
5. Integration of high-rises

This article is part of the series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Read how the design of high-rises might comply with the quality of the urban environment.
High-rises are under scrutiny in two respects. First, its necessity or desirability. Secondly, their integration in the urban fabric. This post is about the latter.
Options for high-rises
Suppose you want to achieve a density of 200 housing equivalents in a newly to build area of one hectare. A first option is the way in which Paris and Barcelona have been built: Contiguous buildings from five to eight floors along the streets, with attractive plinths. In addition, or as an addition, others prefer high-rises because of their capacity of enhancing the metropolitan appearance of the area. Not to increase the density in the first place.
Integrative solution
Almost all urban planners who opt for the latter option take as starting point rectangular blocks, which height along the streets is limited to 4-6 storeys, including attractive plinths. The high-rise will then be realized backwards, to keep its massiveness out of sight. The image at top left gives an impression of the reduced visibility of high-rises at street level on Amsterdam's Sluisbuurt. According to many, this is a successful example of the integration of high-rises, just like the Schinkelkwartier under development, also in Amsterdam(picture top right).
Separate towers
The last option is also recognisable in all urban plans with a metropolitan character in Utrecht and Rotterdamand more or less in The Hague too. This represents a turnaround from the past. Research by Marlies de Nijsshowed that only 20% of all high-rises built before 2015 met this condition. These buildings consist of separate towers without an attractive plinth. What you see at ground floor-level are blank walls hiding technical, storage or parking areas. The Zalmtoren in Rotterdam, the tallest building in the Netherlands, exemplifies this (picture below right). This kind of edifices is mostly surrounded by a relatively large space of limited use. Other disadvantages of detached high-rises are the contrast with adjacent buildings, their windy environment, the intense shadows, its ecological footprint, and the costs.
Paris
Two extreme examples of disproportionate high-rises can be found in Paris. Paris has always applied a limitation of the building height to 37 meters within the zone of the Périférique. The exception is the Eiffel Tower, but it was only meant to be temporary. In the two short periods that this provision was cancelled, two buildings have risen: The first is the 210-meter-high Tour Montparnasse, which most Parisians would like to demolish immediately. Instead, the building will be renovated at a cost of €300 million in preparation for the Olympic Games. After 10 years of struggle, construction of the second has started in 2021. It is the 180-meter-high Tour Triangle, designed by Herzog & de Meuron, so-called star architects. The photos at the bottom left and centre show the consequences for the cityscape.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fi/x39qvzkw687rxsjvhsrzn/overzicht-blogposts-Eng.docx?rlkey=vpf7pwlfxkildpr9r062t5gf2&dl=0
4. Informative plinths

This article is part of the series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Read how design, starting from street-level view contributes to the quality of the urban environment.
Plinths express the nature of activities inside
The visual quality, design and decoration of the plinth, the 'ground floor' of a building, contributes significantly to the quality of the streetscape and to the (commercial) success of the activities that take place at plinth level. This also applies, for example, if the activities of a workshop can be observed through the windows. Blank walls speed up visitors' pace, unless this wall has attractive art. Vacancy is disastrous.
A plinth displays the destination of a building or a part of it (photo bottom left). Fashion stores and suppliers of delicacies depend on its ability to attract buyers. There is nothing against allowing the plinth to expand slightly onto the street - think of beautiful displays of fresh vegetables - if a sufficiently wide barrier-free pedestrian route is maintained.
The total length of streets that must generate customers and visitors must not be too long in order to keeps vacancy to a minimum. This may mean that still profitable shops in streets where the number of vacancies is increasing must consider moving if revitalization of the street is infeasible. The space left behind can best be revamped into space for housing or offices to prevent further dilapidation.
Plinths of non-commercial destinations
The need for an attractive plinth also applies to non-commercial spaces. This may concern information centers, libraries, day care centers for children or the elderly, places where music groups rehearse, etcetera. Co-housing and co-working centers might also concentrate several activities in a semi-public print. In an apartment building, you might like to see an attractive portal through the glass, with stairs and elevators and a sitting area.
