Stay in the know on all smart updates of your favorite topics.
Amsterdam Region’s Insights on Local Green Deals during COP28
Participating in a COP28 side event organized by the European Commission, the Amsterdam Region delved into Local Green Deals as instrument for achieving the green transition. The primary goal for the session was to uncover actionable strategies and prerequisites essential for fostering public-private collaboration to realize the sustainability transition. Marja Ruigrok, vice-mayor for the municipality of Haarlemmermeer, represented the Amsterdam Region alongside political and business leaders from Braga (Portugal), Aalborg (Denmark) and Skelleftea (Sweden).
Commencing the session, Valentina Superti, DG for Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship, and SMEs at the European Commission, highlighted Europe's ambition to become the first climate-neutral continent by 2050. This necessitates a transformative shift towards sustainability, digitalization, and resilience, which is why the Commission is introducing critical legislation like the Net-Zero Industry Act and the Critical Raw Materials Act.
Ruigrok shared insights from the Amsterdam Metropolitan Region’s efforts in establishing Local Green Deals, emphasizing her role as political ambassador and champion for the Green Deal Bikes initiative. She stressed the importance of cycling, explaining that despite its reputation as a cycling paradise, approximately 20% of young people in the Amsterdam Region can not ride a bike: “If you don’t learn to ride a bike at a young age, you are also much less likely to use a bike for commuting later in life. That’s why in this Green Deal, we stimulate young people to learn to ride bikes, and encourage employers to support commuting by bike. This is crucial because employees who bike take on average 2.5 fewer sick days compared to those who don’t bike.”
Reflecting on success factors, Ruigrok emphasized the need for political commitment, and clear project ownership: "From a political point of view, you need long term commitment, and you have to create ownership. Someone has to take ownership and say ‘this is my project.’ This might be a governmental agency, a company, a knowledge institution, or civil society organisation - but someone has to take the lead. Otherwise, you will continue to talk, and nothing will happen."
Throughout the session, participants provided practical insights and recommendations for fostering successful public-private collaborations in general, and Local Green Deals in specific:
- Lasse Frimand Jensen, mayor of the City of Aalborg, emphasized the necessity of accountability mechanisms: “Mutual commitment is necessary and there must be mechanisms in place to keep each other accountable.”
- Ricardo Rio, mayor of City of Braga and Member of the European Committee of the Regions, highlighted the role of local authorities in mobilizing capacity and engaging stakeholders: “Local authorities need to have the spirit to engage stakeholders and shape partnerships. We also need governance models that tranced political cycles, and that allow people to participate and hold us accountable.”
- Jens Broberg, representing the business sector, emphasized the urgent need for appropriate incentives: “Governments must use policy frameworks to incentivize and regulate businesses and industry towards a green economy.”
- Evelina Fahlesson, vice-mayor of Skelleftea Municipality emphasized the need for open and honest dialogue: “As a municipality, you have to be open about your challenges and willing to start a dialogue with your citizens and companies. Use procurement and new financing models as tools to implement a shared vision.”
- David Nordberg, from Skanska Sweden, encouraged business leaders to align their business models with sustainability ambitions: "Be brave: try new ways of doing business and work in collaborations. In the long term, there is no conflict between sustainability and the economy."
The session highlighted the pivotal role of collaborative multi-stakeholder partnerships in achieving the green transition, emphasizing sustained political commitment, robust governance structures transcending political timelines, and policy frameworks incentivising sustainable businesses.
In the context of COP28, the true challenge lies in replicating these successful approaches on a wider scale, extending beyond the relatively affluent European context to a global landscape with more limited resources. In many regions, the urgent and acute impacts of climate change are already pervasive, amplifying the need for swift, comprehensive action. This necessitates a global and concerted effort of nations and industries, to surmount the hurdles posed by resource scarcity and varying levels of socio-economic development. This calls for collaboration not only within regions but across continents, fostering knowledge-sharing, technology transfer, and collective efforts in tackling climate challenges. The urgency of the climate crisis demands a united global front, where the lessons learned and successes achieved in Local Green Deals can serve as guiding principles towards a more sustainable and resilient future for all.
CTwalk Map

What opportunities for social cohesion do cities provide?
Is your neighbourhood park frequented by a homogenous or diverse mix of people? How many hashtag#amenities can you reach within a short hashtag#walking distance? And do you often encounter people from different walks of life?
I am very excited to introduce to you CTwalk Map, a web tool that seeks to highlight the social cohesion potential of neighbourhoods while also unmasking local access hashtag#inequities. CTwalk maps opportunities that different age groups can reach within a 5 or 15-minute walk.
🚶♀️🚶♂️ It uses granular population, location, and pedestrian network data from open sources to estimate how many children, adults, and elderly hashtag#citizens can reach various destinations in a city within a short walk.
🌐 It offers a simple and straightforward understanding of how the 5 and 15-minute walking environments are shaped by the street network.
➗ It estimates the degree of pedestrian co-accessibility of various hashtag#city destinations.
CTwalk Map is now available for the five largest cities in The Netherlands.
Take a look at the web tool:
https://miliasv.github.io/CTwalkMap/?city=amsterdam
... learn more about CTwalk Map at this link:
[currently does not support mobile phones or tablets]
...and let us know what you think!
Hoe creëer je Levende Lerende Netwerken die impact hebben?

