Stay in the know on all smart updates of your favorite topics.
BewustwordingsModel Smart City

Hoe slim is de ideale leefomgeving wat jou betreft, nu en in de toekomst? Wat betekent dat voor o.a. je strategie, diensten en technologie?
Vanuit phbm voegen we graag een gereedschap toe aan jouw Toolbox voor Smart City-vraagstukken. Eén waarbij we het voorstellings- en inlevingsvermogen activeren en welzijn centraal staat: het BewustwordingsModel. Dit model maakt de positie en wensen van jou en de ander expliciet en voorkomt dat er ruis ontstaat over het niveau van ‘slimheid’ in de leefomgeving. Door de toelichting van de passende organisatie, samenwerking, strategie e.d. bij de niveaus ontstaat een scherp beeld van wat het gekozen niveau betekent voor het individu, de organisatie of zelfs de samenleving als geheel. Eén van de centrale vragen bij het model is: hoe ‘smart’ wil je zijn en waar zit de optimale balans tussen mens en technologie?
Eerste gepubliceerde versie is tot stand gekomen samen met partners in de City Deal (‘Een slimme stad, zo doe je dat’). Het laat op vijf niveaus zien in welke mate een organisatie of bedrijf slim is. Eén van de doelen hiervan is om te bepalen of opdrachtgever en opdrachtnemer dezelfde taal spreken. Vanuit phbm zijn we doorgegaan op het model en hebben onder andere ethiek en mobiliteit als pijlers toegevoegd.
Het model is openbaar inzichtelijk, phbm begeleidt graag in het proces om samenwerkingspartners gezamenlijk bewuster te maken op welk niveau ze staan (gebruikmakend van het model) en met welke ontwikkelingen je rekening kan houden in het vraagstuk wat op tafel ligt (op vlak van organisatie, diensten of ethiek bijvoorbeeld).
Research Interview on Digitalization and Big Data in City Administrations

My name is Joe Calodich and I work as a researcher at Erasmus University Rotterdam in the research group Vital Cities and Citizens. I am currently looking for members of the city administrations in Amsterdam, Rotterdam, Prague, Tallinn, Vienna, Zurich, Brussels, or Munich who are interested in participating in a research interview.
The study which I am asking your participation for focuses on how large European cities have undertaken the digitalisation process of the public administration and how this process has affected the workings and the policies. I would also like to learn about some concrete examples on the use of big data related to this digitalisation process.
I hope to complete the interviews by the end of February 2023. Each interview will last between one hour and fifteen minutes and one hour and a half. The interview will be recorded and the content will be exclusively used for academic purposes (analysis, scientific publications, presentations, reports) and within the boundaries of the study’s goals. The gathered information will be treated by complying with anonymity and confidentiality criteria as defined in the social sciences regarding the use of personal information.
If you, or a colleague, is interested in participating, please send me an email at: 627583jc@eur.nl.
I look forward to hearing from some of you soon!
Responsible smart doorbells

Photo: Daan Rozinga, The Incredible Machine
The Responsible Sensing Lab is currently working on a few projects regarding smart doorbells.
Smart doorbells are like a security camera's, but available for everyone. Always on, and owned by private parties, the smart doorbell is destined to have an impact on our privacy. As of now, there could be thousands of smart doorbells in Amsterdam, filming public space. We don t have a clear view on the numbers, and we do not know what the owners do with the collected data. Smart doorbell owners are often not aware of the privacy issues.
One of the Responsible Sensing Lab's projects is Shutterring. The Shutterring project aims to make smart doorbells more responsible by ensuring the privacy of bypassers and owners while keeping the main functionality of the device intact. Shutterring is a design by The Incredible Machine.
Inspired by Shutterring, the Lab has started another project regarding responsible smart doorbells: Challenging the design of smart doorbells. In order to challenge the current design of smart doorbells (IoT doorbells with integrated cameras) a few alternative smart doorbells have been created through speculative design. The goal of this project is to kickstart a conversation about how to deal with the presence of smart doorbells in the city of Amsterdam. How could smart doorbells be designed in a way that they align better with the values of the city and its population?
The Responsible Sensing Lab team will present both their smart doorbell projects during the demo day on 11 October. Stay tuned!
Simple Sensors for responsible sensing