Residential plinths
Houses in the more central parts of the city can also have an attractive plinth. In practice, this happens often by placing plants and creating a seat on the sidewalk. The so-called Delft plinths are narrow, sometimes slightly raised additional sidewalks for plants, a bench, or stalling bicycles (photo bottom middle). The worst is if the plinth of a private house is mainly the garage door.
The aesthetics of the plinth
In many pre-war high streets, the plinth was designed as an integral part of the building. In the ‘60s and ‘70s, many retailers modernized their businesses and demolished entire ground floors. The walls of the upper floor, sometimes of several buildings at the same time, rested on a heavy steel beam and the new plinth was mainly made of glass (photo top left). Often a door to reach the upper floors is missing, complicating the premises’ residential function. Initially, these new fronts increased the attractivity of the ground floor. However, the effect on the streetscape has turned out to be negative. In Heerlen, artist and 'would be' urban planner Michel Huisman (the man behind the Maankwartier) is busy restoring old shopfronts together with volunteers and with the support of the municipality (photos top right). In Amsterdam, shopfronts are also being restored to their original appearance (photo bottom right).
Plinths policy
The sky is the limit for improving plinths, as can be seen in the book Street-Level Architecture, The Past, Present and Future of Interactive Frontages by Conrad Kicker and the *Superplinten Handbook</em> , commissioned by the municipality of Amsterdam.
In 2020, a plinth policy was introduced in the Strijp-S district in Eindhoven from a social-economic background. 20% of the available plinths is destined for starters, pioneers and 'placemakers'. Continuous coordination with the target group is important here. In The Hague, 100 former inner-city shops have now been transformed into workplaces for young and creative companies. Differentiating rents is part of the plinth policy too.
Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
3. Attractive streetscape

This article is part of the series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Read how design, starting from the physical aspects of the streetscape en -pattern contributes to the quality of the urban environment. Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Streets and squares are appreciated best if there is cohesion between several elements, such as the block height, the number of floors, the type of houses, the building line and the colour. When some elements work together, others can vary. Uniformity without variation results in people avoiding a street.
Coherence and variation in balance
Variation creates liveliness and will extend the time visitors spend on a street. This principle is applied almost everywhere in the world. Walls are fitted with arches, pillars, porches, porches, pitched roofs, windowsills, canopies, balustrades, cornices, dormer windows, linear and vertical elements, see the bottom-centre image of a Paris’ building. At the same time, the attributes of separate buildings that provide variety are most effective against a coherent background. The Parisian avenues illustrate this too, because most edifices are built according to the same principles while the ornamentation of each facade differs. The attractive streetscape in Sicily (top right) and in the Alsace (bottom right) demonstrate an almost perfect balance between similarity and difference.
Use of colour
A good example are the painted houses in the Canadian settlement of Lunenburg, which was founded in the 18th century by German woodworkers and is a UNESCO world heritage site today (top centre). The nature of the construction and the type of buildings ensure cohesion; the colour provides the variation.
Street pattern
A manageable pattern of similarly important streets contributes to the spread of visitors and provides a level playing field for shops and restaurants. A mesh, which does not necessarily have to be rectangular, facilitates orientation. A rectangular street pattern is at the expense of the element of surprise and detracts from the feeling that there is something to discover. Squares will often be found at street intersections.
Landmarks
Understanding of the pattern of the streets is reinforced by providing intersections with landmarks, such as statues, fountains, or distinguishing buildings (photo, top right). These elements help visitors developing a mental map. Maps every here and there are more helpful than signposts. The fewer poles in the ground, the better.
Canals and moats
Canals and moats also contribute to the attractivity of the streetscape. They restore the human dimension in too wide streets, also in new parts of the city. The images on the left show a central street in Zaandam (top) and a 'waterway' in the Amsterdam Houthavens quarter (bottom). The edges of waterways should never be used as parking spaces. Definitely not in Amsterdam, because its unique streetscape.
2. Human density

This article is part of the series 25 building blocks to create better streets, neighbourhoods, and cities. Read how design, departing from the human dimension contributes to the quality of the urban environment. Follow the link below to find an overview of all articles.