Hoe maak je de stap van gezamenlijk leren, naar samen echt dingen doen? Er is al veel over gezegd en geschreven... Communities of practice, smeden van allianties, enz enz... Vaak blijft het dan een beetje hangen bij het organiseren van een toffe sessie, vast met veel energie. En daarna gaat iedereen - als het goed is met nieuwe ideeën en inspiratie - weer verder met waar 'ie al mee bezig was. Vaak is dat al genoeg, maar zeker in transities wil je eigenlijk een stapje verder komen.
Is eigenlijk al wel voldaan aan een aantal belangrijke condities om het netwerk levend te maken en te houden?
Reflecterend op onze eigen praktijk, ontdekten we een aantal kenmerken die belangrijk en beïnvloedbaar zijn bij het bouwen van impactvolle levende lerende netwerken. Amsterdam Smart City zelf is zo'n voorbeeld, waarin we voortdurend met elkaar op zoek zijn naar hoe we onze samenwerking van betekenis kunnen laten zijn voor de duurzame transities in onze regio. De Green Deal Circular Festivals, het MRA Platform Smart Mobility, Sail Amsterdam, en het Initiatief Bewust Bodemgebruik zijn enkele andere voorbeelden van levende lerende netwerken. Ook hier zagen we telkens dat de volgende kenmerken van belang zijn om verder te komen, en om de stap te maken van samen leren, naar samen doen:
(1) Wederzijdse afhankelijkheid tussen deelnemers
(2) Beweging door gedeelde energie
(3) Diversiteit daagt uit
(4) Persoonlijke ontwikkeling, empathie, ego overstijgend
(5) Veilige ruimte om te leren en ontwikkelen
Op basis van onze ervaringen in de praktijk, hebben we onze kijk op het ontstaan, de kenmerken en het begeleiden van Levende Lerende Netwerken opgeschreven in een whitepaper. Wil je meer weten, dan kun je die downloaden via onderstaande link (naar beneden scrollen naar de download knop van de Levende Lerende Netwerken Whitepaper).
Tijdens het PGM Open Congres op 26 september organiseren we hierover een workshop voor programmamanagers (https://lnkd.in/gcRPv4V8). En, je kunt me natuurlijk altijd een berichtje sturen als je meer wilt weten!
How to live with global warming larger then 3 degrees C
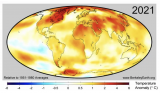
In my previous post (in Dutch) I summarized the main conclusions of the IPCC's Final Report: The probability that the world will have warmed by more than three degrees by 2100 is much greater than that we hold it at 1 1/2 degrees Celsius. In this post I will discuss the consequences of this for the world, whether there is still a way out and what the consequences are for Dutch policy.
23. Epilogue: Beyond the 'Smart City'

In the last episode of the Better cities: The contribution of digital technology-series, I will answer the question that is implied in the title of the series, namely how do we ensure that technology contributes to socially and environmentally sustainable cities. But first a quick update.
Smart city, what was it like again?
In 2009, IMB launched a global marketing campaign around the previously little-known concept of 'smart city' with the aim of making city governments receptive to ICT applications in the public sector. The initial emphasis was on process control (see episode 3). Especially emerging countries were interested. Many made plans to build smart cities 'from scratch', also meant to attract foreign investors. The Korean city of Songdo, developed by Cisco and Gale International, is a well-known example. The construction of smart cities has also started in Africa, such as Eko-Atlantic City (Nigeria), Konzo Technology City and Appolonia City (Ghana). So far, these cities have not been a great success.
The emphasis soon shifted from process control to using data from the residents themselves. Google wanted to supplement its already rich collection of data with data that city dwellers provided with their mobile phones to create a range of new commercial applications. Its sister company Sidewalk Labs, which was set up for that purpose, started developing a pilot project in Toronto. That failed, partly due to the growing resistance to the violation of privacy. This opposition has had global repercussions and led in many countries to legislation to better protect privacy. China and cities in Southeast Asia - where Singapore is leading the way - ignored this criticism.
The rapid development of digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence, gave further impetus to discussion about the ethical implications of technology (episodes 9-13). Especially in the US, applications in facial recognition and predictive police were heavily criticized (episode 16). Artificial intelligence had meanwhile become widespread, for example to automate decision-making (think of the infamous Dutch allowance affair) or to simulate urban processes with, for example, digital twins (episode 5).
This current situation - particularly in the Netherlands - can be characterized on the one hand by the development of regulations to safeguard ethical principles (episode 14) and on the other by the search for responsible applications of digital technology (episode 15). The use of the term 'smart city' seems to be subject to some erosion. Here we are picking up the thread.
Human-centric?
The dozens of descriptions of the term 'smart city' not only vary widely but they also evoke conflicting feelings. Some see (digital) technology as an effective means of urban growth; others see it as a threat. The question is therefore how useful the term 'smart city' is still. Touria Meliani, alderman of Amsterdam, prefers to speak of 'wise city' than of 'smart city' to emphasize that she is serious about putting people first. According to her, the term 'smart city' mainly emphasizes the technical approach to things. She is not the first. Previously, Daniel Latorre, place making specialist in New York and Francesco Schianchi, professor of urban design in Milan also argued for replacing 'smart' with 'wise'. Both use this term to express that urban policy should be based profoundly on the wishes and needs of citizens.
Whatever term you use, it is primarily about answering the question of how you ensure that people - residents and other stakeholders of a city - are put in the center. You can think of three criteria here:
1. An eye for the impact on the poorest part of the population
There is a striking shift in the literature on smart cities. Until recently, most articles focused on the significance of 'urban tech' for mobility, reduction of energy use and public safety. In a short time, much more attention has been paid to subjects such as the accessibility of the Internet, the (digital) accessibility of urban services and health care, energy and transport poverty and the consequences of gentrification. In other words, a shift took place from efficiency to equality and from physical interventions to social change. The reason is that many measures that are intended to improve the living environment led to an increase in the (rental) price and thus reduce the availability of homes.
2. Substantial share of co-creation
Boyd Cohen distinguishes three types of smart city projects. The first type (smart city 1.0) is technology- or corporate-driven. In this case, companies deliver instruments or software 'off the shelf'. For example, the provision of a residential area with adaptive street lighting. The second type (smart city 2.0) is technology enabled, also known as government-driven. In this case, a municipality develops a plan and then issues a tender. For example, connecting and programming traffic light installations, so that emergency services and public transport always receive the green light. The third type (smart city 3.0) is community-driven and based on citizen co-creation, for example an energy cooperative. In the latter case, there is the greatest chance that the wishes of the citizens concerned will come first.
A good example of co-creation between different stakeholders is the development of the Brain port Smart District in Helmond, a mixed neighborhood where living, working, generating energy, producing food, and regulating a circular neighborhood will go hand in hand. The future residents and entrepreneurs, together with experts, are investigating which state-of-the-art technology can help them with this.
3. Diversity
Bias among developers plays a major role in the use of artificial intelligence. The best way to combat bias (and for a variety of other reasons, too) is to use diversity as a criterion when building development teams. But also (ethical) committees that monitor the responsible purchasing and use of (digital) technologies are better equipped for their task the more diverse they are.
Respecting urban complexity
In his essay The porous city, Gavin Starks describes how smart cities, with their technical utopianism and marketing jargon, ignore the plurality of the drivers of human behavior and instead see people primarily as homo economicus, driven by material gain and self-interest.
The best example is Singapore – the number 1 on the Smart City list, where techno-utopianism reigns supreme. This one-party state provides prosperity, convenience, and luxury using the most diverse digital aids to everyone who exhibits desirable behavior. There is little room for a differing opinion. A rapidly growing number of CCTV cameras – soon to be 200,000 – ensures that everyone literally stays within the lines. If not, the culprit can be quickly located with automatic facial recognition and crowd analytics.
Anyone who wants to understand human life in the city and does not want to start from simplistic assumptions such as homo economicus must respect the complexity of the city, try to understand it, and know that careless intervention might have huge unintended consequences.
The complexity of the city is the main argument against the use of reductionist adjectives such as 'smart', but also 'sharing', circular, climate-neutral', ‘resilient' and more. In addition, the term smart refers to a means that is rarely seen as an aim as such. If an adjective were desirable, I prefer the term 'humane city'.
But whatever you name a city, it is necessary to emphasize that it is a complex organism with many facets, the coherence of which must be well understood by all stakeholders for the city to prosper and its inhabitants to be happy.
Digitization. Two tracks
City authorities that are aware of the complexity of their city can best approach digitization along two tracks. The first aims to translate the city's problems and ambitions into policy and consider digital instruments a part of the whole array of other instruments. The second track is the application of ethical principles in the search for and development of digital tools. Both tracks influence each other.
Track 1: The contribution of digital technology
Digital technology is no more or less than one of the instruments with which a city works towards an ecologically and socially sustainable future. To articulate what such a future is meaning, I introduced Kate Raworth's ideas about the donut economy (episode 9). Designing a vision for the future must be a broadly supported democratic process. In this process, citizens also check the solution of their own problems against the prosperity of future generations and of people elsewhere in the world. Furthermore, policy makers must seamlessly integrate digital and other policy instruments, such as legislation, funding, and information provision (episode 8).
The most important question when it comes to (digital) technology is therefore which (digital) technological tools contribute to the realization of a socially and ecologically sustainable city.
Track 2: The ethical use of technology
In the world in which we realize the sustainable city of the future, digital technology is developing rapidly. Cities are confronted with these technologies through powerful smart city technology marketing. The most important question that cities should ask themselves in this regard is How do we evaluate the technology offered and that we want to develop from an ethical perspective. The first to be confronted with this question—besides hopefully the industry itself—is the department of the Chief Information or Technology officer. He or she naturally participates in the first track-process and can advise policymakers at an early stage. I previously inventoried (ethical) criteria that play a role in the assessment of technological instrument.
In the management of cities, both tracks come together, resulting in one central question: Which (digital) technologies are eligible to support us towards a sustainable future in a responsible way. This series has not provided a ready-made answer; this depends on the policy content and context. However, the successive editions of this series will have provided necessary constituents of the answer.
In my e-book Cities of the Future. Always humane, smart if helpful, I have carried out the policy process as described above, based on current knowledge about urban policy and urban developments. This has led to the identification of 13 themes and 75 actions, with references to potentially useful technology. You can download the e-book here:
Leer over blauw-groene daken tijdens een Pakhuis de Zwijger bijeenkomst (21 maart)