City officials require sensor data to optimize operations, plan projects, or measure effects of interventions. Citizens often do not notice the sensors deployed by the City in public space. Also, the benefit for the public is not directly obvious to city residents or immediately shown by the sensing systems in place. Namely, in many cases only after data is processed, it informs an action that affects citizens.
Public concerns about sensors are often connected to concerns about potential action (to be taken by, for example, city officials), and that the action has negative implications. With ‘Simple Sensors’ we address these concerns.
The Simple Sensors project, which is part of the Responsible Sensing Lab, investigates these questions: What if sensors are designed to be seen? What if they communicate clearly what data they collect and how? And what if sensors invite you to interact with them?
Modules for responsible and ‘simple sensing’
Simple Sensors consists of a family of modules, designed by The Incredible Machine, that can be combined: some modules improve transparency over what data is being collected, other modules encourage interaction, and some modules just make it understandable how sensors work. The Simple Sensors family allows the City of Amsterdam to design sensors to fit any context or purpose.
A privacy friendly alternative for CCTV
The first Simple Sensor prototype called millimeter wave (mmWave) has been developed as a proposal for the City’s crowd management sensor at the Marineterrein Amsterdam Living Lab. It consists of four modules: 1) sensor module 2) transmission module, 3) data module, 4) threshold module... Continue reading about the project on our website >>
Shuttercams for a responsible smart city

Shuttercam is a project by Responsible Sensing Lab (RSL), a collaboration between the City of Amsterdam and AMS Institute. In essence, RSL is a testbed for conducting research and experiments on how smart sensing technologies in public space – like cameras – can be designed in a way that makes the digital city 'responsible’.
At the Lab we invite academics and practitioners responsible for digital systems in the city to explore how to integrate social values such as autonomy, privacy and transparency in the design of these sensing systems in public space.
How to know when a camera ‘sees’ you?
The Shuttercam project originated based on the notion that citizens currently can not directly know or see if and when cameras in public space are monitoring you or not. The project also questions the necessity for many non-security related cameras in the city to be switched on indefinitely.
Experimenting with 3 prototypes at Marineterrein
The Shuttercam project will test 3 prototypes. These are installed at Marineterrein Amsterdam Living Lab (MALL) in the upcoming weeks.
First and foremost, the cameras within this project are all part of the crowd monitoring system by the City of Amsterdam, which is a privacy friendly system. So what do these cameras record or see for example?
A crowd monitoring system works with a camera that has an algorithm read out and analyzes video images. In addition to measuring crowds and displaying those crowds in usable numbers, the algorithm can also determine whether people keep a distance of 1.5 meters. All this is done in an anonymous manner that naturally complies with all privacy legislation.
The video images are not watched by a human but are processed automatically. Only a few frames are saved with unrecognizable, blurred people's faces. Those frames help to "train" the algorithm. Furthermore, the images are not saved. Continue reading about the the Shuttercam project >>
The 100 Intelligent Cities Challenge

The 100 Intelligent Cities Challenge (ICC) is a European Commission initiative that supports 136 cities in using cutting-edge technologies to lead the intelligent, green and socially responsible recovery. The ICC cities and their local ecosystems will be engines for the recovery of their local economy, create new jobs, and strengthen citizen participation and wellbeing.
The ICC is part of a wider EU support system that recognises the importance of delivering on the promises made by the European Green Deal, the digital strategy, and other EU policies. It looks to move towards a more digital, service-oriented and low-carbon economy, supported by a knowledge-based society, that enables circular economy systems through ‘local value loops’, evidence-based reskilling, and sustainable investments.
Participating cities receive one-to-one strategic advice from international experts on fine thematic strands: green economy and local green deals, improving the citizen participation and the digitalisation of public administration, green and digital transition in tourism, resilience of local supply chains, up- and reskilling of the workforce. ICC Cities are also supported by transversal services on access to data, access to finance and through a marketplace full of innovative solutions.
The Amsterdam Region, represented by Amsterdam Economic Board and Amsterdam Smart City (ASC) is one of the ICC mentor regions, alongside European mentor cities Aarhus, Antwerp, Barcelona, Espoo, Hamburg, Nice, Porto, Rijeka and international mentors Medellin, Singapore and Toronto. By participating in the ICC, the Amsterdam Region will share its experience and learn from other best practices related to multi-stakeholder collaboration, innovation ecosystems, circular economy and citizen participation.
ICC Updates:
• Launch of 100 Intelligent Cities Challenge
• ICC Challenge Mayors’ Summit
• Launch of ICC Renovation Action Group
• Public Kick-off 2nd ICC City Lab
• ICC - 3rd City Lab
• 200 Intelligent & Climate Neutral Cities Jam
• ICC - 4th City Lab
• Invitation to co-create European transition pathways for more resilient, greener and digital industrial ecosystems
• ICC - 5th City Lab
• Developing circular and sharing economy practices in cities
• The 100 Intelligent Cities Challenge: Looking Back & Looking Forward (End of Phase 1)
Responsible Sensing Lab