Human dimension means that residents nor visitors feel overwhelmed by the environment. An urban planner must avoid them thinking that it is all about other things, such as commerce, traffic, or the buildings themselves, which unfortunately often is the case indeed. Constructions by 'star architects' can be crowd pullers but usually also result into a disproportionate use of space. Cities therefore better tolerate only a limited number of such edifices. Alexander Herrebout (OTO Landscape) believes that space has a human dimension if you experience attention for you as a human being and that there are objects you can connect with. For many, this will be more often a historic building (church, town hall) than a modernist one.
Compactness (‘enclosure’)
Compact streets and squares give a sense of security. They encourage people to linger there, increasing the chance of unforeseen encounters. Sjoerd Soeters considers squares in the first place as a widening in the street pattern and therefore they are preferably no larger than 24 by 40 meters. A round or oval shape enhances the feeling of security. If the height of the surrounding buildings is also in line with this, there may be contact between residents and people on the street. Good examples are the square he designed in the Oostpoort shopping center in Amsterdam, but also a square in <em>The Point</em>, a new shopping center in Utah (US), resp. bottom left and bottom center and of course the Piazza der Campo in Siena.
If streets are too wide or narrow or buildings are too high?
Trees, for example a double row all around, will help if a street is too wide or a square is too big. Trees are also a source of reducing urban heat. The extent to which trees contribute to the sense of intimacy is expressed by comparing the images at the top left (Herring Cove Road, Halifax, Canada) and the top right (Course Mirabeau, Aix-en-Provence). A square or a street that is too wide can be further visually reduced by the construction of terraces, the placement of a pavilion or the presence of water features, such as on the Brusselplein, Leidsche Rijn (bottom right). Sometimes also by allowing destination traffic and public transport.
A street that is too narrow can be widened psychologically by designing sidewalks and a carriageway in the same level and shades, possibly separated by a narrow band, as illustrated in the image of the Sluisbuurt in Amsterdam (top center).
If case of high-rises, the human dimension can be respected by planting trees and by placing taller buildings back from the plinth to limit their visibility from the street. This is also illustrated by the image of the Sluisbuurt (top center).
Density
Compactness presupposes a certain density. In a very dense city center is only room for pedestrians and not for traffic, in some cases except for the tram. Though, these areas must be always accessible to emergency services. Waste removal, deliveries and parking must be solved differently, for example on the inner space of blocks or by introducing strict time slots. Every city also needs space for events such as concerts, fairs, etcetera. Accessibility is more important than a central location.
Free KNX Smart Energy IoT workshop at FLEXCON2023 September 20 - 14.00 – 16.30 hours – max 8 developers.

KNX and FLEXCON2023 are hosting an in-depth KNX IoT development workshop. Are you a developer who wants to build Smart Energy applications? Bring your RPi’s and other Linux devices and come to Les Brigittines in Brussels on September 20th ! Connect heatpumps, EV's, Solar systems, smart meters, sensors, batteries etc to the smartgrid
In this workshop, you will get to understand the KNX IoT development approach. You will get your hands om a state-of-the-art test bench, equipped with a virtual KNX installation featuring actuators with load control and real-time current detection, providing instant power consumption insights.
The workshop is free of charge. We have only 8 spots available, so apply now! For more information and subscription to the KNX IoT workshop on September 20th:
https://survey.alchemer.com/s3/7460981/FLEXCON-2023-KNX-IoT-Workshop
For information on the #FLEXCON2023 event:
https://flexcon.energy
Civity wint Green Innovation Hub Contest 2023

Almere, 6 juli 2023 – Civity is de winnaar van de Green Innovation Hub Contest 2023, waar verschillende start- en scale-ups hun innovatieve oplossing voor een duurzame en inclusieve leefomgeving presenteerden. Dat bepaalde de jury (UPAlmere!, Amsterdam Smart City, BTG, Future City Foundation, Floor Almere, Windesheim, Aeres, Provincie Flevoland, PRICE, Horizon en VodafoneZiggo) gisteren tijdens de Green Innovation Hub Contest tijdens een stormachtige dag. Na een succesvolle pitch won de start-up uit Amersfoort de Golden Award voor hun innovatieve oplossing: een smartcity dataplatform voor de energietransitie. Hiermee verzekert Civity zich van begeleiding om haar concept verder te ontwikkelen, kantoorruimte en tickets voor de Smart City Congres 2023 in Barcelona.