Drie jaar lang werkten 9 partners aan het RESILIO project. Amsterdam is nu ruim 10.000m2 aan innovatieve, groene, waterbergende daken rijker!
Op 21 maart tijdens een WeMakeTheCityGreen event van Pakhuis de Zwijger presenteert RESILIO de onderzoeksresultaten. Daarna volgt een workshop waarin alle stappen van ambitie tot aanleg van blauw-groen in kaart worden gebracht. Welke hobbels en kansen kwamen we tegen tijdens de aanleg en realisatie? Reserveer hier voor de presentatie en hier voor de workshop.
Hoe zorgen we er samen voor dat er in de toekomst voldoende drinkwater aanwezig blijft in onze regio?

Drinkwater is wereldwijd een schaars goed. In Nederland is onze drinkwatervoorziening gelukkig goed geregeld. En toch. Als gevolg van
onze veranderende wereld stapelen de transities op. Zekerheden die we lang voor lief namen worden omgegooid. Onze steden groeien, wat nieuwe kansen brengt, maar ook nieuwe uitdagingen. Dat betekent ook iets voor onze
drinkwatervoorziening. Ons gebruik neemt toe en het aanbod staat onder druk.
Binnen de Provincie Flevoland is men aan het onderzoeken wat er nu al voor nodig is om dit probleem een halt toe te roepen. Momenteel zien we de vraag naar drinkwater stijgen, de drukte in de ondergrond toenemen en door klimaatverandering (denk aan droogte en hete zomers) het watergebruik stijgen. Om voldoende drinkwater van een goede kwaliteit te garanderen moeten we werken aan een systeemverandering. Waterbesparing moet worden gestimuleerd en laagwaardig gebruik van hoogwaardige kwaliteit water moet worden voorkomen.
Het huidige drinkwatergebruik bestaat voor ca. 70% huishoudelijke- en 30% zakelijke gebruikers (regio afhankelijk). Hoe maken we bij deze doelgroepen waterbesparing de norm? En hoe zorgen we ervoor dat de kwaliteit van het water bepalend is voor het gebruik? Dit zijn vraagstukken die in de toekomst steeds relevanter worden, maar ook nú al onze aandacht vragen.
Halverwege maart zal er binnen de Provincie Flevoland een Adviseur Drinkwatertransitie aan de slag gaan die zich met deze vragen bezighoudt.
We vragen jou om hulp!
Samen met de Provincie Flevoland zoeken we daarom alvast de ideeën, ervaringen en het draagvlak van het netwerk op. We zijn op zoek naar actuele kennis over dit onderwerp en mogelijke oplossingen. Daarnaast zijn we ook specifiek geïnteresseerd in ideeën om nu al urgentie te creëren voor dit onderwerp, ondanks dat het mogelijk pas in de toekomst gaat spelen.
Ben jij een expert op het thema, of heb jij relevante ideeën en ervaringen uit andere onderwerpen? Laat je reactie achter in de comments!
City deals: Shaping collaboration between cities