Smart city systems can help solve urban challenges. But when collecting data, what public values are involved? The Responsible Sensing Lab explores how to integrate social values such as autonomy, privacy, transparency, inclusiveness and empowerment in the design of sensing systems in public space.
In January 2021 the Responsible Sensing Lab was officially launched during an interactive livestream event. In essence the Lab is a testbed for conducting rigorous, transparent, and replicable research on how our smart technologies placed in public space can be designed in a way that makes the smart city ‘responsible’. Responsible Sensing Lab is a collaboration between the City of Amsterdam and AMS Institute.
A lab for a ‘responsible’ smart city
The City of Amsterdam has many smart technologies in place: from smart devices that measure things (i.e. sensors) to smart devices that steer processes in the city (i.e. actuators) such as traffic lights, charging stations, adaptable street lights, barriers that go up and down, and adaptive digital signs.
At the Responsible Sensing Lab we research, develop and integrate smart technologies like the aforementioned to help solve urban challenges. At the same time, we explore how to embed society’s public and democratic values in the design of these innovations.
(Re)designing, prototype testing and implementing responsible sensing systems
Within the Lab academics are invited to connect and work with practitioners who are responsible for digital systems in the city to (re)design, prototype and test (more) responsible ways of sensing in public space.
Hence, Responsible Sensing Lab is a place where teams of multi-disciplinary stakeholders – such as computer scientists, policy makers, psychologists, designers and hardware experts – can address existing hardware, software and other city sensing systems.
Core values
At the Responsible Sensing Lab, we use the City’s values (TADA, Digital City Agenda) as our starting point. We explore what these values mean when applied to actual software, hardware, user-experience design and governance.
Also, we are inspired by the methodology of value sensitive design. This approach allows us to focus on design choices inherent in the type of sensing hardware, the distribution of intelligence between cloud and back-end, the physical design and placement of sensors in public space, and interaction possibilities for citizens.
Do you want to know more or are you looking to collaborate? Contact us via our website!
Wicked Problems

Te wicked? Niet voor ons.
Wij werken allemaal aan urgente, complexe, maatschappelijke uitdagingen. Issues die schier onoplosbaar lijken, van dilemma’s en paradoxen omgeven, nog niet duidelijk hoe het moet. Wel is duidelijk dát het moet, dat we elkaar nodig
hebben en dat we er NU aan moeten beginnen. Om met de woorden van Jan Rotmans te spreken; we leven niet in een tijdperk van verandering maar in een verandering van tijdperk. En hier hoort een nieuwe gereedschapskist bij.
En of je nou aan energietransitie werkt, andere mobiliteitssystemen, creëren van waterstofhubs, peer to peer autodeelsystemen, het maakt niet uit, we zien dat al deze opgaven op enig moment tegen gelijksoortige barrières aanlopen. Op samenwerking, financiering, privacy, onvoldoende aansluiting op de maatschappij, om maar een paar voorbeelden te noemen.
Unieke samenwerking
Als Amsterdam Smart City netwerk willen en kunnen we deze opgaven niet laten liggen. Door het bundelen van onze kennis en expertise kunnen we als netwerk iets unieks bieden en de wil en durf tonen om deze barrières te doorbreken. De betrokken partners die dit uitdenken en begeleiden zijn RHDHV, Kennisland, Drift, NEMO, Arcadis, Alliander, HvA en Metabolic. Zij bundelen hun expertise en ervaring om de echte vragen boven tafel te krijgen, tot nieuwe manieren van samenwerken te komen en barrières te doorbreken. We richten ons met name op de start van de samenwerking. Gezamenlijk ontwikkelen we een ‘wicked problem aanpak’. Op een nieuwe manier, lerend door te doen, exploratief.
Waar moet je aan denken?
Wat is eigenlijk het echte probleem? Wiens probleem is dit? Hoe kijken anderen er tegenaan? Welke andere partijen lijken nodig? Hoe vind je ze? Hoe ga je om met eigenaarschap en botsende frames? Hoe zorg je dat je al in
een vroeg stadium de maatschappij (bewoners, ondernemers, werknemers, etc) betrekt en hun ervaringen in het project trekt? Het wicked problem team zet nieuwe methoden in voor het beantwoorden van deze vragen. En het creëren van de benodigde commitment om het vraagstuk aan te pakken. Niets staat van te voren vast, want we passen ons aan aan wat we tegenkomen. Met elkaar ontwikkelen we een nieuwe aanpak om de barrières te doorbreken.
Conscious Cities