De komende jaren worden er in de provincie Flevoland 130.000 nieuwe woningen gebouwd.. Nederlands grootste bouwopgave. Daarom hebben de gemeente Almere, de provincie Flevoland, VodafoneZiggo en haar partners de handen ineengeslagen met de organisatie van de Green Innovation Hub Contest 2023. Het doel van de wedstrijd is het vinden van innovatieve oplossingen die bijdragen aan een duurzame en inclusieve leefomgeving.
“We zitten in de grootste transitie van de afgelopen 50 jaar, waarin we zowel op ruimtelijk als op sociaal gebied uitdagingen hebben. Het is mooi dat de Green Innovation Hub Contest hier met nieuwe organisaties en nieuwe ideeën mee aan de slag gaat en dat Almere blijft geloven en investeren in groene innovatie.”, aldus hoofdjurylid Jan-Willem Wesselink, programmamanager bij Future City Foundation.
Contest Day
Start-ups en scale-ups konden zich tot 22 juni aanmelden. Uit alle inzendingen heeft de jury tien organisaties met de beste oplossingen geselecteerd. Zij hebben hun producten en diensten gisteren tijdens de Innovation Hub Contest Day gepresenteerd.
“De inspirerende oplossingen die zijn gepresenteerd, dragen allemaal bij aan de ontwikkeling van Almere als een duurzame en natuur-inclusieve stad.” vertelt jurylid Debby Kruit, Ecosystem Advisor UPALMERE! en Startup Mentor bij Startupbootcamp. “Ik kan niet wachten om te zien welke innovaties over een tijdje echt in Almere worden gerealiseerd.”
Golden Award
De oplossing van Civity werd tijdens de finale van de Green Innovation Hub Contest door de jury bekroond met de Golden Award. Dit betekent dat zij meegaan met de partners naar de Smart City Congres in Barcelona en dat zij coaching en ondersteuning ontvangen om hun product verder op te schalen in de markt.
Arjan Eeken, senior Architecture manager en innovatiestrateeg bij VodafoneZiggo: “De presentatie ging niet in op de technologische oplossing, maar op de toegevoegde waarde voor de maatschappij. De meest belangrijke discussie die er is: hoe deel je data voor de energieconsumptie.”
Directeur Roelof Schram van Civity is erg opgetogen: ”Hiermee zetten wij met ons bedrijf een fantastische volgende stap om onze smartcity dataplatform samen met experts verder op te schalen”.
Call for Social Innovators: Join the SoTecIn Factory for Circular Economy Solutions in Agrifood, Textiles, Plastics & Packaging Industries!

Exciting opportunity for all social innovators! SoTecIn Factory calls individuals and organizations in the agrifood, textiles, plastics & packaging industries with tech solutions based on circular economy & social innovation!
SoTecIn supports mission-driven circular ventures in leading the industry towards a low-carbon and circular economy transition through sustainable solutions, utilising higher R circular strategies. We provide up to 100k EUR in funding, help you to get to a pre-market demonstration, and provide capacity-building and mentorship.
Is this interesting for you or for someone in your network? Make sure to apply or share this with them!
Apply here: https://lnkd.in/eJnjfpDS
Find out more about the program: https://lnkd.in/exTueWti
Investeren in de Metropool Amsterdam doen we samen

Welke investeringen zijn nodig voor de transitie naar de slimme, groene, gezonde Metropool van Morgen? Onderzoeksbureau Birch bracht het in kaart, in opdracht van de Metropoolregio Amsterdam en Amsterdam Economic Board.