The 15th episode of the Better cities - The contribution of digital technology- series is about collaboration between Dutch cities within the City Deals in the Agenda stad en regio project.
Over the past years, the interest Dutch municipalities in digitization at urban level has increased, partly because of the initiating role of the VNG, G40, the Future City Foundation and forerunners such as Apeldoorn, Helmond, and Zwolle as well. Initially, these were small-scale and isolated projects. In this post, I'll discuss two projects that aim at scaling through collaboration.
A mission-driven approach to public sector projects
In her new book, Mission Economy, Mariana Mazzucato advocates a mission-driven approach to public sector projects at the local level in the way that a man was put on the moon. She refers at large-scale projects with a high degree of complexity, such as the energy transition, the construction of affordable housing, the well-being of the poor part of the population and the conservation of nature.
What is a mission-driven approach? At first, it includes an ambitious vision, followed by breaking down silos within the governmental organization, collaboration within the quadruple helix, and cooperation between higher and lower governments.
A mission-driven approach is appropriate for the major transitions facing the world and digitization as a part of these. The following pertains to a couple of projects that aim at such an approach. The first, Agenda city and region has been running for some time and will be dealt with extensively. The other is initiated by G40 will be discussed briefly.
Agenda stad and City deals
In Agenda city and region, cities, governments at different levels, companies, and organizations, including the VNG, G4, G40 and Platform31, work together to drive innovation in cities. The mission is summarized in SDG 11: Make cities inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable. The most important instrument are City Deals: collaborative ventures around a themes.
The first City Deals started in 2016, there are now 27, about half of which have been completed, but six new ones are about to start. 125 municipalities, 8 provinces, 9 ministries, 10 other government agencies, 5 water boards, more than 100 companies, 30 knowledge institutions and more than 20 other partnerships are involved. There are now 14 partnerships with municipalities outside the Netherlands.
Examples of City Deals are: Working and doing business across borders, cleantech, food on the urban agenda, local resilience against cybercrime, inner city building, the inclusive city, and smart city, that's how you do it. The latter will be discussed below.
Within a City Deal, the parties involved work together in their own way on concrete products, ranging from legislation to policy instruments. The main principles are:
- Formulating an ambition and a strategy.
- Enabling scaling through cooperation between and/or within (urban) regions.
- Realizing collaboration between public and private parties, including the central government
- Innovating by realizing new forms of problem-solving.
- Scaling up, also across national borders.
City Deals also work together and new deals are created from among them, such as ‘Smart customization', a new City Deal that arises from the existing City Deals 'Simple customization' and 'Smart city, that is how you do it'. If I had to imagine how a moonshot works, which I referred to in the introduction of this article, then Agenda city and region could be a good example.
City deal 'A smart city, this is how you do it'
The goal of this City Deal, as we read in the annual report, is to use digitization to tackle the major challenges facing Europe and the Netherlands, such as poverty, social cohesion, and insecurity, and to achieve a society in which everyone can live in freedom. 60 parties are now involved in this City Deal.
The aim is to change at least 12 processes by which regions, cities and towns are designed, organized, managed, and governed, and to make the most of the opportunities offered by digitization. The starting point is the existing practice and aimed at matching city’s demands.
The City Deal 'Smart city, this is how you do it', has 14 working groups. Each of those have chosen which a process to tackle, on the understanding that three municipalities must be prepared to test the results and can be scaled eventually. The City Deal 'A smart city, this is how you do it' has been underway for almost two years now, and the processes to be tackled have crystallized. In a few cases prototypes are ready, most are under development. Below is a brief description of the situation on November 15th, 2021. A lively description of some participants’ experience can be read in ROMmagazine, volume 39, no. 11.
1. Open urban data platform
This project is developing a procedure for tendering an open data platform, which is shareable and scalable, in which privacy and data autonomy are guaranteed and that offers sufficient precautions for cybersecurity. The result will be a step-by-step plan, in which technical questions (what it will looks like), legal questions (who is the owner) and financial questions (funding) are discussed.
2. Cookbook for effective data strategy
This project develops a procedure for the acquisition and storage of data. A 'data cookbook' has been developed that supports the collection, storage, and application of data. It offers an 11-step plan from the formulation of a measurable questions to the interpretation of the measurement results. It accentuates the importance to make explicit the assumptions behind the selection of data. The usability of the steps is tested in practice. A first concept can be found here.
3. Smart initiatives test
The aim of this project is to allow initiators (citizens, companies) to make optimal use of available public data, including those that will be provided by the DSO (digitaal stelsel omgevingswet). The DSO will provide information about which rules apply at a specific location and ultimately also about the quality of the physical living environment itself. Ideally, the ‘smart initiatives test’ will collect and optimize all data needed for a plan. The project group is currently investigating which types of (geo) data users need most ('usercases').
4. Sensor data and privacy
The aim of the project is to develop a tool that allows a municipality to tender for the installation of sensors that exactly match the type of data that will be collected and that consider ethical questions and GDPR rules.
5. Design of the new city
The growing availability of various types of (real-time) data, for example about air quality and noise pollution) has implications for the way in which cities and neighborhoods are developed. The working group is developing a canvas that functions as a ‘translator' of available data. The starting point for its development was a matrix with as inputs the phases of the design process (initiative, design and realization phase) and the area type (urban, Randstad and suburban area). This matrix must indicate which data is needed at what time. The usability will be tested through pilots.
6. Everyone (and everything) a sensor