How might we automate access to a public digital ecosystem for citizens and machines in order to grow a conscious city? How might we incentivize all citizens and companies to interact with the public digital ecosystem of the city in order to improve livability, democratic representation and societal engagement?
Read our ecosystem document
Join our online ecosystem platform
Digital Perimeter

By implementing innovative smart & digital solutions, the digital perimeter allows us to experiment with applications that deliver safety & security while providing the visitor with an even better fan experience.
Please do share your comments and thoughts with us as we are currently exploring our technical options with partners within the eco-system.
5G
5G will be the new generation of mobile connectivity. The connection will be faster and more reliable, and will bring previously unknown possibilities for citizens and business. Amsterdam is exploring the opportunities and obstacles on the road to a safe and useful 5G network. One of the ways we do this is with our field lab in Amsterdam South East, from the train station to the Johan Cruijff ArenA. But also through regional, national and international collaborations.
Amsterdam Data Exchange (AMDEX)

If data is the new gold, how can we ensure that we can all benefit from the possibilities?
Read the report about the principles of AMDEX (link)
The idea originated during the Science and Business dinner organized by Amsterdam Science Park (ASP). With Science Park’s history in the field of technological innovation and digital connectivity, the Amdex was a logical next step. As argued by Margo Keizer (ASP), "data sharing is already happening here, but at an informal level. We bring all these different initiatives together. To do this, we need to address various infrastructural and legal issues." The Amsterdam Data Exchange is an initiative to do exactly that, she adds.
Wouter Los questions: "how can we work efficiently with all this data?” With his extensive experience in the European scientific community, Los helped in the investigation of the function of the data marketplace. He explains "we want to go to an open, democratic playing field. In this model - in contrast to the monopolistic models that you now come across - the data remains from its owner and they decide which data can be shared with whom and under what conditions. We build a market model in which everyone is able to consult and use data in a transparent, familiar manner."
Chief Technology Officer, Ger Baron mentions, "since 2011, the municipality have had an open data policy. Municipal data is from the community and must therefore be available to everyone, unless privacy is at stake. In recent years we have learned to open up data in different ways.” He adds, “panorama photos, for example, are freely accessible on our data portal. In addition, we share data with market parties to find a parking space. We want to share data, but under the right conditions. This requires a transparent date market which is exactly what the Amsterdam Data Exchange can offer."
TechConnect

As part of the TechConnect action programme, a number of initiatives are being launched to increase equal opportunities in the tech sector by making related study programmes and tech jobs accessible to everyone. In practice, this means that thousands of women, people from disadvantaged neighbourhoods and owners of SMEs will be trained to become coders, data analysts, growth hackers, UX designers or tech administrators.
For more information, visit the website: <https://techconnect.city/>
Jouliette

Spectral and Alliander have launched a new blockchain-based energy sharing token at De Ceuvel in Amsterdam. Named the ‘Jouliette’, the new token aims to empower individuals and communities to easily manage and share their locally produced renewable energy.
To read the full article, please go here: https://spectral.energy/news/jouliette-at-deceuvel/
Full article: <https://spectral.energy/news/jouliette-at-deceuvel/>

A birds-eye view image of the De Ceuvel which consists of 16 office buildings, a greenhouse, a restaurant, and a bed and breakfast – all connected to a private, behind-the-meter smart-grid.