Het rapport van Birch inventariseert de ambities en plannen van regionale kennisinstellingen, bedrijven, maatschappelijke organisaties en overheden. En analyseert welke belangrijke vervolgstappen de regio nog moet nemen. Door voort te bouwen op de aanbevelingen hopen we de mogelijkheid tot investeren in de hele metropool te vergroten.
De focus ligt daarbij op transitie-thema's binnen digitalisering en duurzaamheid:
⦿ Gezondheid en preventie
⦿ Veilig datadelen
⦿ Artificial Intelligence
⦿ Duurzame digitale infrastructuur
⦿ Biobased en modulair bouwen
⦿ Slimme mobiliteit
⦿ Waterstof
⦿ Slimme energiesystemen
Ben jij met jouw organisatie betrokken bij een van die thema's? Lees het artikel en neem contact op om mee te denken over investeringsmogelijkheden.
Demoday #20: ChatGPT and the Government: Opportunities and challenges

Are language processing tools powered by AI, such as ChatGPT, revolutionising the way we work and live together? How should governments, such as the province of North Holland, deal with this? What is the impact as the technology behind ChatGPT evolves and is used more and more prominently, outside and within their own organisations? Is it an efficient way to communicate with citizens, write policy documents, or answer state questions? Or should we avoid or discourage the use of ChatGPT for governments? During Demo Day #20, we explored the possibilities and potential impact of ChatGPT on the work of governments. We will discuss not only the technology itself, but especially the ethical aspects involved. How can officials be included in the responsible use of this technology?
Case & Set-up of the Session
After an introduction of the question by the Jeroen Silvis and Martijn Veerman from the province of North-Holland, the participants first identified opportunities and threats when using ChatGPT for a concrete case study: writing a housing vision for the region using ChatGPT. The opportunities and threats were identified from perspectives: political administrators, civil servants working for the province and municipality, citizens and housing developers and associations. After this round of identifying opportunities & threats, the participants discussed some important factors the province of North Holland should keep in mind when developing a framework for the use of ChatGPT.
Insights
Opportunities for political administrators, civil servants working for the province and municipality, citizens and housing developers:
Make civil service more efficient and effective; compose and read policy documents;
Civil servants working for the province can save a lot of time as ChatGPT makes it easier to write large policy document; it can also serve as a source for creativity and inspiration;
ChatGPT could be beneficial for civil servants working for municipalities, as ChatGPT might help simplify complicated documents;
Citizens benefit as complicated plans become more readable and accessible through the use of ChatGPT;
ChatGPT could help broaden visions for area development and housing (in this specific case) which is beneficial to housing developers.
Threats for political administrators, civil servants working for the province and municipality, citizens and housing developers:
Through using ChatGPT, internal and privacy-sensitive information will be in hands of big tech multinationals, which is a big risk for political administrators; dependence on AI might lead to a loss of autonomy;
Using ChatGPT for writing policies might lead to tunnel vision for civil servants working for the province; Does the policy fully reflect the vision of the civil servant when using ChatGPT?;
ChatGPT makes use of existing content, which may lead to less innovation. This is a risk for civil servants working for the municipality as they have to execute the policy;
Citizens might worry about their privacy, as ChatGPT is owned by a big tech multinational;
ChatGPT might simplify housing visions whilst the realisation of housing is a complex issue, this is a threat for housing developers.
After identifying the opportunities & threats, the participants discussed what the province of North Holland should keep in mind for the development of a ChatGPT framework for internal use. Some remarks from the group:
Always remain critical and check everything, make sure to identify your sources;
Pay attention to public values and explore open-source language model alternatives that are more responsible and open source. Be aware of the influence of big tech;
Provide clear frameworks and instructions for the use of ChatGPT or a similar tool;
Make clear rules about who is responsible;
Knowledge and experience is also within people, not everything is public or published and thus accessible for ChatGPT;
Learn to ask the right questions: what is the input for ChatGPT? Educate your colleagues about the use, the do’s and don’ts;
Hire ChatGPT expert(s) and organise internal strategy sessions;
Be transparent about the use of ChatGPT within the government;
Choose for one tool, preferably open-source, that can be used organisation-wide.