Citizen measurement initiatives (via telephones and with sensors attached to bicycles, cars, and homes) have a double goal: to increase citizen’s involvement and to improve the insight into living environment of those who execute the measurement. It can also contribute to behavioral change, especially if the measurements match the needs of residents and they are also involved in the interpretation of the results. The working group is striving for a roadmap based on several user cases.
7. Local measurement: comparing projects
Measuring data locally – as was done in the previous project – may be redundant if data from elsewhere is available. In that case, comparability is required with data being searched for and standardization is needed to enable such a comparison. However, standardization can lead to mistrust and remove the incentive for resident groups to get started themselves. Ultimately, the working group opts for the development of a self-service portal, which will be developed together with the Healthy Urban Living Data and Knowledge Hub. Resident groups can then choose for themselves to participate in a standardized project that reads their measurement results directly or for a 'do-it-yourself' solution. A manual will be written for this last option.
Both projects are being further developed in collaboration with Eurocities, a network of 190 cities in 38 countries, under the name CitiMeasure - using citizen measurement to create smart, sustainable and inclusive cities.
8. Smart mobility: Towards a safe and sustainable city
Digitization in traffic has already taken off, for example by intelligent traffic systems (IVRIs), but usually the existing situation, for example private use of cars, is the starting point. The question is how to connect to the pursuit of a better quality of life. To this end, the working group has chosen three themes: better accessibility for emergency services, shared mobility, and city logistics.
A step-by-step plan is being developed for emergency services, with which municipalities can realize the necessary facilities to always priorize emergency vehicles – and possibly other target groups as well.
If everyone were to travel with the most suitable means of transport at that time (varying from walking, (shared) bicycle or scooter, public transport to (shared) car, private car use would decrease considerably and thus improve the quality of city live. Additionally, the working group is developing a 'map' to encourage shared mobility, which provides answers to all related questions.
Developments in city logistics are already taking place via other routes. Therefore, the contribution of the working group in this regard will be limited.
9. A business model for the smart city
New forms of collaboration between governments, the business community, knowledge institutions and citizens can result in new 'values' for areas, but also to the need to allocate costs and benefits in a different way. A new 'business model' may then be necessary. To this end, the working group is investigating the consequences for companies and organizations of entering partnerships for the successful development of products and services. This compared to more traditional client/contractor relationships.
10 Ethical Boards
Within the City Deal 'A smart city, this is how you do it', a rule is that digital instruments to be developed always comply with ethical principles. The implications of such principles are often situational. That is why municipalities are setting up an 'ethical board', which includes experts and residents. To support its work, the committee wants to create a knowledge platform that informs which ethical principles or tools suit best for different digitization projects.
11 Model Acquisition
Local authorities want to regulate the use of digital tools such as sensors in public spaces. Anita Nijboer, who works as a lawyer at Kennedy Van der Laan, who is also a partner of the City Deal 'Smart city, this is how you do it', has drawn up a model regulation for this purpose, which has already been tested in Rotterdam and Helmond. The most important learning effect is that departments within a municipality have fundamentally different view of the way in which these types of questions should be legally framed. In response to this, the working group is examining the question of whether a model regulation is an appropriate answer to obtaining consent for the use of digital tools.
12 Dealing with crowds in the city
Measuring (too large) crowds in parts of the city was a problem long before corona times. The aim is to develop a digital model ('digital twin') of the city - a so-called crowd safety manager - that provides real-time insight into pedestrian flows and concentrations. Such a model must also be able to communicate with people in the city. A prototype of a dashboard, developed by partner company Argaleo, is now being used in 's-Hertogenbosch, Breda and The Hague. This instrument does not use any personal data. It is being further developed at European level with external subsidies.
The instruments to be developed and existing instruments have been brought together via a website, the Toolbox. Other City Deals also develop knowledge, which is far from being systematically documented. That is why the best way to distribute this knowledge is investigated together with the Knowledge Lab for Urbanism.
G40: Smart sustainable urbanization
In March 2021, G40, the umbrella organization of 40 medium-sized municipalities, submitted a project proposal to promote digitalization and thus also create opportunities to the business community.
The project plan rejects the current approach of 'smart urbanization' and the realization of 'main social tasks'. Decentralization, broadening of tasks, narrowing of implementation funds and a fragmented central government policy have led to an impeding control gap and financing deficit in municipalities. Instead, a bundled approach is wanted, led by representatives of municipalities and central government, and the latter is being asked to invest € 1 billion.
When studying this plan, I was surprised by the absence of any reference to the activities of Agenda city and regioand the City Deals. Instead, one wonders whether Agenda city and region is the subject of criticism of the fragmented approach and G40 wants to get rid of it.
The strength of Agenda city and region is the cross connections between urban projects of all kinds, the involvement of citizens and intermunicipal cooperation. This is something to cherish.
In my opinion, G40 would be better off by ushering in a new phase of Agenda city and region, characterized by economies of scale and acceleration of the findings so far. The aims of this new phase could be consolidation of the cohesion between the themes of the individual City Deals within the framework of the major transitions facing the Netherlands. The theme of digitization thrives best in this context. After all, the ultimate value of digitization lies in the contribution to the energy transition, the reduction of traffic nuisance and the growth of a circular economy, to name a few examples. However, that requires a different plan.
In the meantime, I hope that in the foreseeable future we will be able to see the results of the working groups of the City Deal 'Smart city, this is how you do it', together with those of the other 'Deals'.
Follow the link below to find one of the previous episodes or see which episodes are next, and this one for the Dutch version.
We can navigate wickedness together