A screenshot of the real-time power-flow map of the De Ceuvel microgrid, which is one of the features of the Jouliette platform. The energy data of each building is visualized in real-time, with the green lines representing renewable energy feed-in, and red lines signifying that the building is consuming from the grid.
Smart Stories
Check the article about Jouliette featured in our online magazine 'Smart Stories':
DECODE

DECODE is an EU funded project to make tools that put people in control of whether they keep their personal information private or share it for the public good.
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon
2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No. 732546.
Open Data API's Municipality of Amsterdam

DataLab is a workshop, knowledge-center and open stage.
<https://github.com/DatapuntAmsterdam>
DataLab is een werkplaats, kenniscentrum en open podium
Om letterlijk ruimte te creëren voor dataprofessionals en in data geïnteresseerde ambtenaren, bewoners en partners van de gemeente Amsterdam is het DataLab op initiatief van rve Onderzoek, Informatie en Statistiek opgezet. Een fysieke werkplaats, kenniscentrum en open podium voor Amsterdam.
City Alerts
City Alerts provides adequate information of relevant information (personal and non-personal) between emergency services during emergency incidents.
Data and information
The website Amsterdam City Data and the website of Research, Information and Statistics (OIS) have been merged under the name Data en informatie (Data and information), with the url data.amsterdam.nl. The advantages of the merging are:
- topical data, statistics and research are coherently presented
- quick and new ways can be developed to make visual and interactive presentations of data and information
You will find data sources from researches which will be shown in the form of tables, factsheets, dashboards, animations and reports. As well as datasets and topical data from, among other sources, municipal records databases.
You can easily search for all these data and have them shown in a map, download them as a data set, or link them automatically to your own system via a so-called ‘web service’ or API.
The buttons in the green square on the user interface give access to maps, the panorama viewer and the data catalogue.
Under the moniker ‘In beeld’ (‘In pictures’) we present data and research results interactively and visually as animations, dashboards and data stories, among other formats.
The menu offers help while using these functionalities.
The data portal is for anyone who is looking for reliable and up-to-date information about the city. For Amsterdam’s public officials who want to make the right decisions and civil servants who want to work effectively. But also for civilians, researchers and journalists who are looking for facts. Data en informatie is openly accessible and data that is public can be freely used by anyone. Some of the data are available to authorized city employees only.
If you have any questions or remarks about Data en informatie please contact us through redactie.ois@amsterdam.nl.
CitySDK
The CityService Development Kit (CitySDK) is a system that collects open data of governments, in order to provide their availability uniformly and in real-time. Within this project Waag Society is responsible for the domain Mobility. We will talk to potential data suppliers and application developers to meet the needs of both parties. Combined with questions from various cities in Europe, these needs lead to services that are both generic and dynamic.
CitySDK is assisting seven European cities to release their data and offers tools to develop digital services. It also helps cities anticipate ever expanding technological possibilities. Over the past twenty years, Waag Society amassed much knowledge of technology and governmental sources. This was put to good use in the development of CitySDK. Think of services that help developers to make applications that offer personalized travel advice.
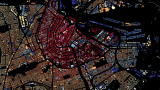
Bert Spaan, developer at Waag Society, has made a map within the framework of the European Smart CitySDK project to show all 9,866,539 buildings in The Netherlands, shaded according to their year of construction. This give us a complete new image of the country and clearly shows the age of cities, whether they are still relatively young (in blue, built after 1960) or very old (in red). A nice example is a city like Haarlem, of which the old inner city clearly lights up, or Almere, covered in blues as it is built in recent times.
With these services, a pilot study will be conducted in Amsterdam. Then, the applicability of the services will be tested in Helsinki, Manchester, Barcelona, Rome, Istanbul and Lamia.
As part of the City Service Development Kit and the Open Data Exchange projects the City Dashboard Amsterdam has been developed, in which lot of effort has been expended to make existing data sets available in realtime. A true treasure, that contains an enormous insight in what make the city tick.
Stay up to date
Get notified about new updates, opportunities or events that match your interests.