Conclusion and Next Steps?
It is clear that the technology around AI powered language models is developing very quickly. As colleagues of the province of North Holland are already using ChatGPT, it is important to develop a framework for internal use. Jeroen and Martijn from the province of North Holland will use the concrete input from this session and work on plan/framework the coming months. It is unclear whether this question will have next step within the Amsterdam Smart City network, but a valuable connection has been made between the University of Applied Sciences of Amsterdam and the province of North Holland. Do you have any input for Jeroen and Martijn about this topic? Please contact me via sophie@amsterdamsmartcity.com, or leave a comment below.
Demoday #20: Knowledge session ‘Power in Transitions’

When working together on transitions, it is important to be aware of and sensitive to the impact of power and systemic oppression in participatory processes. Within the Amsterdam Smart City network, the question of inclusion and civic participation, is often brought up in worksessions and discussions. However, we often lack the tools to find the bottlenecks and really include all important beneficiaries.
Therefore, we asked our valued partners Kennisland and DRIFT to lead a workshop about Power in Transitions at Demoday #20 on May 16. Dave van Loon and Faduma Mukhtar (Kennisland) together with Aron Teunissen (DRIFT) taught the participants more about power in transitions, based on the Power Literacy Framework and Field Guide from Kennisland. This guide describes five different forms of power and offers a set of tools for professionals to become more aware of power dynamics in their work.
The five forms of power
According to the Power Literacy Guide by Kennisland, there are five forms of power in design process. If you want to learn more about this, you can download the Power Literacy guide here. The five forms of power are:
Privilege: The type of power you get from a social relation whereby you benefit due to the social group you belong to, at the expense of another social group. It is an unearned advantage and often invisible to those who have it.
Access power: The ability to influence who is included in and excluded from the design project and process.
Goal power: The ability to initiate the design project to begin with, as well as the ability to influence decisions related to framing the problem, goals, and structure of the design process.
Role power: The ability to influence the roles that different stakeholders take on. This includes the ability to assign any roles or titles in the design process, as well as influencing the role each stakeholder plays in making decisions.
Rule power: The ability to influence the way that those in the design process will work together. It includes the ability to influence what is considered normal, what is allowed and what isn’t, how actors will communicate with each other, what language is used, and beliefs about what types of knowledge are valid.
Power check
After a theoretical introduction of the five forms of power, we split into smaller groups to perform a so-called power check for different Amsterdam Smart City projects, such as the Mobility Challenge and “Wat mensen beweegt”. Using this power check, the participants looked at access power and goal power. We identified all actors affected by the project and indicated which actors were not involved. The different actors were then assigned a role in different stages of the process: listener, co-creator, advisor, partner or director.
Most important take-aways
The goal of this exercise was to create more awareness about involving target groups in different stages of the project. The main take-aways were:
The role for the for the ‘benefit group’, the people that are impacted by the project, is often too small. If beneficiaries are involved, this often happens in the last stages of the project. In this phase in the project, it is often more difficult or not possible at all to influence decision-making;
To create equal power, some parties have to ‘give away’ (some of) their power;
Truly inclusive work takes time, effort and money. It is not something takes place overnight;
Awareness is half of the battle: make the topic of systemic oppression in participatory process a structural part of your (work)process).
Want to learn more about power in transitions? Read more.
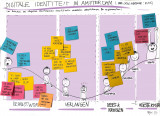
Transition Day 2023: Digital identity and implementing new electronic identification methods
The Digital Government Act (Wet Digitale Overheid) aims to improve digital government services while ensuring citizens' privacy. An important part of this law is safe and secure logging in to the government using new electronic identification methods (eIDs) such as Yivi (formerly IRMA). The municipality of Amsterdam recently started a pilot with Yivi. Amsterdam residents can now log in to “Mijn Amsterdam” to track the status of complaints about public area’s. But how do you get this innovation, which really requires a different way of thinking, implemented?