On the 25 and 26st of November the Amsterdam Smart City network worked together to tackle big wicked problems that exist in the region. But is it even possible to tackle wicked problems? In a masterclass on the first day, initiated by the ASC wicked problems team, Marije Poel (HvA) and Nora van der Linden (Kennisland) tried to change the perspective: what if we aim to navigate wickedness together?
While we work on big and complex issues like the energy transition or the digital transition, we try to get a grip on problems and come up with a structured plan or linear project. But that approach is not always in line with reality, where we struggle with complex, unstructured and undefined messiness. In this masterclass, we shared a perspective on the character of wicked problems and on the consequences of working on these kind of challenges. Most of the participants recognised the reflexes we have, trying to master or control a wicked problem and come up with a concrete solution.
To give some perspective on how to deal with wickedness, we presented some overall strategies on navigating in wickedness. We suggested to make room for little mistakes (to prevent big ones), invite different perspectives and voices to the table, to be adaptive all along the way, and create time and space for reflection and learning.
The Wicked problems team got positive feed back on the workshop, leading to the idea next time we might dive a bit deeper into this topic and try to apply one or more concrete approaches and tools to navigate around wickedness.
We continue learning and sharing learnings about wickedness in the ASC network. Therefore we are open to work with wicked cases. So, Is your organization a partner of Amsterdam Smart City and do you deal with wicked problems? Let the Wicked Problems know and find out if we can inspire you and find innovative ways to navigate through them together. You can contact Francien who is coordinating this team from the Amsterdam Smart City Baseteam.
In the Wicked problems team are: Dave van Loon (Kennisland), Christiaan Elings (RHDHV), Gijs Diercks (Drift), Giovanni Stijnen (NEMO), Bas Wolfswinkel (Arcadis) en Marije Poel (HvA).
5. Collect meaningful data and stay away from dataism
The fifth episode of the series Better cities: The role of technology is about the sense and nonsense of big data. Data is the new oil is the worst cliché of the big data hype yet. Even worse than data-driven policy. In this article, I investigate - with digital twins as a thread - what the contribution of data can be to urban policy and how dataism, a religion that takes over policy making itself, can be prevented (must read: Harari: Homo Deus).
I am a happy user of a Sonos sound system. Nevertheless, the helpdesk must be involved occasionally. Recently, it knew within five minutes that my problem was the result of a faulty connection cable between the modem and the amplifier. As it turned out, the helpdesk was able to remotely generate a digital image of the components of my sound system and their connections and saw that the cable in question was not transmitting any signal. A simple example of a digital twin. I was happy with it. But where is the line between the sense and nonsense of collecting masses of data?
What is a digital twin.
A digital twin is a digital model of an object, product, or process. In my training as a social geographer, I had a lot to do with maps, the oldest form of 'twinning'. Maps have laid the foundation for GIS technology, which in turn is the foundation of digital twins. Geographical information systems relate data based on geographical location and provide insight into their coherence in the form of a model. If data is permanently connected to reality with the help of sensors, then the dynamics in the real world and those in the model correspond and we speak of a 'digital twin'. Such a dynamic model can be used for simulation purposes, monitoring and maintenance of machines, processes, buildings, but also for much larger-scale entities, for example the electricity grid.
From data to insight
Every scientist knows that data is indispensable, but also that there is a long way to go before data leads to knowledge and insight. That road starts even before data is collected. The first step is assumptions about the essence of reality and thus the method of knowing it. There has been a lot of discussion about this within the philosophy of science, from which two points of view have been briefly crystallized, a systems approach and a complexity approach.
The systems approach assumes that reality consists of a stable series of actions and reactions in which law-like connections can be sought. Today, almost everyone assumes that this only applies to physical and biological phenomena. Yet there is also talk of social systems. This is not a question of law-like relationships, but of generalizing assumptions about human behavior at a high level of aggregation. The homo economicus is a good example. Based on such assumptions, conclusions can be drawn about how behavior can be influenced.
The complexity approach sees (social) reality as the result of a complex adaptive process that arises from countless interactions, which - when it comes to human actions - are fed by diverse motives. In that case it will be much more difficult to make generic statements at a high level of aggregation and interventions will have a less predictable result.
Traffic models
Traffic policy is a good example to illustrate the distinction between a process and a complexity approach. Simulation using a digital twin in Chattanooga of the use of flexible lane assignment and traffic light phasing showed that congestion could be reduced by 30%. Had this experiment been carried out, the result would probably have been very different. Traffic experts note time and again that every newly opened road becomes full after a short time, while the traffic picture on other roads hardly changes. In econometrics this phenomenon is called induced demand. In a study of urban traffic patterns between 1983 and 2003, economists Gilles Duranton and Matthew Turner found that car use increases proportionally with the growth of road capacity. The cause only becomes visible to those who use a complexity approach: Every road user reacts differently to the opening or closing of a road. That reaction can be to move the ride to another time, to use a different road, to ride with someone else, to use public transport or to cancel the ride.
Carlos Gershenson, a Mexican computer specialist, has examined traffic behavior from a complexity approach and he concludes that self-regulation is the best way to tackle congestion and to maximize the capacity of roads. If the simulated traffic changes in Chattanooga had taken place in the real world, thousands of travelers would have changed their driving behavior in a short time. They had started trying out the smart highway, and due to induced demand, congestion there would increase to old levels in no time. Someone who wants to make the effect of traffic measures visible with a digital twin should feed it with results of research into the induced demand effect, instead of just manipulating historical traffic data.
The value of digital twins
Digital twins prove their worth when simulating physical systems, i.e. processes with a parametric progression. This concerns, for example, the operation of a machine, or in an urban context, the relationship between the amount of UV light, the temperature, the wind (speed) and the number of trees per unit area. In Singapore, for example, digital twins are being used to investigate how heat islands arise in the city and how their effect can be reduced. Schiphol Airporthas a digital twin that shows all moving parts at the airport, such as roller conveyors and stairs. This enables technicians to get to work immediately in the event of a malfunction. It is impossible to say in advance whether the costs of building such a model outweigh the benefits. Digital twins often develop from small to large, driven by proven needs.
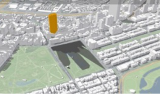
Boston also developed a digital twin of part of the city in 2017, with technical support from ESRI. A limited number of processes have been merged into a virtual 3D model. One is the shadowing caused by the height of buildings. One of the much-loved green spaces in the city is the Boston Common. For decades, it has been possible to limit the development of high-rise buildings along the edges of the park and thus to limit shade. Time and again, project developers came up with new proposals for high-rise buildings. With the digital twin, the effect of the shadowing of these buildings can be simulated in different weather conditions and in different seasons (see image above). The digital twin can be consulted online, so that everyone can view these and other effects of urban planning interventions at home.
Questions in advance
Three questions precede the construction of a digital twin, and data collection in general. In the first place, what the user wants to achieve with it, then which processes will be involved and thirdly, which knowledge is available of these processes and their impact. Chris Andrews, an urban planner working on the ESRI ArcGIS platform, emphasizes the need to limit the number of elements in a digital twin and to pre-calculate the relationship between them: To help limit complexity, the number of systems modeled in a digital twin should likely be focused on the problems the twin will be used to solve.
Both the example of traffic forecasts in Chattanooga, the formation of heat islands in Singapore and the shadowing of the Boston Common show that raw data is insufficient to feed a digital twin. Instead, data are used that are the result of scientific research, after the researcher has decided whether a systems approach or a complexity approach is appropriate. In the words of Nigel Jacob, former Chief Technology Officer in Boston: For many years now, we've been talking about the need to become data-driven… But there's a step beyond that. We need to make the transition to being science-driven in ...... It's not enough to be data mining to look for patterns. We need to understand root causes of issues and develop policies to address these issues.
Digital twins are valuable tools. But if they are fed with raw data, they provide at best insight into statistical connections and every scientist knows how dangerous it is to draw conclusions from that: Trash in, trash out.
If you prefer the Dutch version of the Better cities series, find an overview of the already published episodes via the link below.
Inschrijving voor versnellingsprogramma GO!-NH geopend!

Ben jij een MKB-er, start-up of scale-up die wil bijdragen aan een schone, duurzame en gezonde wereld? Dan weet je als geen ander hoe lastig het soms kan zijn om je idee of product aan de man te brengen. En je bent niet de enige! Provincie Noord-Holland heeft speciaal voor ondernemers zoals jij het GO!-NH versnellingsprogramma ontwikkeld om je te helpen bij het op de markt brengen en opschalen van jouw innovatieve, duurzame product of dienst. Ons doel is om jou te helpen impact te maken op de maatschappij!
GO!-NH biedt drie verschillende trajecten die aansluiten bij de fase en omvang waarin je bedrijf zich bevindt: het Accelerator traject voor MKB bedrijven en start-ups met een idee maar nog geen of beperkte markt, het Growth traject voor bedrijven die in de volgende fase willen groeien, en het Scale traject voor grotere MKB bedrijven en scale-ups die al flinke omzet hebben maar nieuwe markten aan willen boren.
In het voorjaar starten de Accelerator en het Growth traject. Je kunt je vanaf nu aanmelden voor de selectie! Surf voor meer informatie naar de website van GO!-NH: https://go-nh.nl/meer-informatie/
Can Amsterdam even better support growth of its startup ecosystem?

This post is the third and last in a series of articles about the startup ecosystem in Amsterdam Delta (Amsterdam metropolitan region). The first dealt with the dual challenge for start-ups to become socially and environmentally sustainable and to empower employees to be entrepreneurial through shared leadership. The second one was a review of the strengths and weaknesses of the Amsterdam startup ecosystem by the authors of the 2021 Global Startup Ecosystems Ranking.
Weaknesses and strengths
The 2021 Global Startup Ecosystem Report revealed several weaknesses in the Amsterdam startup ecosystem, which – I accentuate - should not overshadow the city’s position of Amsterdam as the world number 13 startup ecosystem. In terms of market reach, the overall score is satisfactory (7), but the Amsterdam Delta startups are primarily focused on global markets and score low on the local market. In the field of talent, the overall score is more than sufficient (7), due to the quality of technology students and graduates, but their number is inadequate, resulting in high vacancies and salary costs. Partly related to this, the growth potential (scalability) of the Amsterdam startup ecosystem is also insufficient, due to a limited reservoir of experienced entrepreneurs. Overall knowledge success is assessed as poor (1!) due to the unsatisfactory number of life science patents.
Amsterdam Policy plan 2019 - 2022
Most of the underlying data of the 2021 report is from 2019 – 2021, a time frame that coincides with the start of the new policy plan for startups in Amsterdam in the period 2019 - 2022. The inventory of challenges in this report mirrors several weaknesses mentioned above. Looking at the future, the report states: We have reached a point where growth of the local ecosystem does not have to mean that the local government wants to encourage as many companies in Amsterdam as possible but encourages activity that adds value to the city in new ways. In the coming years, we must also lay the foundations for a more inclusive society, in which the local startup and scaleup ecosystem also plays a role. A step towards inclusiveness means significantly increasing the business sector’s ambitions for social responsibility. In other words, a focus on quality in general that is aligned with at least the first challenge in the first post I referred to above.
How cities can support their startup ecosystem?
Below, I discuss highlights from the policy report 2019 - 2022 within a broader vision of possibilities for municipalities to support start- and scale-ups, partly based on an earlier edition of a The Global Startup Ecosystem Report.
Financial support
According to the 2021Global Startup Ecosystems Report, the funding of new businesses is not a big problem in Amsterdam Delta, also because of the generous tax facilities(!) in the Netherlands. However, investment relies heavily on local investors and governmental grants: 54% of the capital flowing into the ecosystem comes from domestic sources, 25% from the rest of Europe, and just 21% from the rest of the world.
The City of Amsterdam subsidized the Innovation Center for AI (ICAI) at Amsterdam Science Park, requiring that at least 20% of its revenues will be reserved for innovative SMEs and startups.
While funding is not an overriding problem, Amsterdam can improve its coordinating role in providing financial support, as for example Seoul has done by the creation of the Dream bank, a one-stop agency for all financial matters.
Growth of markets
The market position of Amsterdam start- and scaleups can be improved, especially in the home market, but also internationally. Besides, every new startup must start from scratch by creating a market. An agency called Amsterdam Trade and Innovate has commissioned trade developers to organize domestic and international activities that support promising companies in clusters such as technology, health, life sciences, and creative industry.
Expanding the reservoir of entrepreneurs
Amsterdam focuses on women and young people with a migration background, most of whom never received tech-related training. Initiatives such as House of Skills, Action Plan W&T, House of Digital offer a range of technology-based courses to make up for these shortcomings, alongside startup schools such as BSSA, Growth Tribe and The Talent Institute.
In December 2020, the City of Amsterdam announced it will invest yearly US$ 856,500 in RISE, the Female Hub Amsterdam. There is a high demand in sectors such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, robotics, life science and energy storage, while relatively many university students in technology seem to prefer media studies and gaming and the fintech market is almost satorized. Studying will become more attractive by combining study and jobs and affordable (co-)housing and childcare options, both of which are both are seriously lacking.
In addition, the ‘Warm Welcome’ program aims to attract ambitious tech talent from abroad. Unfortunately, the pandemic has significantly reduced the influx of potential talent from abroad while market opportunities for innovative tech startups and scaleups were improving.
Campuses
Innovative and research-oriented start-ups prefer the proximity of comparable small and medium-sized companies in campuses. They also prefer locations in mixed urban environments. A campus offers space for complementary companies, large and small, and facilities to collaborate, such as shared laboratory spaces. Amsterdam develops urban innovation districts through regional development and transformation. These areas that can accommodate rapid growth and opportunity for clustering ‘anchor companies’, leading (knowledge) institutions, startups, scaleups, incubators and accelerators. The main areas are: West Innovation Park, Amsterdam Sciencepark, Marineterrein , AMC-Amstel III and VU-Kenniskwartier/Zuidas.
Participation in the network of incubators and accelerators
Startups and scaleups need support. Incubators help companies to settle, accelerators help them to grow steadily. One of the best things any city can do is actively participation in these incubators and accelerators. They can become a one shop-stop for all prospective participants, providing virtually all the support start- and scaleups need. 31 of the 89 incubators and accelerators in the Netherlands, are active in the Amsterdam metropolitan area. A rich pallette of incubators and co-working spaces such as TQ, WeWork, Spaces, Startup Village, Rent24 and B.Amsterdam have been set up. Accelerators are Rockstart, Startupbootcamp, Fashion for Good, ACE and Collider.
Within an incubator or accelerator, the municipality can be primary responsible for legal matters, offering work- and living spaces (initially for free and later rented out at attractive rates), trade missions and procurement.
Internships
In some cities, startups can practice aspects of social and environmental sustainability in public administration. An example is the Startup in Residence program that started in Amsterdam and has now been spread over 20 other Dutch cities, regional governments, and ministries. The program is open to both Dutch and foreign entrepreneurs. Professional coaches provide intensive training and support. Workspace is available too. Under certain conditions, local, regional, and national governments become launching customers or partners. A report provides a detailed overview of the program in Amsterdam and its impact on the participants and the community.
Taking care of starters in general
Only a small but previously unknown part of all starters becomes a startup. Moreover, the number of starters outsizes that of startups and some can become valued companies too In the Netherlands, each year more than 100.000 starters are registered with the Chamber of Commerce.
Short evaluation Amsterdam policy plan 2019 - 12022
I doubt whether the current Amsterdam policy on start- and scaleups will result in a better ranking next year, also because in many cities startup ecologies are growing faster. Personally, I believe that consolidating a position in the top 20 is the best possible and still admirable result. This certainly applies if Amsterdam can achieve its ambitions in the field of qualitative rather than quantitative growth. Amsterdam wants to become an inclusive community and the first circular city in the world. The city wants that start- and scaleups becoming forerunners in reaching these objectives. I am partly disappointed in the content of the policy report 2019 - 2022 regarding this ambition. Indeed, becoming a more inclusive community is reflected in supporting the growth of the number female entrepreneurs. However, I looked in vain at policies encourage activity regarding developing start- and scaleups that add value to the city in new ways for instance contributing to the development of the circular economy. These businesses will make the difference in the future startup ecosystem.
I will regularly share ‘snapshots’ of the challenge of bringing socially and ecologically sustainable cities closer using technology if useful. These posts represent findings, updates, and additions to my e-book Humane cities. Always humane. Smart if helpful, chapter 4 in particular. The English version of this book can be downloaded for free below.
The birth of a new green cooperative