Using the Change Curve to categorise barriers
At the Transition day (June 2023), Mike Alders (municipality of Amsterdam) invited the Amsterdam Smart City network to help identify the barriers and possible interventions, and explore opportunities for regional cooperation. Led by Coen Smit from Royal HaskoningDHV, the participants identified barriers in implementing this new technology from an organisational and civil society perspective. After that, the participants placed these barriers on a Change Curve, a powerful model used to understand the stages of personal transition and organization stage. Using the Change Curve, we wanted to give Mike some concrete guidance on where to focus his interventions on within the organisation. The barriers were categorised in four phases:
- Awareness: associated with anxiety and denial;
- Desire: associated with emotion and fear;
- Knowledge & ability: associated with acceptance, realisation and energy;
- Reinforcement: associated with growth.
Insights and next steps
In the case of digital identity and the implementation of eID’s, such as Yivi, it appears that most of the barriers are related to the first phase of awareness. Think of: little knowledge about digital identity and current privacy risks, and a lack of trust in a new technology. Communication is crucial to overcome barriers in the awareness. To the user, but also internally to employees and the management. Directors often also know too little about the topic of digital identity.
By looking at the different phases in the change process, we have become aware of the obstacles and thought about possible solutions. But we are still a long way from full implementation and acceptance of this new innovation. For that, we need different perspectives from business, governments and knowledge institutions. This way, we can start creating more awareness about digital transformations and identity in general, which will most likely lead to wishes for more privacy-friendly and easier way of identifying online. Besides focusing on creating more awareness about our digital identity, another possible next step is to organise a more in-depth session (deepdive) with all governmental organisations in the Amsterdam Smart City network.
Do you have any tips or questions in relation to Mike’s project about Digital Identity and electronic Identification? Please get in touch with me through sophie@amsterdamsmartcity.com or leave a comment below.
Green Innovation Hub Contest 2023!

Green Innovation Hub Contest 2023! "Pitch voor Impact"
In Flevoland en Almere worden de komende jaren 130.000 nieuwe woningen gebouwd. De grootste bouwopgave van Nederland! Heb jij een innovatief product of dienst waarmee jij kunt bijdragen aan duurzame en inclusieve leefomgeving. En impact kunt maken op deze regio én de rest van Nederland. Doe dan mee met de Green Innovation Hub Contest 2023 en win de Golden Award.
🏆 Een trip naar Smart City Expo 2023 in Barcelona, coaching door expert, gratis office space, ondersteuning bij businesscases en modellen door partners, V.I.P.-tickets voor Ziggo Dome concert naar keuze en nog veel meer prijzen.
Hoe werkt het?
1️⃣ Doe mee en maak impact met jouw product of dienst.
2️⃣ Meld je uiterlijk woensdag 21 juni vóór 23.59 uur via de onderstaande link.
3️⃣ Op donderdag 22 juni maakt de jury bekend welke start-ups
en scale-ups mogen pitchen.
4️⃣ Mag je pitchen, dan nemen wij contact met je op zodat jij
jouw pitch goed kunt voorbereiden.
5️⃣ Woensdag 5 juli is de Green Innovation Hub Contest Day
waarbij je mag pitchen!
Wil jij deelnemen aan de contest of ben je geïnteresseerd om naar de pitches te kijken? Meld je dan nu aan via de onderstaande link.
Metabolic CEO, Eva Gladek, was nominated for the Big Little Talk at Circularity 23!

Creating a sustainable planet for future generations is essential, and understanding our impacts on nature is a critical step toward achieving this goal.
Unfortunately, measuring impact on nature is complicated and requires specific expertise. We need to combine impact data with geospatial analysis to really see where the different activities along companies’ value chains are taking place, and how those impact nature and biodiversity locally.
By voting for Eva's Big Little Talk, you will Metabolic showcase the importance of nature assessments on the big stage at Circularity 23.
It takes only 1 minute, vote for our video in the link below.
#circularity23 #LinkByMetabolic #natureassessment
Stay up to date
Get notified about new updates, opportunities or events that match your interests.