In the city of Arnhem a new green cooperative is founded by the students and teachers of the course "Organic Growing in the City". The new cooperative is two years old and has 54 organic urban growers as members. You will watch the green cooperative growing in the future years.
Rethinking ownership for mission-driven ventures

Mission-driven ventures are a big part of the transition towards a circular economy. However, unlike conventional startups, these ventures face an important challenge: how can they prioritize purpose over profit, while also overcoming the hurdles of venture-building?
Part of the answer lies in rethinking ownership, to welcome investment without compromising long-term impact. Metabolic has recently written an article explaining the concept of "steward ownership" and we'd love to hear your thoughts!
More of a webinar person? Take a look at this Fresh Talk instead: https://lnkd.in/dNJDXVSY
Space to fit 3.250.000 solar panels on Amsterdam rooftops

Energy ambitions of the City of Amsterdam
The City of Amsterdam has the ambition to become climate neutral by 2050. To achieve this, major transformations of, among others, the current energy system are required.
To illustrate, the City wants to eliminate the use of natural gas by 2040, phase out fossil fuels by 2050, and have 80% of the electricity that households use to be generated by solar and wind energy in 2030. Regarding the latter, Amsterdam aims to install a total solar energy capacity of 550 megawatts (MW) by 2030. Taking into account modern solar panels of 330 watt-peak, this adds up to 1.67 million solar panels.
With these ambitions set, what is the 'true' implementation potential for solar panels in Amsterdam – in terms of space on the city's rooftops? Which neighborhoods, streets, or even houses have the highest yield? And how can this be calculated best? The PV Advent Calendar project, led by AMS institute and TU Delft, investigates the city's solar panel implementation potential.
True solar panel implementation potential up to 6.5x bigger
A tool – also referred to as the “multi-layer framework” – developed for the PV Calendar project measures the optimal allocation of solar panels for each roof section.
The tool calculates that a total of 3.250.000 solar panels can be installed on Amsterdam rooftops. That means in Amsterdam there’s room to potentially install 6.5 times as many photovoltaic (PV) systems than the 500,000 currently installed on the city’s roofs.
What would this look like in the city? To give you an impression, with the true potential of 3,25 million solar panels installed this comes down to approximately 6.5 solar panels per residential address (taking into account 527755 addresses in total). The tool calculates that 1/4 Amsterdam’s electricity consumption could be solar based... Click on the link to read the full article >>
Innovation Hub Almere is officially open
On April 15th the first onsite Innovation Hub was opened in Almere, part of Amsterdam Metropolitan Area.
As a partner of the hub, you will have the right ecosystem and business opportunities.
As a participant of the hub, you can rent seats in the hub, starting with 1 day a week.
Contact Manuela Krull-Mancinelli if you want to know more!
For the press release, see this link: Innovation Hub Almere
Metropolitan Mobility Podcast with Karen Vancluysen (Polis Network)

How can local governments deal with (technological) innovations? Listen to the #podcast with Karen Vancluysen of POLIS Network: https://bit.ly/mobilitypod
YIMBY Arnhem! groeit.

Dit voorjaar bouwen de makers van de zorgboerderij Hoeve Klein Mariëndaal in Arnhem-West YIMBY moestuinbakken voor de nieuwe stadsboeren in de wijken Klarendal, Geitenkamp, Presikhaaf, 't Broek en Malburgen van de stad Arnhem.
Angela Jong heeft haar buurtgenoten in de wijk Klarendal warm gemaakt voor het biologische tuinieren in de stad met YIMBY's. "Het komt mooi uit dat de Gemeente Arnhem 50% van de aanschafprijs bijdraagt door de groene subsidieregeling De Eetbare Stad". Bart van Dalsem van de Hoeve Klein Mariëndaal geeft aan: "Door de lokale sponsoring door de bedrijven Welkoop Elst en De Bolster kunnen we de YIMBY;s leveren met biologische moestuinaaarde en biologische zaden"
Zéger Nieuweboer heeft met zijn groene onderwijsbedrijf learningisgrowing.nl al acht jaar ervaring met de begeleiding van YIMBY Arnhem! "In de periode 2013-2020 zie je dat nieuwe stadsboeren starten met een YIMBY moestuinbak en doorgroeien naar een biologische voedseltuin". https://lnkd.in/eYbrQiH
#YIMBY #voordeoogstvanmorgen
Recycling, downcycling and the need for a circular economy

What happens to the plastic and paper that you’ve carefully sorted into separate bins?
Many of the products we recycle today are essentially downcycled. While this generally helps to preserve the life of raw materials and some of the value that went into creating them, there might be better ways to do it.
Find out more about the nuances between recycling, downcycling, and a truly circular economy, in this article.
Metropolitan Mobility Podcast met Maurits van Hövell: van walkietalkies naar het Operationeel Mobiliteitscentrum

“Voorheen werd er gewoon rondgebeld: ‘Wij zitten in de instroom van de ArenA. We hebben nu 20.000 man binnen. Hoe gaat het bij jullie op straat?’” In de achtste aflevering van de serie A Radical Redesign for Amsterdam, spreken Carin ten Hage en Geert Kloppenburg met Maurits van Hövell (Johan Cruijff ArenA). Hoe houdt je een wijk met de drie grootste evenementenlocaties van het land, bereikbaar en veilig? Ze spreken elkaar in het Operationeel Mobiliteitscentrum over de rol van de stad Amsterdam, data delen en het houden van regie. A Radical Redesign for Amsterdam wordt gemaakt in opdracht van de Gemeente Amsterdam.
Luister de podcast hier: http://bit.ly/mvhovell
Stay up to date
Get notified about new updates, opportunities or events that match your interests.

